properties 文件是一种键值对(key-value pair)格式的文本文件,通常用于存储配置信息,例如数据库连接信息、系统设置等,它的特点是:
- 键值对格式:
key = value或者key:value - 注释:以 或 开头的行被视为注释。
- 编码:通常使用 ISO-8859-1 编码,如果需要存储中文等非 ASCII 字符,需要进行转码。
读取 Properties 文件
读取 properties 文件是最常见的操作,主要有两种方式:从文件系统读取和从类路径(classpath)读取。推荐使用从类路径读取的方式,因为它更具可移植性,无论是在开发环境还是打包后的 JAR/WAR 文件中都能正常工作。
从类路径 读取 (推荐)
这种方式将 config.properties 文件放在 src/main/resources 目录下(对于 Maven/Gradle 项目),这样它会被自动打包到最终的输出目录中。
步骤:
- 使用
ClassLoader获取资源文件的输入流。 - 创建
Properties对象。 - 调用
load()方法加载输入流。 - 使用
getProperty(String key)或getProperty(String key, String defaultValue)方法获取值。
示例代码:
假设你的项目结构如下:
your-project/
├── src/
│ └── main/
│ └── resources/
│ └── config.properties
└── ...config.properties 文件内容:
# Database Configuration db.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb db.username=root db.password=password123 # System Settings system.timeout=30 system.debug=true
ReadProperties.java 文件:
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class ReadProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建 Properties 对象
Properties props = new Properties();
// try-with-resources 语句可以自动关闭流,推荐使用
try (InputStream input = ReadProperties.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config.properties")) {
// 2. 检查文件是否存在
if (input == null) {
System.out.println("Sorry, unable to find config.properties");
return;
}
// 3. 加载 properties 文件
props.load(input);
// 4. 获取属性值
String dbUrl = props.getProperty("db.url");
String dbUsername = props.getProperty("db.username");
String dbPassword = props.getProperty("db.password");
String timeout = props.getProperty("system.timeout");
// key 不存在,可以设置一个默认值
String debugMode = props.getProperty("system.debug", "false");
System.out.println("Database URL: " + dbUrl);
System.out.println("Database Username: " + dbUsername);
System.out.println("Database Password: " + dbPassword);
System.out.println("Timeout: " + timeout);
System.out.println("Debug Mode: " + debugMode);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
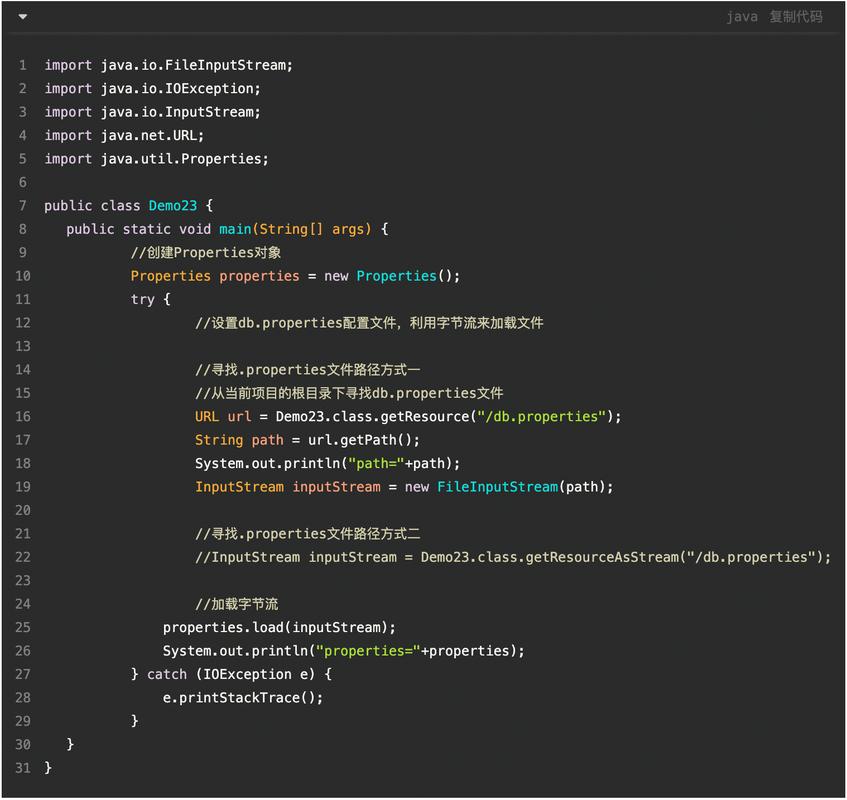
从文件系统 读取
这种方式直接通过文件路径读取,灵活性高,但可移植性差,路径可以是绝对路径或相对路径。
示例代码:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class ReadFromFileSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
// 文件路径,请根据你的实际情况修改
String filePath = "C:/projects/myapp/config/config.properties";
try (FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(filePath)) {
props.load(input);
// 获取属性值
String dbUrl = props.getProperty("db.url");
System.out.println("Database URL from file: " + dbUrl);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
写入 Properties 文件
写入 properties 文件通常用于保存或更新配置,写入时,它会覆盖文件中原有的内容。
步骤:
- 创建
Properties对象。 - 使用
setProperty(String key, String value)方法设置键值对。 - 使用
store(OutputStream out, String comments)方法将属性保存到输出流中。comments参数是写入文件顶部的注释,可以为null。
示例代码:
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class WriteProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
// 设置属性
props.setProperty("app.name", "My Awesome App");
props.setProperty("app.version", "1.2.0");
props.setProperty("last.updated", "2025-10-27");
// 定义输出文件路径
String outputPath = "app_config.properties";
try (OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(outputPath)) {
// 将属性列表写入输出流
// 第一个参数是输出流,第二个参数是写入文件顶部的注释
props.store(output, "Application Configuration File");
System.out.println("Properties file saved to: " + outputPath);
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
执行后,会生成一个 app_config.properties 文件,内容如下:
#Application Configuration File #Fri Oct 27 10:30:00 CST 2025 app.version=1.2.0 last.updated=2025-10-27 app.name=My Awesome App
注意: store() 方法会自动添加时间戳注释,并且会按照一定的顺序(通常是字母顺序)保存键值对。
处理中文等特殊字符
properties 文件默认使用 ISO-8859-1 编码,直接保存中文会导致乱码,有两种解决方案:
在代码中进行转码 (推荐)
在读取时,将 String 从 ISO-8859-1 转码到 UTF-8;在写入时,将 String 从 UTF-8 转码到 ISO-8859-1。
示例:
config_ch.properties 文件内容:
# 注意:这里直接写中文会乱码,但我们会用代码处理 greeting=你好,世界! author=张三
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class HandleChineseProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 读取包含中文的 properties 文件
