Of course! The command shell java -jar is a common way to refer to running a Java application from a command-line interface (the "shell"). The shell part isn't a command itself; it's just context meaning you're in a shell like Bash (on Linux/macOS) or PowerShell/CMD (on Windows).
Let's break down the actual command: java -jar <filename>.jar.
The Command: java -jar
This command tells your operating system to:
- Use the
javacommand to start the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). - Load and execute a program packaged inside a
.jar(Java Archive) file.
Syntax
java -jar <your-application.jar> [arguments...]
Breakdown of Parts
-
java: This is the command to invoke the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). It's the launcher for your Java application.- Prerequisite: The
javaexecutable must be in your system'sPATHenvironment variable. If you get an error like'java' is not recognized..., you need to install the JDK or JRE and configure yourPATH.
- Prerequisite: The
-
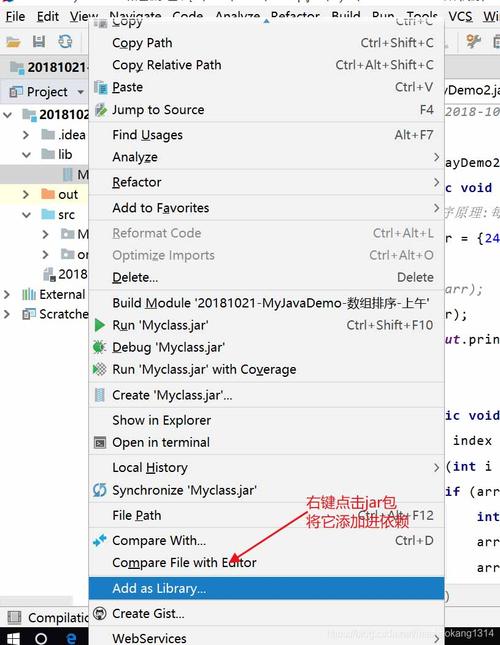
-jar: This is a crucial option or flag. It tells thejavacommand that the next argument is a.jarfile and that you want to run it as a standalone application.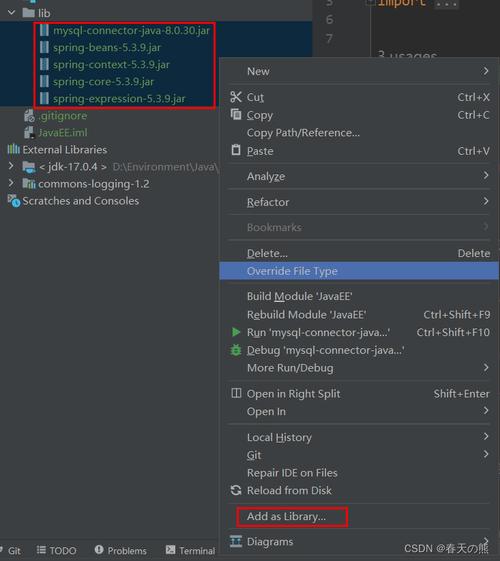 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- When you use
-jar, the JVM looks for a special file inside the.jarcalledMETA-INF/MANIFEST.MF. This manifest file contains metadata about the application, most importantly theMain-Classattribute, which specifies the entry point (the main class) of your application.
- When you use
-
<your-application.jar>: This is the argument that follows the-jarflag. It's the path to your Java Archive file. You can use a relative path (e.g.,./my-app.jar) or an absolute path (e.g.,/home/user/apps/my-app.jar). -
[arguments...]: These are optional command-line arguments that you can pass to your running Java application. Your application's code can read these arguments to change its behavior (e.g., specifying a configuration file, setting a port number, or turning on verbose logging).
How It Works: The MANIFEST.MF File
The magic of java -jar happens inside the .jar file. A .jar file is essentially a .zip archive. Inside it, there must be a file at META-INF/MANIFEST.MF.
This file contains key-value pairs. The most important one is:
Main-Class: com.example.MyMainAppThe java command reads this line, knows it needs to start the com.example.MyMainApp class, and automatically invokes its public static void main(String[] args) method.
Example MANIFEST.MF file:
Manifest-Version: 1.0 Created-By: Apache Maven 3.8.1 Build-Jdk: 11.0.12 Main-Class: com.mycompany.app.MainApplication
Practical Examples
Let's assume you have a Java application file named my-cool-app.jar.
Basic Execution
This is the simplest way to run your app. It will run with default settings.
java -jar my-cool-app.jar
Passing Arguments to Your Application
Imagine your app is a server that needs to know which port to listen on. You can pass this as an argument.
# Run the app, telling it to use port 8080 java -jar my-cool-app.jar --server.port=8080
Inside your Java code, you would use a library like Apache Commons CLI or Spring Boot's argument parsing to read the --server.port=8080 value.
Running with Different Java Versions
If you have multiple Java versions installed, you can explicitly specify which one to use by providing its full path.
# On Linux/macOS /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java -jar my-cool-app.jar # On Windows (in CMD or PowerShell) "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11.0.12\bin\java.exe" -jar my-cool-app.jar
Increasing Memory (Very Common)
Java applications can run out of memory. You can increase the amount of memory allocated to the JVM using flags like -Xms (initial heap size) and -Xmx (maximum heap size).
# Start with 512MB of memory and allow it to grow up to 2GB java -Xms512m -Xmx2g -jar my-cool-app.jar
Running in the Background
If you don't want your terminal to be blocked by the running application, you can run it in the background.
-
On Linux/macOS (using Bash):
# The ampersand (&) runs the command in the background java -jar my-cool-app.jar &
-
On Windows (using PowerShell):
# Start-Job runs the command as a background job Start-Job -ScriptBlock { java -jar my-cool-app.jar }
Common Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
'java' is not recognized... |
Java is not installed or not in your system's PATH. |
Install the JDK/JRE and add Java to your PATH. |
Error: Could not find or load main class |
The Main-Class is missing or incorrect in the MANIFEST.MF file. |
Rebuild your .jar file, ensuring the manifest is correctly generated by your build tool (like Maven or Gradle). |
Error: Invalid or corrupt jarfile |
The .jar file is corrupted or not a valid archive. |
Redownload the file or rebuild your project. |
OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space |
The application needs more memory than the default JVM allocation. | Increase the maximum heap size with the -Xmx flag (e.g., -Xmx4g for 4 gigabytes). |
Alternatives to java -jar
While java -jar is standard for standalone apps, you might also see:
-
For Library Jars:
java -cp my-library.jar com.example.MainClass-cp(or-classpath) specifies the classpath. This tells the JVM where to find your.classfiles. It's more flexible than-jarbut requires you to specify the main class manually.
-
For "Fat" Jars (Spring Boot, etc.):
java -jar my-spring-boot-app.jar- Modern frameworks like Spring Boot create "fat" or "uber" jars. These are special
.jarfiles that contain your application code and all its dependencies. Thejava -jarcommand works perfectly with them.
- Modern frameworks like Spring Boot create "fat" or "uber" jars. These are special