最基础版本
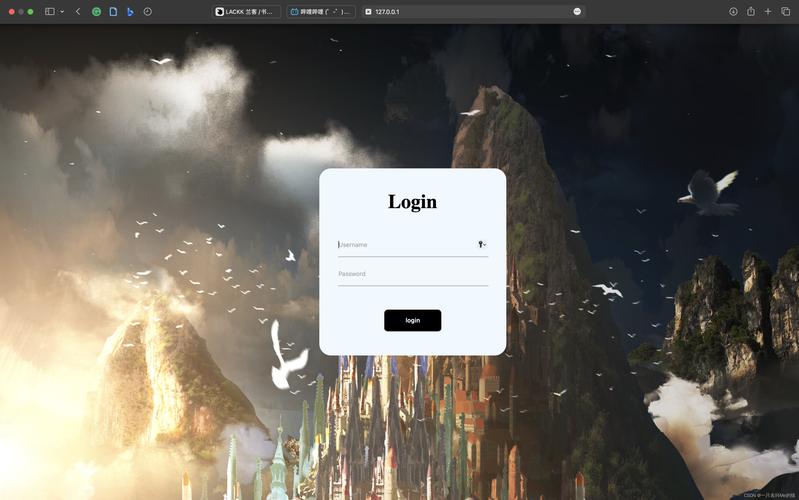
这是一个最简单的登录界面,包含用户名、密码输入框和登录按钮,并处理最基础的点击事件。
核心组件
JFrame: 窗口JPanel: 面板,用于布局组件JLabel: 标签,用于显示“用户名”、“密码”JTextField: 单行文本框,用于输入用户名JPasswordField: 密码框,用于输入密码(显示为星号)JButton: 按钮
代码实现
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class SimpleLoginUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个窗口
JFrame frame = new JFrame("简单登录界面");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 关闭窗口时退出程序
frame.setSize(350, 200); // 设置窗口大小
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null); // 窗口居中显示
// 创建一个面板,使用流式布局
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER, 20, 20));
// 创建组件
JLabel userLabel = new JLabel("用户名:");
JTextField userText = new JTextField(15); // 列数为15
JLabel passLabel = new JLabel("密码:");
JPasswordField passText = new JPasswordField(15); // 密码框
JButton loginButton = new JButton("登录");
// 将组件添加到面板
panel.add(userLabel);
panel.add(userText);
panel.add(passLabel);
panel.add(passText);
panel.add(loginButton);
// 将面板添加到窗口
frame.add(panel);
// 为登录按钮添加点击事件
loginButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String username = userText.getText();
String password = new String(passText.getPassword()); // 从密码框获取文本
// 这里只是一个简单的示例,实际应用中应该连接数据库进行验证
if ("admin".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(frame, "登录成功!");
// 登录成功后可以打开新窗口或关闭当前窗口
// frame.dispose(); // 关闭登录窗口
// new MainApplicationUI(); // 打开主应用窗口
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(frame, "用户名或密码错误!", "错误", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
}
}
});
// 设置窗口可见
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
运行效果
使用 GridBagLayout 的专业版
FlowLayout 布局比较简单,无法精确控制组件位置。GridBagLayout 是 Swing 中最强大、最灵活的布局管理器,可以创建对齐良好、间距均匀的专业界面。
代码实现
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class ProfessionalLoginUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建主窗口
JFrame frame = new JFrame("专业登录界面");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(400, 250);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
// 2. 使用 GridBagLayout
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
panel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(10, 10, 10, 10)); // 添加内边距
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
gbc.insets = new Insets(5, 5, 5, 5); // 组件间距
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL; // 水平填充
// 3. 创建组件
JLabel titleLabel = new JLabel("用户登录", JLabel.CENTER);
titleLabel.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 20)); // 设置字体
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 0;
gbc.gridwidth = 2; // 占据两列
panel.add(titleLabel, gbc);
JLabel userLabel = new JLabel("用户名:");
JTextField userText = new JTextField(15);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 1;
gbc.gridwidth = 1; // 占据一列
panel.add(userLabel, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
panel.add(userText, gbc);
JLabel passLabel = new JLabel("密码:");
JPasswordField passText = new JPasswordField(15);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 2;
panel.add(passLabel, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
panel.add(passText, gbc);
// 登录按钮
JButton loginButton = new JButton("登录");
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 3;
gbc.gridwidth = 2; // 占据两列,使其居中
