Of course! Let's break down the Python string method isdigit() in detail.
Summary
The isdigit() method is a built-in Python string method that returns True if all characters in the string are digits and there is at least one character. Otherwise, it returns False.
Syntax
string.isdigit()
- It takes no arguments.
- It returns a boolean value:
TrueorFalse.
Key Rules (When is it True?)
For isdigit() to return True, a string must meet all of the following conditions:
- All characters must be digits. This includes:
- Numbers:
'0','1','2', ...,'9' - Special digit characters from other languages (e.g., superscripts, subscripts, Devanagari numerals).
- Numbers:
- The string cannot be empty. An empty string will always return
False.
Examples
Let's look at various cases to understand how it behaves.
Simple Cases (Returns True)
These strings contain only standard digits.
print("12345".isdigit()) # Output: True
print("9876".isdigit()) # Output: True
print("0".isdigit()) # Output: True
Negative Cases (Returns False)
These are common cases where people expect True but get False.
# Contains a decimal point
print("123.45".isdigit()) # Output: False
# Contains a negative sign
print("-100".isdigit()) # Output: False
# Contains a positive sign
print("+50".isdigit()) # Output: False
# Contains a space
print("100 200".isdigit()) # Output: False
# Contains a letter
print("a100".isdigit()) # Output: False
# Is an empty string
print("".isdigit()) # Output: False
Advanced Cases (Returns True)
This is where isdigit() differs from similar methods like isdecimal() and isnumeric(). It recognizes certain special digit characters.
# Superscript two (²)
print("²".isdigit()) # Output: True
# Subscript three (₃)
print("₃".isdigit()) # Output: True
# Devanagari digit (१, which is 1 in Devanagari script)
print("१".isdigit()) # Output: True
isdigit() vs. isdecimal() vs. isnumeric()
This is a very important distinction. While they all check for digits, they have different scopes.
| Method | What it Checks | Returns True for... |
Example |
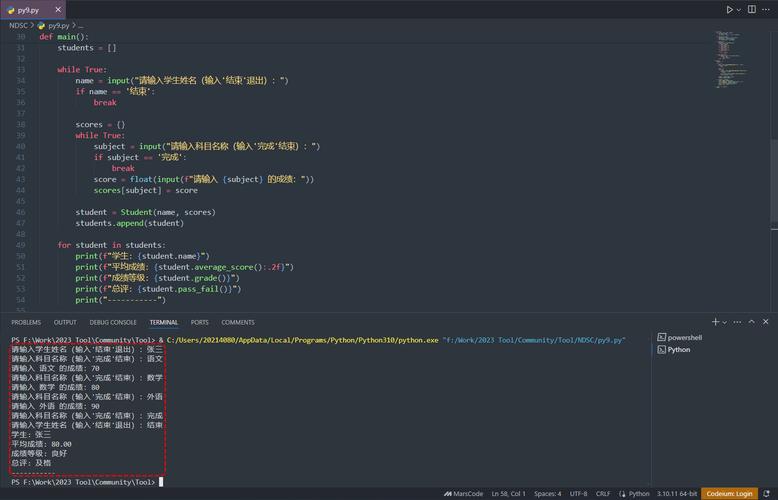
|---|---|---|---|
isdigit() |
Digits | Standard digits (0-9) and special digit characters like superscripts/subscripts. |
"123"(superscript) |
isdecimal() |
Decimal Characters | Only standard digits (0-9). It's the most restrictive. |
"123"(False) |
isnumeric() |
Numeric Characters | The broadest category. Includes everything isdigit() and isdecimal() recognize, plus fractions, Roman numerals, and other numeric symbols. |
"123"(fraction) |
Visual Comparison:
s = "²10½" # Contains a superscript, decimal, and a fraction
print(f"String: '{s}'")
print(f"s.isdigit(): {s.isdigit()}") # True (² is a digit)
print(f"s.isdecimal(): {s.isdecimal()}") # False (² and ½ are not decimals)
print(f"s.isnumeric(): {s.isnumeric()}") # True (all are numeric)
Output:
String: '²10½'
s.isdigit(): True
s.isdecimal(): False
s.isnumeric(): TruePractical Use Cases
You would typically use isdigit() for input validation where you need to ensure a string represents a whole, non-negative integer.
Validating User Input
Imagine you're asking a user for their age.
user_input = input("Please enter your age: ")
if user_input.isdigit():
age = int(user_input)
print(f"Thank you! You are {age} years old.")
else:
print("Invalid input. Please enter a whole number without any symbols.")
Example Runs:
Please enter your age: 25
Thank you! You are 25 years old.Please enter your age: twenty-five
Invalid input. Please enter a whole number without any symbols.Please enter your age: -5
Invalid input. Please enter a whole number without any symbols.Checking for a Pin Code
pin_code = "1234"
if len(pin_code) == 4 and pin_code.isdigit():
print("Valid PIN code.")
else:
print("Invalid PIN code. Must be 4 digits.")
Important Caveat: Checking for a Number
Do not use isdigit() to check if a string can be converted to a number.
It fails for negative numbers, floats, and numbers with scientific notation.
# This is a common mistake!
my_string = "-123.45"
if my_string.isdigit():
print("This will never be printed.")
else:
# The correct way to check for any number is to use a try-except block.
try:
number = float(my_string)
print(f"Successfully converted to a number: {number}")
except ValueError:
print(f"Could not convert '{my_string}' to a number.")
Output:
Successfully converted to a number: -123.45Summary Table
| Method | Purpose | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
isdigit() |
Check if a string contains only digits. | Includes special digits like superscripts (). |
isdecimal() |
Check if a string contains only decimal characters (0-9). |
More restrictive than isdigit(). |
isnumeric() |
Check if a string contains only numeric characters. | Most inclusive; includes fractions, Roman numerals, etc. |
isalnum() |
Check if a string contains only alphanumeric characters (letters and numbers). | isalnum() = isalpha() OR isdigit() for each character. |
isalpha() |
Check if a string contains only alphabetic characters (letters). |