Of course! This is a fundamental concept in Java (and object-oriented programming in general). Let's break down extends and super clearly.

extends (Inheritance)
The extends keyword is used to create a new class (the subclass or child class) that inherits attributes and methods from an existing class (the superclass or parent class).
Think of it as an "is-a" relationship. For example, a Dog is a Animal, so a Dog class can extend an Animal class.
Why use extends?
- Code Reusability: You don't have to write the same code over and over again. You can put common code in a parent class and have child classes inherit it.
- Method Overriding: A child class can provide a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in its parent class. This is a key part of polymorphism.
- Logical Structure: It helps you model real-world relationships in your code, making it more organized and understandable.
Simple Example of extends
Let's create an Animal parent class and a Dog child class.
The Superclass (Animal.java)
This class contains general properties and behaviors that all animals might share.
// File: Animal.java
public class Animal {
// A field (attribute) in the parent class
String name;
// The constructor for the parent class
public Animal(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// A method in the parent class
public void eat() {
System.out.println(name + " is eating.");
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println(name + " is sleeping.");
}
}
The Subclass (Dog.java)
This class extends Animal. It inherits name, eat(), and sleep(). It also adds its own specific properties and methods.
// File: Dog.java
public class Dog extends Animal { // "Dog extends Animal" means Dog inherits from Animal
// A new field specific to Dog
String breed;
// The constructor for the Dog class
// It MUST call the parent's constructor using super()
public Dog(String name, String breed) {
super(name); // Calls the constructor of the Animal class
this.breed = breed;
}
// A new method specific to Dog
public void bark() {
System.out.println(name + " the " + breed + " says: Woof!");
}
// Method OVERRIDING: Providing a new implementation for an inherited method
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(name + " the " + breed + " is eating dog food.");
}
}
The Main Class (Main.java) - To see it in action
// File: Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of the Dog subclass
Dog myDog = new Dog("Buddy", "Golden Retriever");
// You can use methods inherited from the Animal class
myDog.eat(); // Calls the OVERRIDDEN eat() method in Dog
myDog.sleep(); // Calls the inherited sleep() method from Animal
myDog.bark(); // Calls the specific bark() method in Dog
System.out.println("Dog's name: " + myDog.name); // Access inherited field
}
}
Output:
Buddy the Golden Retriever is eating dog food.
Buddy is sleeping.
Buddy the Golden Retriever says: Woof!
Dog's name: Buddysuper (Keyword to Access Superclass Members)
The super keyword is a reference variable used to refer to the immediate parent class object. It's used for two main purposes:
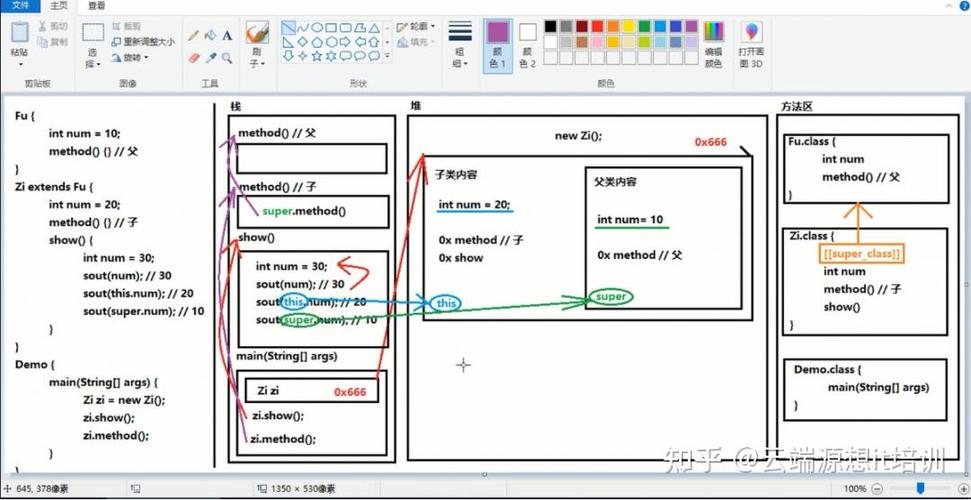
- To call the constructor of the parent class.
- To access a member (field or method) of the parent class when it is hidden by the subclass.
super() in Constructors
When you create an object of a subclass, the constructor of the parent class is always called first. This ensures that the inherited part of the object is initialized correctly.
- If you don't explicitly write
super(...)in the subclass's constructor, Java automatically inserts a call to the no-argument constructor of the parent class (super();). - If the parent class does not have a no-argument constructor, you must explicitly call one of its parameterized constructors using
super(...).
From our Dog example above:
public Dog(String name, String breed) {
super(name); // This line is crucial. It calls Animal's constructor: public Animal(String name)
this.breed = breed;
}
super for Accessing Members
Use super when your subclass has a field or method with the same name as one in the parent class. This is called shadowing.
super.fieldName: Accesses the parent class's field.super.methodName(): Calls the parent class's method.
Example of super for Member Access
Let's modify our Dog class to show this.
// File: Dog.java
public class Dog extends Animal {
String name; // This 'name' SHADOWS the 'name' field in Animal
public Dog(String nameFromUser, String breed) {
super(nameFromUser); // Initialize the parent's 'name' field
this.name = breed; // Initialize the Dog's 'name' field with the breed
}
@Override
public void eat() {
// Call the parent's eat() method first
super.eat();
// Then add some dog-specific behavior
System.out.println("And he's enjoying it!");
}
public void displayNames() {
System.out.println("Parent's name (from super.name): " + super.name);
System.out.println("Dog's name (from this.name): " + this.name);
}
}
Main Class to test this:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog myDog = new Dog("Rex", "German Shepherd");
myDog.displayNames();
System.out.println("---");
myDog.eat();
}
}
Output:
Parent's name (from super.name): Rex
Dog's name (from this.name): German Shepherd
---
Rex is eating.
And he's enjoying it!Summary Table: extends vs. super
| Feature | extends |
super |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Keyword used in a class declaration. | Keyword used inside a method or constructor. |
| Purpose | To establish an inheritance ("is-a") relationship between classes. | To access members (fields, methods, constructors) of the parent class. |
| Analogy | "A Car is a Vehicle." |
"Use the parent's version of this method/field." |
| Common Use | public class Car extends Vehicle { ... } |
super(speed); (call parent constructor)super.startEngine(); (call parent method) |
| Relationship | Defines the structure of the class hierarchy. | Operates within the structure to access parent components. |
Important Related Concept: implements
You might also see implements used with classes. This is different from extends.
extends: Used for class inheritance (a subclass inherits from a superclass). A class can only extend one other class (single inheritance).implements: Used for interface implementation. An interface is a "contract" that defines a set of methods a class must have. A class can implement multiple interfaces.
Example:
// A class can only extend one class
public class Dog extends Animal { ... }
// But can implement multiple interfaces
public class SmartDog extends Animal implements Pet, GuardDog { ... }