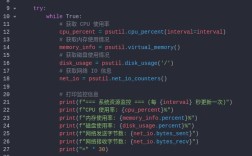
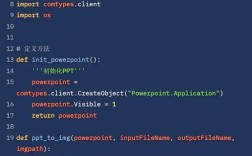
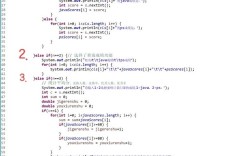
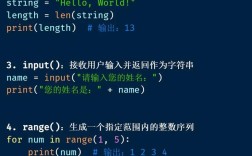
Of course! "Python Development" is a vast and exciting field. Let's break it down into a comprehensive guide, from the absolute basics to advanced career paths.
This guide is structured for everyone:
- Beginners: Just starting out and wondering what all the fuss is about.
- Intermediate Developers: Looking to solidify their skills and explore new areas.
- Experts: Seeking best practices and career advice.
What is Python and Why is it So Popular?
Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. It's known for its simple, readable syntax that makes it a favorite for beginners and experts alike.
Key Reasons for its Popularity:
- Readable and Simple Syntax: Python code looks like plain English, making it easy to learn and maintain.
# A simple Python loop fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] for fruit in fruits: print(f"I like {fruit}s!") - Massive Standard Library: It comes with "batteries included," meaning you have access to a huge library of pre-written code for common tasks (connecting to the web, handling data, etc.).
- Vibrant Ecosystem (The "Batteries Included" on Steroids): Through third-party packages (installed via
pip), Python can do almost anything. - Versatility: It's not tied to one domain. You can use it for web development, data science, artificial intelligence, scripting, and more.
- Huge Community and Support: If you have a problem, chances are someone else has already solved it. There are countless tutorials, forums (like Stack Overflow), and meetups.
Core Concepts and Skills for Python Development
No matter what you do with Python, you need a solid foundation in these core areas.

a. The Language Itself
- Basic Syntax: Variables, data types (strings, integers, floats, booleans).
- Data Structures: This is crucial.
- Lists: Ordered, mutable collections.
[1, 2, 'a'] - Tuples: Ordered, immutable collections.
(1, 2, 'a') - Dictionaries: Unordered collections of key-value pairs.
{'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30} - Sets: Unordered collections of unique items.
{1, 2, 3}
- Lists: Ordered, mutable collections.
- Control Flow:
- Conditional statements:
if,elif,else - Loops:
forloops,whileloops
- Conditional statements:
- Functions: How to define reusable blocks of code with
def. Understanding parameters, arguments, and return values. - Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):
- Classes and Objects: The blueprint and the instance.
- Inheritance, Encapsulation, and Polymorphism: Core principles for writing organized, scalable code.
- Error Handling: Using
try...exceptblocks to manage potential errors gracefully. - File I/O: Reading from and writing to files (
.txt,.csv,.json). - Working with APIs: Making HTTP requests (using the
requestslibrary) to interact with web services and fetch data.
b. Essential Tools
- Code Editor / IDE (Integrated Development Environment):
- VS Code (Visual Studio Code): The most popular choice. Free, lightweight, and has a massive extension library for Python.
- PyCharm: A full-featured IDE from JetBrains. The "Community Edition" is free and excellent for serious development.
- Jupyter Notebooks: Interactive environments perfect for data analysis, visualization, and learning. You can run code in small, isolated cells.
- Version Control:
- Git: The industry-standard system for tracking changes in your code.
- GitHub / GitLab / Bitbucket: Platforms to host your Git repositories, enabling collaboration and showcasing your work.
- Virtual Environments:
venvorpipenv: Tools to create isolated environments for your projects. This prevents conflicts between project dependencies. This is a non-negotiable skill for any professional developer.
- Package Managers:
pip: The default tool for installing Python packages from the Python Package Index (PyPI).conda: Popular in the data science world, as it also manages non-Python dependencies (like libraries for C/C++).
Major Specializations in Python Development
This is where you can choose your path. Python is a gateway to many different careers.
Path 1: Web Development
You build the back-end (server-side logic) of websites and web applications.
- Key Frameworks:
- Django: A high-level, "batteries-included" framework. It's great for building complex, database-driven applications quickly. It has its own ORM (Object-Relational Mapper), admin panel, and templating engine.
- Flask: A micro-framework. It's lightweight and gives you more control. You start with the basics and add only the components you need (e.g., you can choose your own database library). Great for smaller projects and APIs.
- What You'll Build: E-commerce sites, social media platforms, content management systems (CMS), RESTful APIs.
- Essential Libraries:
SQLAlchemy(ORM),Django REST Framework(for APIs),Jinja2(templating).
Path 2: Data Science & Machine Learning
You extract insights and build predictive models from data.
