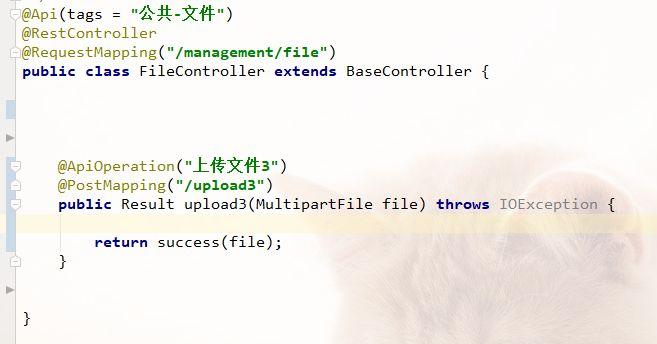
Of course! MultipartFile is a fundamental interface in the Java ecosystem, primarily used for handling file uploads in web applications. It's part of the Spring Framework (spring-web module) and is the standard way to process files submitted through an HTML <form> with enctype="multipart/form-data".
Let's break it down comprehensively.
What is MultipartFile?
MultipartFile is an interface that represents an uploaded file received in a multipart request. It provides a convenient API to access the file's content, name, original filename, content type, and size.
Key Idea: When a user uploads a file, the server doesn't just get a raw stream of bytes. It gets metadata about the file (its name, type, etc.) along with its content. MultipartFile encapsulates all of this information into a single, easy-to-use object.
The Core Interface (Key Methods)
Here are the most important methods you'll use from the MultipartFile interface:
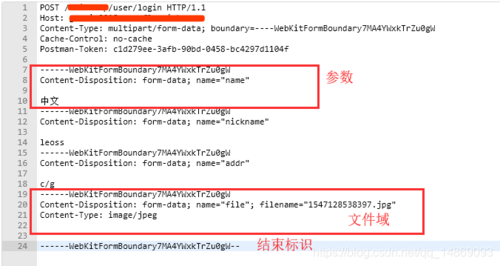
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
byte[] getBytes() |
Gets the file content as a byte array. Be careful with large files, as this can consume a lot of memory. |
String getContentType() |
Returns the content type of the file (e.g., image/png, application/pdf). |
InputStream getInputStream() |
Gets the file content as an InputStream. This is the preferred method for large files as it's memory-efficient. |
String getName() |
Returns the name of the parameter in the multipart request (e.g., the name attribute of the <input type="file">). |
String getOriginalFilename() |
Returns the original filename on the client's machine (e.g., my-photo.png). |
long getSize() |
Returns the size of the file in bytes. |
boolean isEmpty() |
Returns true if the file is empty (i.e., no content was selected). |
void transferTo(File destination) |
A very convenient method. It takes a File object and writes the multipart file's content to that file on the local filesystem. This handles the stream copying for you. |
How to Use MultipartFile in a Spring Boot Controller
This is the most common use case. You'll create a REST endpoint that accepts an MultipartFile as a method parameter.
Step 1: Create the HTML Form
First, you need a client-side form to upload the file. The enctype is crucial.
<!-- src/main/resources/templates/upload-form.html (using Thymeleaf) -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">File Upload</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Upload a File</h1>
<form action="/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file" /> <!-- 'name' attribute must match the @RequestParam in the controller -->
<button type="submit">Upload</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Key Points:
method="post": File uploads must be POST requests.enctype="multipart/form-data": This tells the browser to encode the form data in a multipart format, which is required for file uploads.
Step 2: Create the Spring Boot Controller
Now, let's create the controller that handles this request.
