下面我将详细介绍如何使用 oracledb 来连接 Oracle 数据库,包括安装、基本连接、不同身份认证方式、以及执行查询和关闭连接等操作。
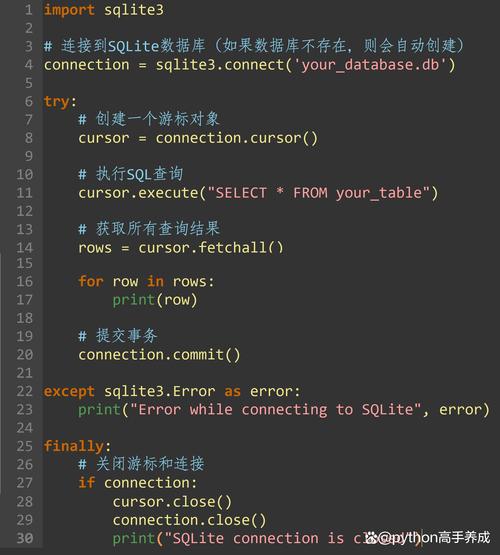
第一步:安装 oracledb 模块
你需要使用 pip 来安装 oracledb。
pip install oracledb
第二步:准备 Oracle 客户端文件
oracledb 需要使用 Oracle 客户端库来与数据库通信,根据你的 Python 环境和 Oracle 数据库版本,有两种主要方式:
使用 Instant Client (推荐,最简单)
这是最常见和推荐的方式,尤其适用于开发环境和大多数生产环境。
-
下载 Instant Client:
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- 访问 Oracle Instant Client 官方下载页面:Oracle Instant Client Downloads
- 根据你的操作系统选择对应的版本(如 Windows x64, Linux x64, macOS x64)。
- 下载 "Basic" 或 "Basic Light" 版本即可,它包含了所有必需的文件。
-
配置环境变量:
- 将下载并解压后的文件夹路径添加到系统的
PATH环境变量中。 - 例如:如果你的 Instant Client 解压在
C:\oracle\instantclient_19_10,那么就将这个路径添加到PATH中。 - 重要提示:在 Python 脚本中,最好通过代码来指定 Instant Client 的路径,而不是依赖全局环境变量,这样可以提高脚本的移植性。
- 将下载并解压后的文件夹路径添加到系统的
使用 Oracle 全家桶客户端 (Full Client)
如果你的机器上已经安装了 Oracle Database、Oracle Client 或其他 Oracle 产品,你可能已经拥有了所需的客户端库(如 oci.dll, libclntsh.so 等)。oracledb 通常能自动找到它们。
第三步:编写 Python 连接代码
下面是连接 Oracle 数据库的几种常见场景。
场景1:基本连接 (用户名/密码)
这是最标准的连接方式。
import oracledb
# --- 1. 设置连接信息 ---
# 建议将敏感信息(如密码)存储在环境变量或配置文件中
username = "your_username"
password = "your_password"
dsn = "hostname:port/service_name" # "localhost:1521/ORCLCDB"
# 或者使用 TNS 名称 (需要配置 tnsnames.ora 文件)
# dsn = "ORCL" # 对应 tnsnames.ora 中的别名
# --- 2. 设置 Instant Client 路径 (如果需要) ---
# Instant Client 不在系统 PATH 中,请取消下面这行的注释并修改为你的路径
# import os
# oracledb.init_oracle_client(lib_dir=r"C:\oracle\instantclient_19_10")
# --- 3. 建立连接 ---
try:
# 使用 with 语句可以自动处理连接的关闭
with oracledb.connect(user=username, password=password, dsn=dsn) as connection:
print("成功连接到 Oracle 数据库!")
# --- 4. 创建游标并执行查询 ---
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql_query = "SELECT * FROM your_table_name WHERE ROWNUM <= 5"
cursor.execute(sql_query)
# --- 5. 获取并打印结果 ---
# cursor.description 可以获取列信息
print("列信息:", [desc[0] for desc in cursor.description])
# fetchone() 获取一行
# row = cursor.fetchone()
# print("第一行数据:", row)
# fetchmany(num) 获取指定数量的行
# rows = cursor.fetchmany(3)
# print("前三行数据:", rows)
# fetchall() 获取所有行 (注意:如果数据量很大,慎用)
for row in cursor:
print(row)
except oracledb.DatabaseError as e:
# 捕获数据库错误
error, = e.args
print(f"数据库错误代码: {error.code}")
print(f"数据库错误消息: {error.message}")
except Exception as e:
# 捕获其他错误
print(f"发生未知错误: {e}")
场景2:使用外部身份验证 (External Authentication)
如果你的 Oracle 数据库配置为使用操作系统认证(例如在 sqlplus / as sysdba 中),你也可以在 Python 中使用这种方式。
import oracledb
# 这种方式不需要用户名和密码
# 它会使用运行 Python 脚本的操作系统的用户身份
dsn = "hostname:port/service_name"
try:
with oracledb.connect(dsn=dsn, mode=oracledb.SYSDBA) as connection:
print("使用外部身份验证成功连接!")
