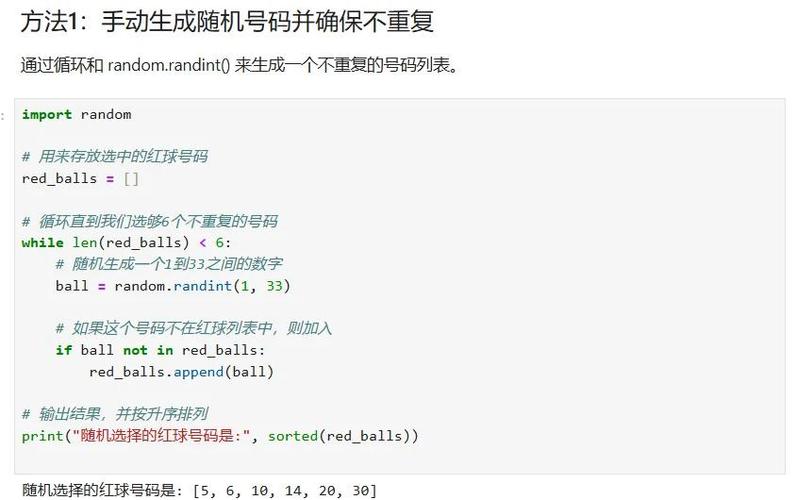
Of course! Let's dive deep into getrandbits, a powerful and fundamental function from Python's random module.

What is getrandbits?
getrandbits(n) is a function that generates a random integer with exactly n random bits. This means the returned integer will be in the range [0, 2^n - 1].
Think of it as a "raw" random number generator. It's the core building block for many other random functions in Python, including randint and choice.
Basic Syntax and Usage
First, you need to import the random module.
import random
Syntax:
random.getrandbits(n)
n: An integer representing the number of random bits you want.- Return Value: An integer
ksuch that0 <= k < 2^n.
Example 1: Getting 8 random bits
This will generate a number between 0 and 255 (since 2^8 - 1 = 255).
import random
# Generate a random integer with 8 bits
random_byte = random.getrandbits(8)
print(f"8 random bits: {random_byte}")
# Let's verify the range
print(f"Is it between 0 and 255? {0 <= random_byte <= 255}")
Possible Output:
8 random bits: 183
Is it between 0 and 255? TrueExample 2: Getting 32 random bits
This will generate a number between 0 and 4,294,967,295 (since 2^32 - 1).
import random
# Generate a random integer with 32 bits
random_32bit_int = random.getrandbits(32)
print(f"32 random bits: {random_32bit_int}")
# Let's verify the range
print(f"Is it between 0 and 4294967295? {0 <= random_32bit_int <= 4294967295}")
Possible Output:
32 random bits: 3128459012
Is it between 0 and 4294967295? TrueWhy Use getrandbits? (Key Advantages)
-
Performance: It's one of the fastest ways to generate a random integer in Python. It directly requests a block of random bits from the underlying OS source, which is very efficient.
-
Control over Size: It gives you precise control over the size of the random number in terms of bits. This is extremely useful in low-level programming, cryptography, or when you need numbers that fit into a specific number of bytes.
-
Foundation for Other Functions: Many other
randomfunctions are implemented usinggetrandbits. Understanding it helps you understand how randomness works in Python.
How getrandbits Compares to Other random Functions
This is the most important part to understand its place in the library.
getrandbits vs. randint(a, b)
randint(a, b) generates a random integer N such that a <= N <= b.
getrandbits can be used to implement randint.
How to implement randint(a, b) using getrandbits:
The logic is:
- Calculate the number of bits needed to represent the range. The number of bits
nisbit_length = (b - a).bit_length(). - Generate a random number
xin that range usinggetrandbits(n). - Add the lower bound
ato shift the number into the correct interval.
import random
def my_randint(a, b):
"""Implements randint using getrandbits."""
if a > b:
raise ValueError("a must be less than or equal to b")
# Calculate the number of bits needed for the range (b - a)
num_bits = (b - a).bit_length()
# Keep generating numbers until one falls within the desired range
# This is important because getrandbits might generate a number
# that is too large for the range.
while True:
x = random.getrandbits(num_bits)
if a <= x <= b:
return x
# --- Example ---
print(f"Using my_randint(10, 20): {my_randint(10, 20)}")
print(f"Using standard randint(10, 20): {random.randint(10, 20)}")
Why is randint better for this use case?
The standard random.randint is more robust. It handles edge cases (like when a and b are very close) more efficiently and avoids the potential infinite loop in the simple implementation above. getrandbits is the tool, randint is the convenient, high-level function built with that tool.
getrandbits vs. random()
random.random() generates a random float in the range [0.0, 1.0).
You can also implement random.random() using getrandbits:
import random
def my_random():
"""Implements random() using getrandbits."""
# 53 bits are used for the mantissa of a double-precision float
# to get good precision.
x = random.getrandbits(53)
return x / (2**53)
# --- Example ---
print(f"Using my_random(): {my_random()}")
print(f"Using standard random(): {random.random()}")
Again, the standard random.random() is preferred for its clarity and optimized implementation.
Important Consideration: The random Module vs. secrets Module
For most general-purpose applications, random is fine. However, for security-sensitive applications like generating passwords, API keys, or security tokens, you must use the secrets module.
The random module uses a pseudorandom number generator (PRNG), which is deterministic and predictable if you know the initial state (the "seed"). The secrets module uses a cryptographically strong random number generator (CSPRNG) provided by your operating system, which is designed to be unpredictable.
secrets also has a getrandbits function.
import secrets
# For security-sensitive data, use secrets
secure_token = secrets.getrandbits(128) # Generate a 128-bit (16-byte) secure token
print(f"Secure 128-bit token: {secure_token}")
# To generate a secure random hex string (e.g., for a session ID)
secure_hex = secrets.token_hex(16) # 16 bytes -> 32 hex characters
print(f"Secure hex token: {secure_hex}")
Rule of Thumb:
- Use
randomfor modeling, simulations, games, shuffling, and general non-critical randomness. - Use
secretsfor anything related to security, cryptography, or generating unpredictable tokens.
Summary Table
| Function | Purpose | Use Case | Module |
|---|---|---|---|
getrandbits(n) |
Generates an integer with exactly n random bits. |
Low-level control, performance, building blocks. | random, secrets |
randint(a, b) |
Generates a random integer in a range [a, b]. |
Most common use case for random integers. | random |
random() |
Generates a random float in [0.0, 1.0). |
Simulations, statistics, Monte Carlo methods. | random |
secrets.getrandbits(n) |
Cryptographically secure version of getrandbits. |
Security tokens, keys, password salts. | secrets |