Of course! "Jupiter Julia Python" sounds like a powerful trio, and in the world of data science, it is! Let's break down what each of these components is and how they work together.
This trio forms the backbone of the modern Python data science ecosystem.
Python: The Engine
What it is: Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. It's famous for its simple, readable syntax and vast ecosystem of libraries.
Its Role in the Trio: Python is the programming language that does the heavy lifting. While Python itself is a general-purpose language, its power for data science comes from specialized libraries:
- NumPy: The fundamental package for numerical computation with Python. It provides powerful N-dimensional array objects.
- Pandas: Built on NumPy, Pandas provides data structures (like the DataFrame) that make it incredibly easy to manipulate and analyze structured data.
- Matplotlib & Seaborn: Libraries for creating static, interactive, and publication-quality visualizations.
- Scikit-learn: The go-to library for machine learning. It provides simple and efficient tools for data mining and data analysis.
- TensorFlow & PyTorch: Leading libraries for building and training deep learning models.
Analogy: If you were building a car, Python is the engine and the chassis. It's the core power and structure, but on its own, it's not a complete, ready-to-drive car for a specific task.

Jupyter: The Interactive Workbench
What it is: Jupyter is not a programming language; it's a web-based interactive computing environment. The most common type is the Jupyter Notebook.
Its Role in the Trio: Jupyter provides the user interface where you can "talk" to Python. It organizes your work into a document called a notebook, which is a collection of cells.
There are two main types of cells:
- Code Cells: You write Python code in these cells. When you run a cell, the Python kernel executes the code and displays the output directly below the cell.
- Markdown Cells: You can write text, explanations, headings, and even embed images and equations in these cells. This allows you to create a narrative around your code.
Analogy: If Python is the engine, Jupyter is the driver's cockpit with all the controls and displays. It's where you sit, give commands (write code), and see the results (output, plots, data tables) in real-time. It turns coding from a purely text-based activity into an interactive, visual experience.

Julia: The Rising Star (The "New Kid on the Block")
What it is: Julia is a high-level, high-performance, dynamic programming language designed specifically for technical and scientific computing. It was created to solve the "two-language problem."
The "Two-Language Problem": For a long time, data scientists often used two languages:
- High-level languages (like Python or R): Great for rapid prototyping and interactive analysis, but slow for computationally intensive tasks.
- Low-level languages (like C or Fortran): Blazingly fast for performance-critical tasks, but difficult to use and slow to write code in.
Julia's Solution: Julia was designed to be as easy to use and as flexible as Python, but with the speed of a compiled language like C. It achieves this through a Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler.
Its Role in the Trio: Julia is a competitor and complement to Python. It's another engine you can use from the Jupyter workbench.
- Why use Julia? If you are doing heavy-duty numerical simulations, complex mathematical modeling, or any task where raw computational speed is the absolute bottleneck, Julia can be significantly faster than Python.
- When to stick with Python? Python has a much larger community and a more mature, vast ecosystem of libraries for almost every data science task. For most data analysis, visualization, and machine learning, Python's performance is already "good enough," and its ecosystem is unbeatable.
Analogy: If Python is a powerful V8 engine, Julia is a next-generation, highly efficient turbocharged engine. Both are incredibly powerful, but the turbocharged one (Julia) might have a slight edge in top-end speed for specific races (computational tasks), while the V8 (Python) has a wider range of compatible parts (libraries) and is more commonly used.
How They All Work Together: The Jupyter Ecosystem
The magic happens when you combine these tools in the Jupyter environment.
The Most Common Workflow:
- Installation: You install a Python distribution like Anaconda, which comes with Python, Jupyter, and hundreds of data science libraries pre-packaged.
- Launch: You open the Anaconda Navigator or your command line and launch
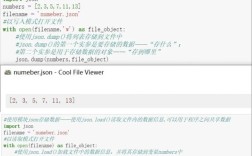
jupyter notebookorjupyter lab. - Create a Notebook: A new tab opens in your web browser showing the Jupyter interface. You create a new notebook, and you choose the kernel.
- You would choose the Python kernel to work with Python libraries (Pandas, NumPy, etc.).
- You could also install the Julia language and choose the Julia kernel to work with Julia packages in the same interface.
- Interactive Analysis: You write code in a cell, hit
Shift + Enter, and immediately see the results. You can plot a graph, clean a dataset, train a model, and write down your observations—all in one single, shareable document.
Summary Table
| Feature | Python | Jupyter | Julia |
|---|---|---|---|
| What It Is | A programming language | An interactive computing environment (web app) | A programming language |
| Primary Role | The engine that performs calculations and analysis | The workbench where you interact with the engine | A high-performance engine alternative |
| Key Strength | Massive ecosystem of libraries (Pandas, Scikit-learn) | Interactivity, visualization, and narrative storytelling | Speed (solves the "two-language problem") |
| Analogy | The Engine | The Driver's Cockpit | A High-Performance Turbo Engine |
Conclusion
When you hear "Jupiter Julia Python," you're hearing about the core tools of modern computational science.
- Jupyter is the interactive interface that brings the process to life.
- Python is the dominant and most versatile engine powering most of the work today.
- Julia is a powerful, high-performance engine that is gaining traction for computationally intensive tasks.
For anyone starting in data science or scientific computing, learning Python within the Jupyter environment is the essential first step. Understanding Julia is beneficial for knowing the cutting-edge alternatives for high-performance computing.