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.NONE; // 不填充
gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.CENTER; // 居中
panel.add(loginButton, gbc);
// 忘记密码标签
JLabel forgotLabel = new JLabel("忘记密码?", JLabel.RIGHT);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 4;
gbc.gridwidth = 2;
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL;
gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.LINE_END; // 右对齐
panel.add(forgotLabel, gbc);
// 4. 添加事件处理
loginButton.addActionListener(e -> {
String username = userText.getText();
String password = new String(passText.getPassword());
if ("admin".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(frame, "登录成功!");
frame.dispose();
// 这里可以跳转到主界面
// SwingUtilities.invokeLater(MainApplicationUI::new);
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(frame, "用户名或密码错误!", "登录失败", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
userText.setText(""); // 清空用户名
passText.setText(""); // 清空密码
userText.requestFocus(); // 让用户名框重新获得焦点
}
});
// 5. 显示窗口
frame.add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
代码解释
GridBagConstraints: 这是GridBagLayout的配置对象,它定义了每个组件的布局规则。gbc.gridx,gbc.gridy: 定义组件在网格中的坐标(列和行)。gbc.gridwidth: 定义组件跨越的列数。gbc.insets: 设置组件与单元格边界的内边距。gbc.fill: 定义组件在单元格内的填充方式(HORIZONTAL,VERTICAL,BOTH,NONE)。gbc.anchor: 定义组件在单元格内的对齐方式(CENTER,NORTH,SOUTH,EAST,WEST等)。panel.setBorder(...): 为面板添加边距,让界面看起来不那么拥挤。
运行效果
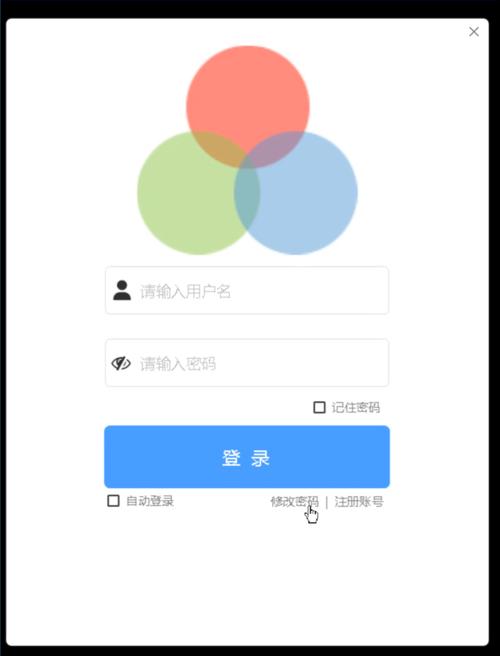
更美观的版本(带背景图片和图标)
这个版本将展示如何添加背景图片、为按钮和标签添加图标,使界面更具吸引力。
准备工作
你需要准备两张图片:
background.jpg(作为窗口背景)user_icon.png和password_icon.png(作为输入框前的图标)
将这两张图片放在项目的 src 目录下(或者创建一个 resources 文件夹,并确保在构建路径中)。
代码实现
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.net.URL;
public class BeautifulLoginUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用 SwingUtilities.invokeLater 确保在事件分发线程中创建和显示 GUI
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
// 创建主窗口
JFrame frame = new JFrame("美观登录界面");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(500, 350);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setResizable(false); // 禁止调整窗口大小
// 创建带背景的面板
BackgroundPanel backgroundPanel = new BackgroundPanel();
backgroundPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
// 创建登录面板(使用方案二的 GridBagLayout)
JPanel loginPanel = createLoginPanel(frame);
// 将登录面板添加到背景面板中央
backgroundPanel.add(loginPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setContentPane(backgroundPanel); // 设置背景面板为窗口内容面板
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
private static JPanel createLoginPanel(JFrame parentFrame) {
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
panel.setOpaque(false); // 设置为透明,以便显示背景
panel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(20, 40, 20, 40));
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
gbc.insets = new Insets(10, 10, 10, 10);
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL;
// 标题
JLabel titleLabel = new JLabel("欢迎登录", JLabel.CENTER);
titleLabel.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 24));
titleLabel.setForeground(new Color(70, 130, 180)); // 设置字体颜色
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 0;
gbc.gridwidth = 2;
panel.add(titleLabel, gbc);
// 用户名行
gbc.gridwidth = 1;