readChineseProperties();
// 2. 写入包含中文的 properties 文件
writeChineseProperties();
}
public static void readChineseProperties() {
Properties props = new Properties();
String fileName = "config_ch.properties";
try (InputStream input = HandleChineseProperties.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(fileName)) {
if (input == null) {
System.out.println("Sorry, unable to find " + fileName);
return;
}
// 加载原始字节流
props.load(input);
// 获取原始值 (ISO-8859-1 编码的字节)
String greeting = props.getProperty("greeting");
String author = props.getProperty("author");
// 将 ISO-8859-1 编码的字节重新解码为 UTF-8 字符串
String greetingUtf8 = new String(greeting.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String authorUtf8 = new String(author.getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Read from properties:");
System.out.println("Greeting: " + greetingUtf8);
System.out.println("Author: " + authorUtf8);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void writeChineseProperties() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("new.key", "新值");
props.setProperty("author.name", "李四");
String fileName = "output_ch.properties";
try (OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(fileName)) {
// 将 UTF-8 字符串编码为 ISO-8859-1 字节后再写入
// store() 方法内部会处理字符编码,但为了清晰,我们可以手动转换
// 现代 Java 版本的 store(Writer writer, String comments) 更好
// 下面是使用 OutputStream 的传统方式
for (String key : props.stringPropertyNames()) {
String value = props.getProperty(key);
// 将 UTF-8 字符串转换为 ISO-8859_1 字节
String isoValue = new String(value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
props.setProperty(key, isoValue);
}
props.store(output, "A properties file with Chinese characters");
System.out.println("\nChinese properties file saved to: " + fileName);
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
使用 Writer (更现代的方式)
Java 提供了 store(Writer writer, String comments) 和 load(Reader reader) 方法,它们直接使用字符流,可以指定编码(如 UTF-8),避免了手动转码的麻烦。
推荐使用这种方式处理中文。
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Properties;
public class HandleChineseWithWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
writeWithWriter();
readWithReader();
}
public static void writeWithWriter() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("app.name", "我的应用");
props.setProperty("welcome.message", "欢迎使用!");
String fileName = "config_utf8.properties";
try (Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(fileName), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) {
// 直接使用 Writer,无需手动转码
props.store(writer, "Configuration file with UTF-8 encoding");
System.out.println("UTF-8 properties file saved to: " + fileName);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void readWithReader() {
Properties props = new Properties();
String fileName = "config_utf8.properties";
try (Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) {
// 直接使用 Reader,自动处理 UTF-8 编码
props.load(reader);
System.out.println("\nRead from UTF-8 properties file:");
System.out.println("App Name: " + props.getProperty("app.name"));
System.out.println("Welcome Message: " + props.getProperty("welcome.message"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
总结与最佳实践
| 操作 | 推荐方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 读取 | ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream() |
可移植性好,适合打包应用。 |
| 写入 | FileOutputStream / OutputStreamWriter |
OutputStreamWriter 可以指定编码,推荐用于处理中文。 |
| 读取中文 | new InputStreamReader(..., StandardCharsets.UTF_8) |
直接使用 Reader 和指定编码,最简单可靠。 |
| 写入中文 | new OutputStreamWriter(..., StandardCharsets.UTF_8) |
直接使用 Writer 和指定编码,最简单可靠。 |
| 资源管理 | try-with-resources |
自动关闭流,防止资源泄漏,是现代 Java 的标准做法。 |
| 获取值 | getProperty(key, defaultValue) |
比 get(key) 更安全,可以在键不存在时返回默认值,避免 NullPointerException。 |
核心要点:
- 优先从类路径加载资源,提高应用的可移植性。
- 处理中文时,务必使用
Reader和Writer并指定UTF-8编码,避免手动转码的繁琐和错误。 - 始终使用
try-with-resources来管理文件流。 - 使用
getProperty(key, defaultValue)来安全地获取配置值。