Of course. This is a very common task, especially when integrating Java and .NET systems. The core concepts are the same, but the APIs and class names differ significantly.
Here’s a complete guide on how to encode and decode Base64 in both Java and .NET, with examples that show how to produce identical output.
The Core Concept: What is Base64?
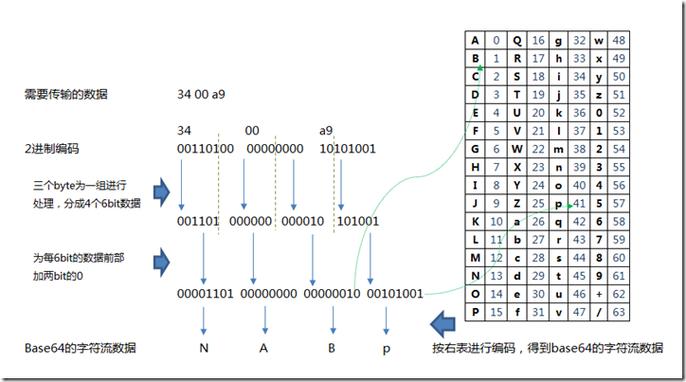
Base64 is an encoding scheme that represents binary data in an ASCII string format by translating it into a radix-64 representation. It's not encryption; it's a way to safely transmit data over media that are designed to handle text.
Java (8 and later)
Modern Java (since version 8) has a dedicated java.util.Base64 class that is the standard way to handle Base64 operations. It's clean and straightforward.
Key Classes:
java.util.Base64: The main utility class.java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets: Specifies the character set (almost always UTF-8).
Encoding in Java
To convert a string to Base64:

- Get the bytes of the string using
.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8). - Use
Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString().
import java.util.Base64;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class JavaBase64Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String originalString = "Hello, .NET World! 🌎";
// 1. Get the encoder
Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
// 2. Encode the string's bytes to a Base64 string
String base64EncodedString = encoder.encodeToString(originalString.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
System.out.println("Original: " + originalString);
System.out.println("Encoded: " + base64EncodedString);
// Expected Output: SGVsbG8sIC5ETlQgV29ybGQhIPCfk4E=
}
}
Decoding in Java
To convert a Base64 string back to the original string:
- Get the decoder using
Base64.getDecoder(). - Use
.decode()to get the original byte array. - Convert the byte array back to a string using
new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8).
import java.util.Base64;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class JavaBase64Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String base64EncodedString = "SGVsbG8sIC5ETlQgV29ybGQhIPCfk4E=";
// 1. Get the decoder
Base64.Decoder decoder = Base64.getDecoder();
// 2. Decode the Base64 string to a byte array
byte[] decodedBytes = decoder.decode(base64EncodedString);
// 3. Convert the byte array back to a string
String decodedString = new String(decodedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Encoded: " + base64EncodedString);
System.out.println("Decoded: " + decodedString);
// Expected Output: Hello, .NET World! 🌎
}
}
.NET (Core / Framework)
In .NET, the System.Convert class is the primary tool for Base64 operations. The process is a bit different: you first convert the string to a byte array (using an Encoding class), then convert that byte array to/from a Base64 string.
Key Classes:
System.Convert: The static class withToBase64StringandFromBase64Stringmethods.System.Text.Encoding: Specifies the character set (almost alwaysUTF8).
Encoding in .NET
To convert a string to Base64:
- Get the byte array of the string using
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(). - Use
Convert.ToBase64String().
using System;
using System.Text;
public class DotNetBase64Example
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string originalString = "Hello, .NET World! 🌎";
// 1. Get the byte array of the string using UTF8 encoding
byte[] bytesToEncode = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(originalString);
// 2. Convert the byte array to a Base64 string
string base64EncodedString = Convert.ToBase64String(bytesToEncode);
Console.WriteLine("Original: " + originalString);
Console.WriteLine("Encoded: " + base64EncodedString);
// Expected Output: SGVsbG8sIC5ETlQgV29ybGQhIPCfk4E=
}
}
Decoding in .NET
To convert a Base64 string back to the original string:
- Use
Convert.FromBase64String()to get the original byte array. - Convert the byte array back to a string using
Encoding.UTF8.GetString().
using System;
using System.Text;
public class DotNetBase64Example
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string base64EncodedString = "SGVsbG8sIC5ETlQgV29ybGQhIPCfk4E=";
// 1. Convert the Base64 string to a byte array
byte[] decodedBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(base64EncodedString);
// 2. Convert the byte array back to a string using UTF8 encoding
string decodedString = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(decodedBytes);
Console.WriteLine("Encoded: " + base64EncodedString);
Console.WriteLine("Decoded: " + decodedString);
// Expected Output: Hello, .NET World! 🌎
}
}
Comparison and Key Differences
| Feature | Java (8+) | .NET |
|---|---|---|
| Main Class | java.util.Base64 |
System.Convert |
| Encoder Method | Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString() |
Convert.ToBase64String() |
| Decoder Method | Base64.getDecoder().decode() |
Convert.FromBase64String() |
| Encoding | .getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8) |
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes() |
| Decoding | new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8) |
Encoding.UTF8.GetString() |
The most important takeaway for interoperability:
Always specify UTF-8 encoding when converting between strings and byte arrays. If you use the platform's default encoding (which can vary), you will get different results and the systems will not be able to communicate correctly.
Cross-Language Interoperability Example
This is the most common scenario. A Java application sends a Base64 encoded string to a .NET application, which must decode it correctly.
Scenario: A Java service encodes a JSON object and sends it to a .NET API.
Java (Sender)
import java.util.Base64;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class JavaSender {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// In a real app, this might be a JSON payload from a file or database
String jsonPayload = "{\"userId\": 123, \"action\": \"login\", \"timestamp\": \"2025-10-27T10:00:00Z\"}";
// Encode the JSON string to Base64
Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
String encodedPayload = encoder.encodeToString(jsonPayload.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
System.out.println("Java is sending this Base64 string to .NET:");
System.out.println(encodedPayload);
// Expected Output: eyJ1c2VySWQiOjEyMywgImFjdGlvbiI6ImxvZ2luIiwgdGltZXN0YW1wIjoiMjAyMy0xMC0yN1QxMDowMDowMCJ9
}
}
.NET (Receiver)
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.Json; // For pretty printing the JSON
public class DotNetReceiver
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// This is the string received from the Java service
string receivedBase64String = "eyJ1c2VySWQiOjEyMywgImFjdGlvbiI6ImxvZ2luIiwgdGltZXN0YW1wIjoiMjAyMy0xMC0yN1QxMDowMDowMCJ9";
try
{
// 1. Decode the Base64 string to a byte array
byte[] decodedBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(receivedBase64String);
// 2. Convert the byte array back to a string using UTF8 encoding
string originalJsonString = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(decodedBytes);
Console.WriteLine(".NET received and decoded this JSON:");
// Pretty print the JSON for readability
var jsonDocument = JsonDocument.Parse(originalJsonString);
Console.WriteLine(JsonSerializer.Serialize(jsonDocument.RootElement, new JsonSerializerOptions { WriteIndented = true }));
// Expected Output:
// {
// "userId": 123,
// "action": "login",
// "timestamp": "2025-10-27T10:00:00Z"
// }
}
catch (FormatException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: The received string is not a valid Base64 string.");
}
}
}
As you can see, when both sides consistently use UTF-8 encoding, the data passes perfectly between Java and .NET.