- Core Stack:
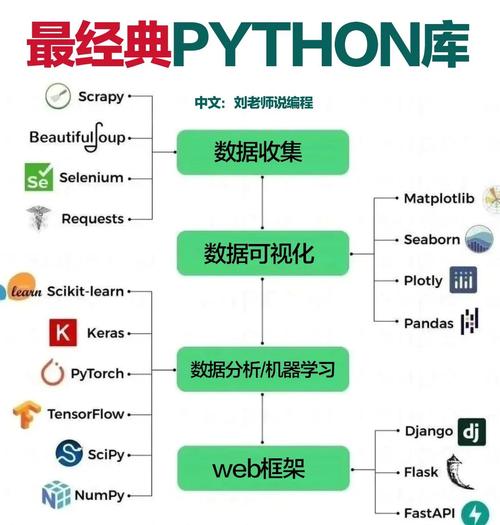
- Pandas: The cornerstone of data analysis in Python. It provides data structures like DataFrames for manipulating and analyzing structured data.
- NumPy: The fundamental package for numerical computation. It provides powerful N-dimensional array objects.
- Matplotlib & Seaborn: For data visualization. Creating charts, graphs, and plots to explore and present your findings.
- Machine Learning:
- Scikit-learn: The go-to library for classical machine learning tasks (classification, regression, clustering).
- TensorFlow & PyTorch: The two dominant libraries for deep learning, used to build complex neural networks for tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and generative AI.
- What You'll Build: Customer churn prediction models, recommendation engines (like Netflix or Amazon), sentiment analysis tools, AI chatbots.
Path 3: Scripting & Automation
You write small programs to automate repetitive tasks.

- Use Cases:
- File Management: Renaming thousands of files, moving files based on their type.
- Web Scraping: Automatically extracting data from websites (using libraries like
BeautifulSoupandScrapy). - System Administration: Automating server backups, monitoring system logs, deploying code.
- Data Cleaning: Automating the process of cleaning and formatting messy data files.
- Key Libraries:
os,shutil(for file system interaction),requests(for web scraping),schedule(for task scheduling).
Path 4: Software Development & DevOps
Using Python to build desktop applications, command-line tools (CLI), and for infrastructure automation.
- GUI Development:
- PyQt / PySide: For building complex, professional desktop applications.
- Tkinter: Python's built-in GUI toolkit, great for simple tools.
- DevOps & Cloud:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Tools like Ansible use YAML and Python-like syntax to automate cloud server provisioning and configuration.
- Cloud SDKs: AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure all have Python SDKs for managing their services.
- Testing Frameworks:
pytestis a powerful and popular choice for writing automated tests for your applications.
A Learning Roadmap
Step 1: Learn the Fundamentals (1-2 Months)
- Goal: Understand the basic syntax and core concepts.
- Action:
- Go through a beginner's tutorial (freeCodeCamp, Coursera, etc.).
- Practice on platforms like HackerRank or LeetCode (start with the "Easy" problems).
- Build a few small command-line projects: a number guessing game, a simple to-do list, a calculator.
Step 2: Choose a Specialization and Dive Deeper (3-6 Months)
- Goal: Get proficient with the tools of your chosen path.
- Action:
- Web Dev: Build a simple blog using Django or Flask. Learn how to connect to a database (like PostgreSQL or SQLite).
- Data Science: Take a course on Coursera like "Applied Data Science with Python". Work with the Iris dataset and analyze a CSV file of your choice.
- Scripting: Automate a task you do daily. For example, write a script that organizes your downloads folder.
Step 3: Build a Portfolio (Ongoing)
- Goal: Showcase your skills to employers.
- Action:
- Pick 3-5 interesting projects. Quality over quantity is key.
- Put them on GitHub. Write a good
README.mdfile for each project explaining what it does, the technologies used, and how to run it. - Make one of your projects a "capstone." A more complex application that ties together everything you've learned.
Step 4: Get a Job (The Next Level)
- Goal: Land your first Python development job.
- Action:
- Tailor your resume to the job description.
- Practice for interviews: Be ready to explain your projects in detail. Expect whiteboard coding sessions or live coding exercises.
- Network: Attend meetups (virtual or in-person) and connect with people on LinkedIn.
Best Practices and Community
- PEP 8: Read the Python Enhancement Proposal 8. It's the style guide for Python code. Following it makes your code clean and readable.
- Read Other People's Code: The best way to learn best practices is to read well-written open-source projects on GitHub.
- Contribute to Open Source: Even fixing a typo in a project's documentation is a great way to start collaborating.
- Stay Updated: The Python ecosystem moves fast. Follow blogs, listen to podcasts, and attend conferences to keep up with the latest trends.