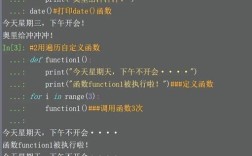
在 Python 中,获取当前 Python 解释器的路径(即 python 或 python3 命令对应的可执行文件路径)可以通过以下几种方法实现,以下是几种常见的方法,并附有详细说明和示例。
方法 1:使用 sys.executable(推荐)
sys.executable 是 Python 标准库 sys 模块中的一个变量,它直接返回当前 Python 解释器的完整路径,这是最直接、最可靠的方法。
import sys print(sys.executable)
示例输出:
/usr/bin/python3或
C:\Users\YourUser\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python39\python.exe方法 2:使用 os 模块(通过环境变量)
可以通过 os 模块访问环境变量 PATH,并从中查找 Python 解释器的路径,这种方法不如 sys.executable 直接,但在某些特殊场景(如需要查找系统中所有 Python 安装路径)时可能有用。

import os
# 获取环境变量 PATH
path_env = os.environ.get("PATH")
# 分割 PATH 并查找包含 python 的路径
python_paths = [p for p in path_env.split(os.pathsep) if "python" in p.lower()]
print(python_paths)
示例输出:
['/usr/bin', '/usr/local/bin', '/usr/sbin'](需要进一步过滤出具体的可执行文件路径)
方法 3:使用 shutil 模块(查找可执行文件)
shutil.which() 可以查找可执行文件在系统中的路径,类似于 Unix 的 which 命令或 Windows 的 where 命令。
import shutil
python_path = shutil.which("python")
python3_path = shutil.which("python3")
print("python:", python_path)
print("python3:", python3_path)
示例输出:
python: /usr/bin/python
python3: /usr/bin/python3方法 4:通过 subprocess 调用系统命令
可以通过 subprocess 模块执行系统命令(如 which python 或 where python)并捕获输出。
Linux/macOS:
import subprocess result = subprocess.run(["which", "python"], capture_output=True, text=True) python_path = result.stdout.strip() print(python_path)
Windows:
import subprocess result = subprocess.run(["where", "python"], capture_output=True, text=True) python_path = result.stdout.splitlines()[0].strip() # 取第一行 print(python_path)
总结与推荐
| 方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
sys.executable |
直接、准确、无需外部依赖 | 仅返回当前解释器路径 | 获取当前 Python 解释器路径 |
os.environ |
可灵活查找所有 Python 路径 | 需要手动解析,可能不准确 | 需要遍历系统 PATH 时 |
shutil.which() |
跨平台,查找系统可执行文件 | 依赖系统 PATH 配置 | 查找 Python 在系统中的安装路径 |
subprocess |
灵活,可执行任意系统命令 | 依赖外部命令,可能有兼容性问题 | 需要复杂系统命令时 |
推荐使用 sys.executable,因为它最直接、最可靠,且是 Python 标准库的一部分。