JLabel userIcon = new JLabel(loadIcon("user_icon.png", 20, 20));
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 1;
gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.EAST;
panel.add(userIcon, gbc);
JTextField userText = new JTextField(15);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 1;
gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.WEST;
panel.add(userText, gbc);
// 密码行
JLabel passIcon = new JLabel(loadIcon("password_icon.png", 20, 20));
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 2;
gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.EAST;
panel.add(passIcon, gbc);
JPasswordField passText = new JPasswordField(15);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 2;
gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.WEST;
panel.add(passText, gbc);
// 登录按钮
JButton loginButton = new JButton("登 录");
loginButton.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 14));
loginButton.setBackground(new Color(70, 130, 180));
loginButton.setForeground(Color.WHITE);
loginButton.setFocusPainted(false); // 去除点击时的焦点框
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 3;
gbc.gridwidth = 2;
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.NONE;
gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.CENTER;
panel.add(loginButton, gbc);
// 事件处理
loginButton.addActionListener(e -> {
String username = userText.getText();
String password = new String(passText.getPassword());
if ("admin".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(parentFrame, "登录成功!");
parentFrame.dispose();
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(parentFrame, "用户名或密码错误!", "错误", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
userText.setText("");
passText.setText("");
userText.requestFocus();
}
});
return panel;
}
// 辅助方法:从类路径加载图标
private static Icon loadIcon(String path, int width, int height) {
URL imageUrl = BeautifulLoginUI.class.getResource(path);
if (imageUrl != null) {
ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon(imageUrl);
Image image = icon.getImage().getScaledInstance(width, height, Image.SCALE_SMOOTH);
return new ImageIcon(image);
}
return null;
}
}
// 自定义背景面板
class BackgroundPanel extends JPanel {
private Image backgroundImage;
public BackgroundPanel() {
try {
// 从类路径加载背景图片
backgroundImage = new ImageIcon(BeautifulLoginUI.class.getResource("background.jpg")).getImage();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
if (backgroundImage != null) {
// 绘制背景图片,并拉伸以填满整个面板
g.drawImage(backgroundImage, 0, 0, this.getWidth(), this.getHeight(), this);
}
}
}
代码解释
SwingUtilities.invokeLater: 这是创建 Swing GUI 的标准做法,确保所有 GUI 相关的代码都在“事件分发线程”(EDT) 上执行,避免线程安全问题。BackgroundPanel: 这是一个自定义的JPanel,通过重写paintComponent方法,我们可以在面板上绘制自定义内容,在这里是背景图片。Image.getScaledInstance: 用于将加载的图片缩放到指定大小。setFocusPainted(false): 移除按钮被点击时默认绘制的焦点矩形,使界面更清爽。setOpaque(false): 对于放置在背景面板上的子面板(如loginPanel),必须设置为透明,才能显示出底层的背景图片。
运行效果
总结与建议
| 特性 | 方案一 (基础) | 方案二 (专业) | 方案三 (美观) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 布局管理器 | FlowLayout |
GridBagLayout |
GridBagLayout |
| 美观度 | 低 | 中 | 高 |
| 灵活性 | 低 | 高 | 高 |
| 复杂度 | 低 | 中 | 高 |
| 适用场景 | 快速原型、学习 | 大多数桌面应用 | 对UI有较高要求的商业应用 |
对于初学者,建议从方案一开始,理解各个组件的基本用法。 对于实际项目开发,方案二是很好的起点,它提供了专业且可控的布局。 如果你的应用需要更好的用户体验,可以参考方案三进行美化,并考虑使用第三方库(如 FlatLaf)来快速实现现代化的界面风格。