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
@Controller
public class FileUploadController {
// Define a directory where files will be saved
private static final String UPLOADED_FOLDER = "/tmp/uploads/";
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String handleFileUpload(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("message", "Please select a file to upload");
return "redirect:uploadStatus";
}
try {
// Create the upload directory if it doesn't exist
Path uploadPath = Paths.get(UPLOADED_FOLDER);
if (!Files.exists(uploadPath)) {
Files.createDirectories(uploadPath);
}
// Get the original filename
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
// Create the destination file
Path destinationFile = uploadPath.resolve(originalFilename);
// Use transferTo to save the file to the destination
// This is the easiest and recommended way
file.transferTo(destinationFile.toFile());
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("message",
"You successfully uploaded '" + originalFilename + "' to '" + UPLOADED_FOLDER + "'");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("message", "Failed to upload the file: " + e.getMessage());
}
return "redirect:/uploadStatus";
}
@GetMapping("/uploadStatus")
public String uploadStatus() {
return "uploadStatus"; // A simple HTML page to show the status message
}
}
Explanation:
@Controller: Marks this class as a Spring MVC controller.@PostMapping("/upload"): Maps POST requests to/uploadto this method.@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file: This is the magic part. Spring Boot automatically:- Checks the request for
multipartcontent. - Finds the part that corresponds to the
nameattribute of the<input>tag (in this case,"file"). - Binds that part to the
MultipartFileparameter.
- Checks the request for
file.isEmpty(): A good practice to check if a file was actually selected.file.transferTo(destinationFile): This method efficiently streams the file content from the request to the specified destination file on the server's filesystem.
Handling Multiple Files
If your form allows multiple file uploads, you can use an array or List of MultipartFile.
HTML Form for Multiple Files
<!-- Note the 'multiple' attribute --> <input type="file" name="files" multiple />
Controller for Multiple Files
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.util.List;
// ... inside your controller
@PostMapping("/upload-multiple")
public String handleMultipleFileUpload(@RequestParam("files") List<MultipartFile> files,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes) {
if (files.isEmpty()) {
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("message", "Please select files to upload");
return "redirect:/uploadStatus";
}
int count = 0;
for (MultipartFile file : files) {
if (!file.isEmpty()) {
try {
// ... (same saving logic as before)
Path destinationFile = Paths.get(UPLOADED_FOLDER).resolve(file.getOriginalFilename());
file.transferTo(destinationFile.toFile());
count++;
} catch (IOException e) {
// Log error, but continue with other files
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("message", "You successfully uploaded " + count + " files.");
return "redirect:/uploadStatus";
}
Configuration: MultipartResolver
For Spring Boot applications, the MultipartResolver is automatically configured for you with sensible defaults. However, you might need to adjust these settings in your application.properties or application.yml file, especially for large files.
application.properties
# Set the maximum file size (e.g., 10MB) spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB # Set the maximum total request size for a multipart request (e.g., 10MB) spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=10MB # Enable or disable temporary storage on disk for files larger than a threshold # Disabled by default in newer Spring Boot versions. If enabled, you must set a location. # spring.servlet.multipart.location=/tmp
Key Properties:
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size: The maximum size of a single file. Exceeding this will result in an exception.spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size: The maximum size of the entire multipart request. This is important if you are uploading multiple files.
Best Practices and Alternatives
- Use
transferTo()for saving to disk: It's simple, efficient, and handles the underlying stream correctly. - Use
getInputStream()for processing in memory: If you need to process the file content (e.g., read metadata, parse a CSV) without saving it, use theInputStream. Be mindful ofOutOfMemoryErrorfor large files. - Store files in a cloud storage service (S3, Google Cloud Storage): Storing files directly on the server's local filesystem is simple but not scalable or durable. For production applications, it's better to upload the file to a dedicated cloud storage service.
- Pattern: Receive the
MultipartFilein your controller. - Use the AWS SDK or Google Cloud SDK to get an
InputStreamfrom theMultipartFile. - Upload this stream to the cloud service (e.g.,
amazonS3Client.putObject(...)). - Delete the temporary file if you used
transferTo()to a local temp location.
- Pattern: Receive the
- Security: Always validate the file. Check its extension, content type, and scan it for malware before saving or processing it. Never trust user input.
Summary
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| What it is | An interface representing an uploaded file in a Spring web application. |
| How to use | Add it as a parameter to a @PostMapping method in a @Controller. Use @RequestParam to bind it to the form input's name. |
| Key Method | transferTo(File) is the easiest way to save the file to the server's disk. |
| Multiple Files | Use a List<MultipartFile> or MultipartFile[] as the method parameter. |
| Configuration | Adjust max-file-size and max-request-size in application.properties. |
| Best Practice | For production, consider uploading to cloud storage (S3, GCS) instead of the local filesystem. |