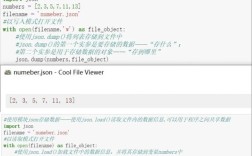
Of course! The EffectScatter is a specialized chart type from the PyEcharts library, a powerful Python library for creating interactive, publication-quality charts. It's not part of standard libraries like Matplotlib or Seaborn.
EffectScatter is essentially a scatter plot with a special "ripple" or "breathe" effect on the data points. This makes the points stand out and is excellent for drawing attention to specific data locations, such as key cities on a map, significant events on a timeline, or critical values in a dataset.
What is EffectScatter?
It's an interactive scatter plot where each data point has a dynamic visual effect, typically a pulsating ripple. This effect helps to:
- Highlight important data: Make key points impossible to miss.
- Add visual appeal: Create a more engaging and modern-looking chart.
- Indicate a "center" or "hub": Often used to mark central locations like cities on a map.
Installation
First, you need to install pyecharts. If you don't have it, open your terminal or command prompt and run:
pip install pyecharts
A Simple EffectScatter Example
Let's start with a basic example to see how it works. We'll create a simple chart with a few data points.

from pyecharts.charts import EffectScatter
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 1. Prepare the data
# The data is a list of lists, where each inner list is [x_value, y_value]
data = [
[10, 15], [20, 25], [30, 20], [40, 60],
[50, 45], [60, 50], [70, 55], [80, 70]
]
# 2. Instantiate the EffectScatter object
chart = EffectScatter()
# 3. Add the data to the chart
chart.add_xaxis([d[0] for d in data])
chart.add_yaxis(
series_name="Data Points",
y_axis=[d[1] for d in data]
)
# 4. Set global options for the chart
chart.set_global_opts(opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Simple EffectScatter Chart"),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name="X Axis"),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name="Y Axis")
)
# 5. Render the chart to an HTML file
chart.render("simple_effect_scatter.html")
print("Chart has been rendered to simple_effect_scatter.html")
When you run this code, a file named simple_effect_scatter.html will be created. Open it in your web browser to see the interactive chart with the ripple effect on the points.
Customizing the EffectScatter
The real power of EffectScatter comes from its customization options. Let's create a more advanced example that demonstrates several key features.
We will:
- Use different symbols for points.
- Vary the color and size of points.
- Customize the ripple effect.
- Add labels to the points.
from pyecharts.charts import EffectScatter
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.faker import Faker # Faker is useful for generating sample data
# 1. Prepare data with more detail
# We'll create data points with x, y, symbol, size, and color.
data = [
{"value": [10, 20], "symbol": "pin", "symbol_size": 50, "itemstyle_opts": {"color": "#d14a61"}},
{"value": [25, 35], "symbol": "arrow", "symbol_size": 60, "itemstyle_opts": {"color": "#675bba"}},
{"value": [40, 50], "symbol": "circle", "symbol_size": 70, "itemstyle_opts": {"color": "#5470c6"}},
{"value": [55, 65], "symbol": "diamond", "symbol_size": 80, "itemstyle_opts": {"color": "#91cc75"}},
{"value": [70, 80], "symbol": "triangle", "symbol_size": 90, "itemstyle_opts": {"color": "#fac858"}},
]
# 2. Instantiate and configure the chart
chart = EffectScatter()
# Add data. We pass the list of dictionaries directly.
chart.add_yaxis(
series_name="Customized Points",
y_axis=data,
# --- Ripple Effect Customization ---
effect_opts=opts.EffectOpts(
symbol="circle", # The shape of the ripple
symbol_size=10, # The size of the ripple
color="rgba(0, 0, 255, 0.5)" # Color and transparency of the ripple
)
)
# 3. Set global options
chart.set_global_opts(opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Customized EffectScatter Chart"),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
type_="value",
name="X Value",
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=True)
),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
type_="value",
name="Y Value",
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=True)
),
# --- Tooltip Configuration ---
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(
trigger="item", # Show tooltip when hovering over an item
formatter="{b}: {c}" # {b} is series name, {c} is data value
)
)
# 4. Render the chart
chart.render("custom_effect_scatter.html")
print("Custom chart has been rendered to custom_effect_scatter.html")
Key Customizations Explained:
symbol: You can change the shape of the data points. Common options include"circle","pin","arrow","diamond","triangle", and"image".symbol_size: Controls the size of the data points.itemstyle_opts: A dictionary for styling the data points themselves, where you can setcolor,border_color,border_width, etc.effect_opts: This is where you control the ripple effect.symbol: The shape of the ripple.symbol_size: The size of the ripple.color: The color of the ripple.
tooltip_opts: Controls the information box that appears when you hover over a data point.formatterlets you customize the text inside it.xaxis_opts&yaxis_opts: You can customize the axes, for example, by setting their type (type_="value"for numerical,type_="category"for categorical), name, and whether to show grid lines (splitline_opts).
Practical Use Case: Highlighting Cities on a Map
A very common and visually appealing use for EffectScatter is to highlight key locations on a map.
from pyecharts.charts import EffectScatter
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.globals import ChartType, SymbolType
# Data for major cities: [longitude, latitude, city_name]
cities_data = [
[116.4074, 39.9042, "Beijing"],
[121.4737, 31.2304, "Shanghai"],
[113.2644, 23.1291, "Guangzhou"],
[114.0579, 22.5431, "Shenzhen"],
[120.1551, 30.2741, "Hangzhou"],
]
# 1. Instantiate a Map chart
chart = EffectScatter()
# 2. Add data to the map
# We use `add` instead of `add_yaxis` for map charts
chart.add(
series_name="Major Cities",
data_pair=[(city[2], [city[0], city[1]]) for city in cities_data],
# --- Map-specific options ---
is_large=True,
large_threshold=100,
symbol_size=12,
# --- Ripple Effect for the map ---
effect_opts=opts.EffectOpts(
symbol=SymbolType.PIN, # Use a pin symbol for the ripple
symbol_size=8,
color="blue"
),
# --- Styling for the points ---
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(
is_show=True,
position="right", # Position the label to the right of the pin
color="black",
font_size=10
)
)
# 3. Set global options for the map
chart.set_global_opts(opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Major Cities in China (EffectScatter)"),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(trigger="item"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(
is_show=False # We can disable the visual map if not needed
)
)
# 4. Render the chart
chart.render("cities_effect_scatter_map.html")
print("Map chart has been rendered to cities_effect_scatter_map.html")
In this example, we use