Of course! This is a fundamental and important topic for anyone managing a Tomcat server. Here’s a comprehensive guide to CATALINA_OPTS and JAVA_OPTS, covering what they are, how they differ, common use cases, and best practices.
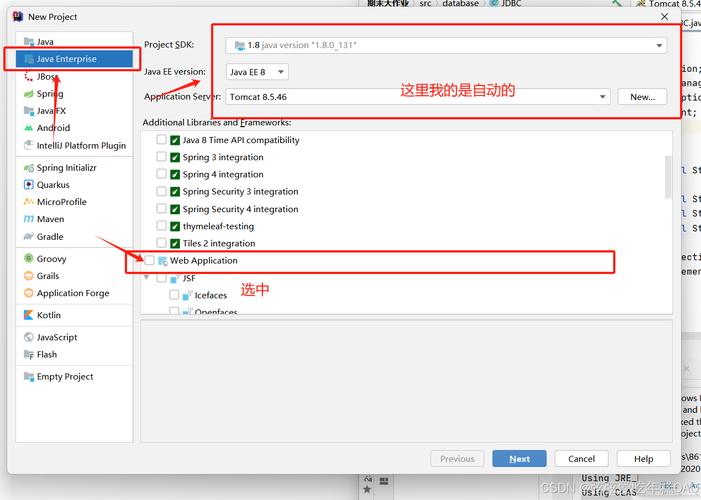
The Big Picture: What are CATALINA_OPTS and JAVA_OPTS?
These are environment variables used to pass command-line arguments to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) when you start Tomcat. They define how much memory the JVM can use, how it should perform garbage collection, and other low-level settings.
JAVA_OPTS: General JVM options.CATALINA_OPTS: JVM options specific to the Tomcat instance.
The Crucial Difference: CATALINA_OPTS vs. JAVA_OPTS
This is the most common point of confusion. The key difference lies in how they are used when you run multiple Tomcat instances on the same machine.
| Variable | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
JAVA_OPTS |
Shared Options. These are JVM arguments that should apply to any Java application run from that environment, not just Tomcat. | You have other Java services running on the same server (e.g., a standalone Spring Boot app, another app server) and you want them all to use the same JVM settings (like a default max heap size). |
CATALINA_OPTS |
Tomcat-Specific Options. These are JVM arguments that should only apply to this specific Tomcat instance. | This is the recommended variable for configuring Tomcat. It ensures that if you run multiple Tomcat instances, each one can have its own unique memory and performance settings without interfering with others. |
Why does this matter?
Imagine you have two Tomcat instances, tomcat-a and tomcat-b, on the same server.
- If you set
JAVA_OPTS="-Xmx1g", bothtomcat-aandtomcat-bwill try to use a maximum heap of 1GB. This could lead to the server running out of memory if both instances are busy. - If you set
CATALINA_OPTS="-Xmx1g"fortomcat-aandCATALINA_OPTS="-Xmx512m"fortomcat-b, each instance is configured independently and safely.
Best Practice: Always use CATALINA_OPTS for configuring your Tomcat instances. Use JAVA_OPTS only if you have a genuine reason to share settings across all Java applications on the host.
How to Set the Variables
You need to set these variables before you start the Tomcat server.
For Linux / macOS
Edit the setenv.sh script located in Tomcat's $CATALINA_HOME/bin/ directory. If this file doesn't exist, create it.
# Go to Tomcat's bin directory cd $CATALINA_HOME/bin # Create or edit the setenv.sh file vi setenv.sh
Add the following content to setenv.sh. This file is automatically executed by Tomcat's startup scripts.

#!/bin/sh # Set CATALINA_OPTS for this Tomcat instance export CATALINA_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx1024m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=256m -XX:+UseG1GC" # You could also set JAVA_OPTS here, but it's not recommended for Tomcat-specific configs # export JAVA_OPTS="-Dsome.global.property=true"
Make the script executable:
chmod +x setenv.sh
For Windows
Edit the setenv.bat script located in Tomcat's %CATALINA_HOME%\bin\ directory. If this file doesn't exist, create it.
