我将从几个层面详细解释如何设置 Session 的生命周期,包括:
- 在
web.xml中设置(传统方式) - 在代码中动态设置(编程方式)
- 在 Spring Boot 中设置(现代主流方式)
- 重要概念:超时时间 vs. 最大不活动时间
- Session 何时会失效?
在 web.xml 中设置(Servlet 3.0 之前)
这是最传统和标准的方式,通过配置部署描述符文件 web.xml 来设置,这种方式设置的是 Session 的最大不活动时间。
参数:
<session-config> 和 <session-timeout>
<session-timeout>: 单位是分钟,如果用户在这个时间间隔内没有对 Session 进行任何操作(即没有请求),服务器就会使该 Session 失效。
示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--
设置 Session 的最大不活动时间为 30 分钟。
30 分钟内用户没有任何请求,Session 将被销毁。
-->
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
</web-app>
注意:
<session-timeout>设置为 0 或负数,Session 将永远不会超时。这通常不推荐,因为它可能导致服务器内存泄漏。- Tomcat 的默认值通常是 30 分钟。
在代码中动态设置(编程方式)
你可以在 Servlet 或任何可以获取到 HttpSession 对象的代码中,动态地设置或获取 Session 的超时时间。
核心方法:
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(int interval): 设置 Session 的超时时间。session.getMaxInactiveInterval(): 获取当前 Session 的超时时间。
参数:
interval 的单位是秒。
示例:
在一个 Servlet 中:
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/sessionExample")
public class SessionExampleServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 获取或创建 Session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
// 2. 获取并打印当前的 Session 超时时间(单位:秒)
int currentTimeout = session.getMaxInactiveInterval();
System.out.println("Current session timeout (seconds): " + currentTimeout);
// 3. 动态设置 Session 超时时间为 1 小时(3600 秒)
// 这个设置会覆盖 web.xml 中的全局设置,但只对当前 Session 有效
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(3600);
System.out.println("New session timeout has been set to 1 hour for this session.");
// 4. 在 Session 中存储一个属性
session.setAttribute("user", "John Doe");
response.getWriter().println("Session timeout has been set dynamically.");
}
}
特点:
- 这种方式的优先级高于
web.xml中的全局设置,它只对当前这个特定的HttpSession对象生效。 - 适用于需要根据不同用户、不同业务场景动态调整 Session 生命周期的场景。
在 Spring Boot 中设置(现代主流方式)
Spring Boot 极大地简化了配置,通常不再使用 web.xml,它提供了多种灵活的方式来配置 Session。
Spring Boot 默认使用内嵌的 Servlet 容器(如 Tomcat),并且默认的 Session 超时时间是 30 分钟。
在 application.properties 或 application.yml 中全局设置
这是最推荐的方式,简单且集中。
在 application.properties 中:
单位是分钟。
# 设置 Session 超时时间为 45 分钟 server.servlet.session.timeout=45m
在 application.yml 中:
server:
servlet:
session:
timeout: 45m # 也可以写成 45
使用 application.properties 和 @Bean 自定义 SessionRepository
如果你需要更高级的配置,比如使用 Redis 来管理 Session,你需要自定义 SessionRepository。
在 application.properties 中启用 Redis Session:
# 启用 Spring Session 和 Redis 存储 spring.session.store-type=redis # Redis 连接配置 spring.redis.host=localhost spring.redis.port=6379 # Session 在 Redis 中的超时时间,单位是毫秒 spring.session.timeout=1800000 # 30分钟,单位是毫秒
在 Java 配置类中设置
你也可以通过一个配置类来设置,这种方式更灵活,可以结合其他逻辑。
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.Session;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
@Configuration
public class SessionConfig {
// 方式一:通过 ServletContextInitializer
@Bean
public ServletContextInitializer servletContextInitializer() {
return servletContext -> {
// 设置 Session 超时时间为 20 分钟
servletContext.setSessionTimeout(20); // 单位是分钟
};
}
// 方式二:直接配置 ServerProperties (更推荐)
// Spring Boot 会自动扫描这个 Bean 并应用配置
/*
@Bean
public ServerProperties serverProperties() {
ServerProperties properties = new ServerProperties();
properties.getServlet().setSessionTimeout(Duration.ofMinutes(20));
return properties;
}
*/
}
注意: 在 Spring Boot 中,application.properties 中的配置通常比 Java 配置类中的 @Bean 优先级更高。
重要概念:超时时间 vs. 最大不活动时间
在 Java Servlet 规范中,这两个概念指的是同一个东西,即 <session-timeout>。
- 含义:这是 Session 的最大不活动时间。
- 计时器:计时器从最后一次客户端请求开始计时,如果在这个时间间隔内,客户端没有发送任何新的请求,服务器就会认为该 Session 已经失效,并将其从内存中移除。
- 不是 Session 的总生命周期:它不是从 Session 创建开始计算的固定时长,只要用户在超时前有活动,Session 就会一直存在。
你设置了超时时间为 30 分钟。
- 用户登录,Session 创建。
- 用户在第 25 分钟时点击了一个链接,刷新了页面。
- Session 的计时器会重置,新的 30 分钟计时开始。
- 如果用户在第 35 分钟(从登录开始算)没有任何操作,那么在第 50 分钟(登录后 25 + 30)时,Session 就会失效。
Session 何时会失效?
除了因为不活动而超时外,Session 还会在以下情况下失效:
-
调用
invalidate()方法: 这是最明确的方式,通常用于用户主动“退出登录”。HttpSession session = request.getSession(); session.invalidate(); // 立即销毁当前 Session
-
服务器关闭或重启: 内存中的 Session 会随着服务器进程的结束而丢失,如果使用了像 Redis 这样的外部存储,Session 数据可以保留。
-
Session 过期: 如上所述,超过了
maxInactiveInterval时间。 -
浏览器关闭: 这是一个常见的误解。默认情况下,关闭浏览器并不会使服务器端的 Session 立即失效。
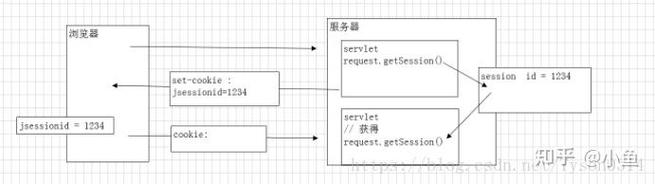
- 服务器端的 Session 仍然存在,并会一直等到其超时。
- 当用户再次打开浏览器并访问该网站时,浏览器通常不会再发送之前的 JSESSIONID cookie(除非浏览器配置了“保持登录”或使用了“记住我”功能)。
- 服务器会认为这是一个新的会话,并创建一个新的 Session。
| 方式 | 配置位置 | 单位 | 作用域 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
web.xml |
web.xml |
分钟 | 全局 | 传统方式,Servlet 规范标准 |
| 代码设置 | Java 代码 | 秒 | 当前 Session | 动态、灵活,优先级高于 web.xml |
| Spring Boot | application.properties |
分钟 或 ms |
全局 | 推荐的现代方式,简洁 |
| Spring Boot (Redis) | application.properties |
毫秒 | 全局 | 用于分布式 Session 管理 |
最佳实践建议:
- 对于传统的 Java Web 项目,优先使用
web.xml进行全局配置,特殊场景下在代码中动态覆盖。 - 对于 Spring Boot 项目,优先使用
application.properties或application.yml进行配置,这是最清晰、最符合 Spring Boot 设计理念的方式。 - 如果你的应用是微服务架构或者需要多实例共享 Session,请务必使用 Spring Session + Redis 等外部存储方案,并在配置文件中设置超时时间。