Of course! "Java and MongoDB" is a very common and powerful combination for building modern applications. This guide will cover everything you need to know, from the basics to advanced topics.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components and how they work together.
The Core Concept: What is MongoDB?
- What it is: A NoSQL, document-oriented database.
- How it differs from SQL:
- SQL (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL): Stores data in tables with rows and columns. Data must have a rigid, predefined schema.
- MongoDB: Stores data in documents (similar to JSON objects). These documents are collected into collections (like tables). It has a flexible schema, meaning documents in the same collection can have different fields.
- Why use it with Java?
- Flexibility: Perfect for applications where data structures change frequently (e.g., product catalogs, user profiles with optional fields).
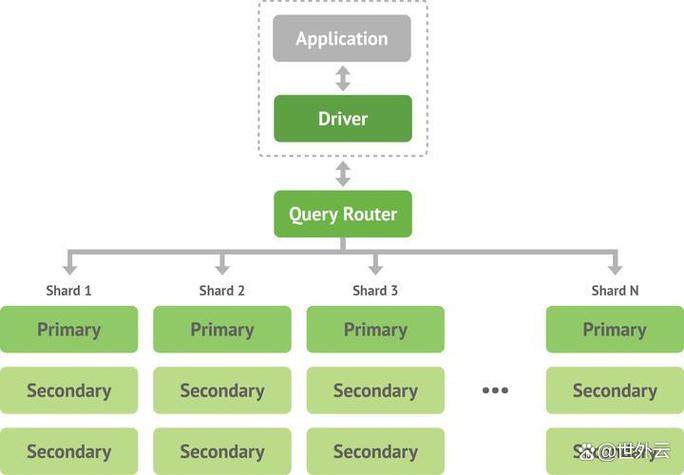
- Scalability: Designed for horizontal scaling (sharding across multiple servers), which is great for high-traffic applications.
- Developer Productivity: The document model maps very naturally to objects in Java, reducing the "impedance mismatch" between your application and your database.
The Official Driver: MongoDB Java Driver
To connect your Java application to MongoDB, you use the official MongoDB Java Driver. This is the fundamental library that handles all communication.
Key Features of the Driver:
- Asynchronous: The driver supports both a synchronous (blocking) and an asynchronous (non-blocking, reactive) API.
- Modern API: Uses the
mongodb-driver-sync,mongodb-driver-reactivestreams, andmongodb-driver-coremodules. - BSON Support: It can serialize and deserialize BSON (Binary JSON), the format MongoDB uses.
The Most Popular ODM: MongoDB Spring Data
While the Java driver is powerful, it requires you to write a lot of boilerplate code for creating connections, serializing objects, and building queries.
MongoDB Spring Data (part of the larger Spring Data project) is the de-facto standard for integrating MongoDB with Spring Boot applications. It dramatically simplifies data access.
What is an ODM (Object Document Mapper)?
It's the NoSQL equivalent of an ORM (Object Relational Mapper). It maps your Java objects (POJOs) to MongoDB documents and vice-versa.
Key Benefits of Spring Data:
MongoRepository: You get a powerful, pre-built repository interface with methods likesave(),findById(),findAll(),deleteById(), etc. You just define an interface that extendsMongoRepository, and Spring provides the implementation at runtime.- Automatic Implementation: You don't write the implementation code for basic CRUD operations.
- Query Methods: You can create complex queries simply by naming your method. For example,
findByFirstNameAndLastName(String firstName, String lastName)is automatically translated into a MongoDB query. - Seamless Integration: Works perfectly with Spring Boot's auto-configuration.
Step-by-Step Guide: Connecting Java to MongoDB
Let's walk through the most common scenario: a Spring Boot application.
Step 1: Set up your Project (using Spring Initializr)
- Go to start.spring.io.
- Project: Maven Project
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: Choose a recent stable version (e.g., 3.x.x).
- Project Metadata:
- Group:
com.example - Artifact:
mongodb-demo - Packaging: Jar
- Java: 17 or newer
- Group:
- Dependencies: Add
Spring WebandSpring Data MongoDB. - Click "GENERATE" and download the ZIP file. Unzip it and open it in your favorite IDE (IntelliJ, VS Code, Eclipse).
Step 2: Configure MongoDB Connection
Open src/main/resources/application.properties and add your MongoDB connection string.
# Connect to a local MongoDB instance spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost:27017/mydatabase # For MongoDB Atlas (cloud), it will look like this: # spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@cluster0.xxxxx.mongodb.net/mydatabase?retryWrites=true&w=majority
Step 3: Create a Document Model (POJO)
Create a Java class that represents a document in your mydatabase collection. The @Document annotation tells Spring that this class is a MongoDB document.