@echo off rem Set CATALINA_OPTS for this Tomcat instance set CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx1024m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=256m -XX:+UseG1GC rem You could also set JAVA_OPTS here, but it's not recommended for Tomcat-specific configs rem set JAVA_OPTS=-Dsome.global.property=true
Common CATALINA_OPTS / JAVA_OPTS Examples
Here are some of the most common and useful options you'll use.
A. Memory Settings (The most common!)
-Xms<size>: Sets the initial heap size. It's a good practice to set this equal to-Xmxto prevent the heap from being resized during startup, which can cause a performance pause.- Example:
-Xms512m(Start with 512 MB of heap)
- Example:
-Xmx<size>: Sets the maximum heap size. This is the most important memory setting.- Example:
-Xmx2g(Allow the heap to grow up to 2 GB)
- Example:
-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize<size>: (For Java 8 and later) Sets the maximum size for the Metaspace (which replaces the older PermGen). If your application uses a lot of libraries or has many classes, you might need to increase this.- Example:
-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m(Limit Metaspace to 512 MB)
- Example:
-XX:MetaspaceSize=size: (For Java 8 and later) Sets the initial Metaspace size. Setting this can help prevent full GCs during the first few minutes of application startup as Metaspace is allocated.
Example for a medium-sized application:
export CATALINA_OPTS="-Xms1g -Xmx2g -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m"
B. Garbage Collection (GC) Tuning
The default GC is generational and can be fine, but for production servers, you often want more predictable pause times.
-XX:+UseG1GC: Uses the G1 Garbage Collector, which is the default for recent Java versions (9+). It's designed for servers with large amounts of memory and aims for predictable pause times.-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=<time>: A hint to the G1 collector that pauses should not exceed this time in milliseconds. It's a goal, not a guarantee.- Example:
-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=200(Aim for GC pauses under 200ms)
- Example:
-XX:+UseParallelGC: Uses the parallel throughput collector. This is good for maximizing throughput but can have longer, less predictable pauses.
Example for a production server with low-latency requirements:
export CATALINA_OPTS="-XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=200"
C. Logging and Debugging
-Djava.awt.headless=true: Essential for running Tomcat on a server without a graphical display. It prevents headless exceptions.-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8: Explicitly sets the default file encoding to UTF-8, which is highly recommended to avoid character encoding issues.-D<property.name>=<value>: Sets a Java system property. Many applications read configuration this way.- Example:
-Dapp.environment=production
- Example:
-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005: Enables remote debugging. This allows you to connect a debugger (like IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse) to the running Tomcat instance.suspend=nmeans Tomcat will start immediately;suspend=ywill pause it until a debugger attaches.
Example for a production environment:
export CATALINA_OPTS="-Djava.awt.headless=true -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Dapp.environment=production"
D. Advanced JVM Flags
-XX:+UseLargePages: Can improve performance by using the OS's large page memory feature. Requires OS-level configuration.-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError: Automatically generates a heap dump if the JVM runs out of memory. This is invaluable for post-mortem analysis.-XX:HeapDumpPath=/path/to/dumps/: Specifies where to save the heap dump file.
Example for robust production monitoring:
export CATALINA_OPTS="-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/var/log/tomcat/heap-dumps"
Putting It All Together: A Production Example
Here is a realistic CATALINA_OPTS string for a production Tomcat instance running a memory-intensive Java application on a server with 8GB of RAM.
#!/bin/sh # Production settings for a Tomcat instance export CATALINA_OPTS=" -Xms2g -Xmx4g -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m -XX:MetaspaceSize=256m -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=200 -Djava.awt.headless=true -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Dapp.environment=production -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=9010 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/var/log/tomcat/heap-dumps "
Explanation of this example:
- Memory: Starts with 2GB heap, allows it to grow to a max of 4GB. Metaspace starts at 256MB and can grow up to 512MB.
- GC: Uses G1GC with a goal to keep pauses under 200ms.
- Environment: Sets standard properties for headless operation, UTF-8 encoding, and a production flag.
- Monitoring: Enables JMX remote management on port 9010 for monitoring tools (like VisualVM or Prometheus).
- Crash Analysis: Will automatically save a heap dump if an
OutOfMemoryErroroccurs.