# ... 执行你的操作 ...
except oracledb.DatabaseError as e:
error, = e.args
print(f"数据库错误代码: {error.code}")
print(f"数据库错误消息: {error.message}")
场景3:使用 Oracle Wallet 进行无缝认证 (无缝连接)
这是现代 Oracle 环境中更安全、更便捷的方式,它使用一个加密的 "钱包" 文件来存储认证信息,无需在代码中明文写用户名和密码。
-
创建和配置 Wallet:
- 使用 Oracle 的
mkstore工具创建一个钱包。 - 使用
orapki工具将用户的证书添加到钱包中。 - 设置
SQLNET.WALLET_LOCATION和SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES参数到sqlnet.ora文件中。
- 使用 Oracle 的
-
Python 代码:
import oracledb
# 设置 Wallet 的路径
wallet_location = r"C:\path\to\your\wallet"
wallet_password = "your_wallet_password" # 如果钱包有密码
# DSN 可以留空,或者只写服务名
dsn = "service_name"
try:
# 使用外部身份验证模式,并指定 Wallet
with oracledb.connect(
user="",
password="",
dsn=dsn,
externalauth=True,
config_dir=wallet_location
) as connection:
print("使用 Wallet 成功连接!")
# ... 执行你的操作 ...
except oracledb.DatabaseError as e:
error, = e.args
print(f"数据库错误代码: {error.code}")
print(f"数据库错误消息: {error.message}")
第四步:执行 DML 语句 (增删改)
执行 INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE 语句后,必须调用 connection.commit() 才能将事务真正提交到数据库。
import oracledb
username = "your_username"
password = "your_password"
dsn = "hostname:port/service_name"
try:
with oracledb.connect(user=username, password=password, dsn=dsn) as connection:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
# --- 插入数据 ---
insert_sql = "INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, last_name, email) VALUES (employee_id_seq.NEXTVAL, 'Smith', 'smith@example.com')"
cursor.execute(insert_sql)
# --- 更新数据 ---
update_sql = "UPDATE employees SET salary = salary * 1.1 WHERE last_name = 'Smith'"
# cursor.execute(update_sql)
# --- 提交事务 ---
connection.commit()
print("操作成功并已提交!")
except oracledb.DatabaseError as e:
# 如果发生错误,回滚事务
connection.rollback()
error, = e.args
print(f"数据库错误: {error.message}")
print("事务已回滚。")
第五步:处理大型数据集 (使用 RETURN_LOBS)
当从数据库中读取 CLOB (大文本) 或 BLOB (大二进制) 数据时,需要使用 RETURN_LOBS 选项。
import oracledb
username = "your_username"
password = "your_password"
dsn = "hostname:port/service_name"
try:
with oracledb.connect(user=username, password=password, dsn=dsn) as connection:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
# 假设 your_table 有一个 clob_column 列
cursor.execute("SELECT clob_column FROM your_table WHERE id = 1")
# 必须在 fetchone 或 fetchall 之前设置
cursor.return_lobs = True
clob_data, = cursor.fetchone()
print("获取到的 CLOB 数据类型:", type(clob_data))
print("CLOB 数据内容 (前100个字符):", clob_data[:100])
except oracledb.DatabaseError as e:
error, = e.args
print(f"数据库错误: {error.message}")
总结与最佳实践
- 使用
oracledb:这是官方推荐的模块,持续更新,性能更好。 - 使用
with语句:它能确保连接和游标在使用完毕后被正确关闭,即使在发生异常时也是如此。 - 不要硬编码密码:将数据库凭据存储在环境变量、配置文件或密钥管理服务中。
- 始终处理异常:使用
try...except块来捕获oracledb.DatabaseError,以便优雅地处理连接失败或查询错误。 - 记得
commit():执行INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE后,不要忘记调用connection.commit()。 - 考虑性能:对于大数据量的查询,避免使用
fetchall(),而应使用for row in cursor:的迭代方式,这样可以逐行处理,减少内存消耗。