// src/main/java/com/example/mongodbdemo/model/User.java
package com.example.mongodbdemo.model;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
import java.util.List;
@Document(collection = "users") // Maps this class to the 'users' collection
public class User {
@Id // Marks this field as the primary key (will be '_id' in MongoDB)
private String id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private List<String> roles;
// Constructors, Getters, and Setters
// (You can use Lombok's @Data annotation to auto-generate these)
public User() {}
public User(String firstName, String lastName, String email, List<String> roles) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.roles = roles;
}
// Getters and Setters...
public String getId() { return id; }
public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; }
public String getFirstName() { return firstName; }
public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; }
// ... and so on for lastName, email, roles
}
Step 4: Create the Repository Interface
Create an interface that extends MongoRepository. Spring will provide all the CRUD methods for you for free.
// src/main/java/com/example/mongodbdemo/repository/UserRepository.java
package com.example.mongodbdemo.repository;
import com.example.mongodbdemo.model.User;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserRepository extends MongoRepository<User, String> {
// You can add custom query methods here
List<User> findByLastName(String lastName);
}
Step 5: Use the Repository in a Service
Now, inject the repository into a service class and use it to perform database operations.
// src/main/java/com/example/mongodbdemo/service/UserService.java
package com.example.mongodbdemo.service;
import com.example.mongodbdemo.model.User;
import com.example.mongodbdemo.repository.UserRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
public Optional<User> getUserById(String id) {
return userRepository.findById(id);
}
public User createUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
public void deleteUser(String id) {
userRepository.deleteById(id);
}
// Using the custom query method from the repository
public List<User> getUsersByLastName(String lastName) {
return userRepository.findByLastName(lastName);
}
}
Step 6: Create a REST Controller to Test
Finally, expose these operations as REST endpoints.
// src/main/java/com/example/mongodbdemo/controller/UserController.java
package com.example.mongodbdemo.controller;
import com.example.mongodbdemo.model.User;
import com.example.mongodbdemo.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return userService.getAllUsers();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUserById(@PathVariable String id) {
return userService.getUserById(id)
.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.orElse(ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<User> createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
User createdUser = userService.createUser(user);
return new ResponseEntity<>(createdUser, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteUser(@PathVariable String id) {
userService.deleteUser(id);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
}
Step 7: Run and Test
-
Make sure your MongoDB server is running.
-
Run the
SpringMongodbDemoApplication.javamain class. -
Use a tool like
curlor Postman to interact with your API:-
Create a User:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/users \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"firstName": "John", "lastName": "Doe", "email": "john.doe@example.com", "roles": ["USER"]}' -
Get All Users:
curl http://localhost:8080/api/users
-
Get User by ID: (replace
<id>with the ID from the created user)curl http://localhost:8080/api/users/<id>
-
Key Considerations & Advanced Topics
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Transactions | MongoDB supports multi-document ACID transactions. Spring Data makes them easy with @Transactional annotations. This is crucial for maintaining data consistency across multiple operations. |
| Indexes | For performance-critical applications, you need to create indexes on frequently queried fields. You can do this via the MongoDB shell or through annotations in your model class: @Indexed(unique = true, name = "email_idx") on the email field. |
| Aggregation Framework | MongoDB's Aggregation Framework is a powerful tool for data processing and analysis. You can perform complex data transformations, filtering, and grouping. Spring Data allows you to define these pipelines as Java code. |
| MongoDB Atlas | For production, use MongoDB Atlas, the fully managed cloud database service. It handles backups, scaling, and security for you, which is highly recommended. |
| Security | Always enable authentication and authorization on your MongoDB instance. Use TLS/SSL for encryption in transit. Store your connection strings and credentials securely (e.g., using environment variables or a secrets manager). |
| Testing | Use an embedded MongoDB instance like de.flapdoodle.embed.mongo for your integration tests. This allows your tests to run without needing a live MongoDB server. |
Summary
- Java Driver: The low-level, essential library for connecting to MongoDB. It's powerful but verbose.
- Spring Data MongoDB: The high-level, recommended approach for Spring Boot applications. It uses the Java driver under the hood but provides immense productivity gains through the
MongoRepositoryand ODM features. - Workflow: Define your Document Model (
@Document) -> Create a Repository Interface (extends MongoRepository) -> Inject and use the repository in a Service -> Expose functionality via a REST Controller.
This combination provides a robust, scalable, and developer-friendly way to build modern data-driven applications.