Of course! Here is a comprehensive description of Python, broken down for clarity.
What is Python?
At its core, Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language.
Let's break that down:
- High-Level: It's designed to be easy for humans to read and write. It abstracts away complex details of the computer's memory management and hardware, allowing you to focus on solving problems with clean, logical code.
- Interpreted: Unlike languages like C++ or Java that need to be compiled into machine code before running, Python code is executed line by line by an interpreter. This makes development and testing faster.
- General-Purpose: Python is not designed for one specific task. You can use it for web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, scientific computing, automation, and much more.
The language's name is a tribute to the British comedy group Monty Python, not the snake.
Key Characteristics and Philosophy
Python's design is guided by a set of principles known as "The Zen of Python," which you can see by typing import this in a Python interpreter. The most famous lines are:

- "Beautiful is better than ugly."
- "Simple is better than complex."
- "Readability counts."
- "There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it."
These principles lead to several key characteristics:
-
Readable and Simple Syntax: Python uses indentation (whitespace at the beginning of a line) to define code blocks, like loops and functions. This enforces clean, readable code and eliminates the need for curly braces or semicolons found in many other languages.
# A simple for loop in Python fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] for fruit in fruits: print(fruit) -
Vast Standard Library: Python comes with a rich set of built-in modules and functions that can handle many common tasks (like connecting to the web, working with files, or manipulating data) without needing external libraries.
-
Huge Ecosystem of Third-Party Packages: If the standard library isn't enough, Python has a massive ecosystem of packages available through the Python Package Index (PyPI). This is one of Python's greatest strengths. You can easily install powerful tools for almost any purpose using a tool like
pip. (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删) -
Cross-Platform: Python code is highly portable. You can write a script on Windows and run it on macOS or Linux with little to no changes.
-
Dynamically Typed: You don't need to declare the type of a variable (e.g.,
int,string). The type is determined at runtime. This makes coding faster but requires careful testing.message = "Hello, World!" # message is a string message = 42 # Now message is an integer
-
Multi-Paradigm: Python supports several programming styles, including:
- Procedural: Organizing code around procedures or functions.
- Object-Oriented (OOP): Using classes and objects to model real-world things.
- Functional: Treating computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions.
What is Python Used For? (Popular Applications)
Python's versatility makes it a top choice in many fields.
-
Web Development:
- Frameworks: Django, Flask, FastAPI.
- Used to build everything from simple blogs to complex, data-driven web applications like Instagram and Spotify.
-
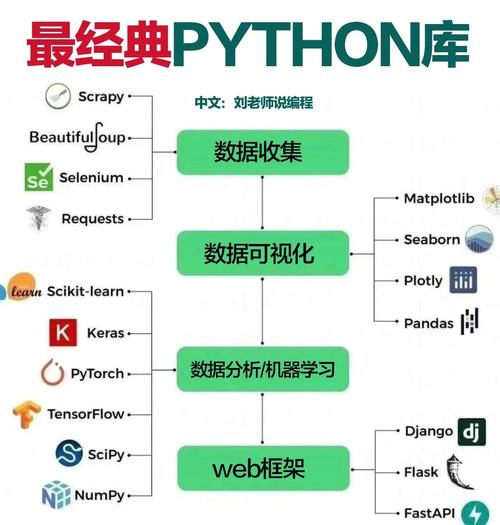
Data Science & Machine Learning:
- Libraries: NumPy (numerical computing), Pandas (data manipulation), Matplotlib/Seaborn (data visualization), Scikit-learn (machine learning).
- This is arguably Python's most popular domain. It's the go-to language for data analysts, scientists, and AI researchers.
-
Automation & Scripting:
- Python is excellent for writing small scripts to automate repetitive tasks.
- Examples: Automatically renaming files, sending emails, scraping data from websites, or system administration tasks.
-
Software Development:
- Used as a "glue language" to connect different components of a software system.
- Example: The software for the Mars rovers (Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity) was heavily written in Python.
-
Game Development:
- Libraries: Pygame, Panda3D.
- While not as powerful as engines like Unity or Unreal, it's great for beginners to learn game development concepts.
-
Scientific Computing & Academia:
- Libraries: SciPy, SymPy.
- Widely used in research, engineering, and mathematics for simulations and complex calculations.
Python 2 vs. Python 3
It's important to know that there are two major versions of Python.
- Python 2: The older version. It is end-of-life as of January 1, 2025. This means it no longer receives updates or security patches.
- Python 3: The current, modern standard. It was released in 2008 with significant improvements, including better Unicode support and cleaner syntax.
For any new project, you should always use Python 3.
Getting Started with Python
- Installation: Download the latest version from the official website: python.org.
- Writing Code: You can write Python code in:
- Interactive Interpreter: A command-line tool for quick, one-line commands.
- Code Editor: A simple text editor like VS Code, Sublime Text, or Notepad++.
- Integrated Development Environment (IDE): A full-featured tool like PyCharm or Spyder that offers debugging, project management, and more.
- Running Code: Save your code in a file with a
.pyextension (e.g.,hello.py) and run it from your terminal with the command:python hello.py
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Easy to Learn: Its simple syntax makes it the perfect first language for beginners.
- Massive Community and Support: If you have a problem, chances are someone else has already solved it. There are countless tutorials, forums, and documentation available.
- Versatility: A single language can be used for web, data, and scripting.
- Productivity: The simplicity and vast library ecosystem allow developers to build and deploy applications quickly.
Disadvantages:
- Slower Performance: Being an interpreted language and dynamically typed makes Python slower than compiled languages like C++ or Java for CPU-intensive tasks.
- High Memory Consumption: Python's flexibility comes at a cost; it uses more memory than statically-typed languages.
- Global Interpreter Lock (GIL): In CPython (the standard implementation), the GIL is a mutex that allows only one thread to execute Python bytecode at a time. This prevents true parallel execution on multi-core processors for CPU-bound tasks, though it's not an issue for I/O-bound tasks.
Summary
Python is a powerful, flexible, and beginner-friendly programming language that has become a dominant force in the tech industry. Its emphasis on readability, combined with a massive ecosystem of tools, makes it an excellent choice for everyone from complete novices to seasoned professionals working on complex projects in data science, web development, and automation.