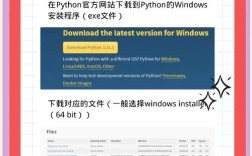
Of course! The wdir argument in Python's runfile function is a crucial parameter for controlling the execution environment of your script. Let's break it down in detail.
What is wdir?
wdir stands for working directory. It's an argument you can pass to the runfile function (commonly found in environments like Spyder) to specify the directory that should be considered the current working directory before your script starts running.
In Python, the "current working directory" (CWD) is the default directory where the interpreter looks for files and saves files if you don't provide a full path.
Why is wdir So Important?
Imagine your project has this structure:
my_project/
├── main_script.py
├── data/
│ └── input.csv
└── utils/
└── helpers.pyAnd inside main_script.py, you have code to read a file:
# main_script.py
import pandas as pd
# This will look for 'input.csv' in the current working directory
df = pd.read_csv('data/input.csv')
print(df.head())
Without wdir:
If you run this script from an IDE like Spyder or from your terminal, the CWD might be the my_project directory. The code works because data/input.csv is a valid path relative to the CWD.
The Problem:
Now, let's say you refactor your code and move helpers.py to the root. You need to import it:
# main_script.py
from utils import helpers # This will fail if the CWD is not my_project
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('data/input.csv')
print(df.head())
If you accidentally change your CWD to somewhere else (like C:\Users\YourName\), the import from utils import helpers will fail because Python can't find a utils folder there. This is a very common source of frustrating "ModuleNotFoundError" or "ImportError".
The Solution with wdir:
By setting wdir in your Spyder run configuration, you are telling Python: "Before you execute a single line of main_script.py, change your current directory to my_project." This ensures that all relative paths and imports work as expected, regardless of where you launched the IDE from.

How to Use wdir in Spyder
This is the most common place you'll encounter runfile. The runfile function is part of Spyder's console API.
-
Open the Run Configuration:
- Go to the menu bar and click
Run->Configuration per file.... - A dialog box will appear. Make sure the "Run" tab is selected.
- Go to the menu bar and click
-
Set the
wdir:- In the "Working directory" field, you have two main options:
Script directory(Recommended): This is the best choice for most projects. It automatically sets the working directory to be the same folder where your script is located. In our example, ifmain_script.pyis inmy_project, this will setwdirtomy_project.Fixed directory: Choose this if you want to hardcode a specific path. For example, you could typeC:/path/to/my_project/here. This is less flexible but useful if your script needs to run from a very specific, non-script location.
- In the "Working directory" field, you have two main options:
-
Run the Script:
- Click "OK" or "Apply".
- Now, when you press the "Run" button (F5), Spyder will execute your script with the specified working directory.
wdir in Other Contexts
While runfile is specific to Spyder, the concept of a working directory is universal.
Standard Python via os.chdir
You can achieve the same effect programmatically within your script using the os module.
import os
import pandas as pd
# Define the path to the directory you want to work in
# Use os.path.join for cross-platform compatibility
project_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'my_project')
# Change the current working directory
os.chdir(project_dir)
# Now, all relative paths are relative to 'my_project'
print("Current Working Directory:", os.getcwd())
# This will now work correctly, assuming you are in 'my_project'
df = pd.read_csv('data/input.csv')
print(df.head())
Pros: Explicit within the code. Cons: Modifies the global state of the script, which can sometimes have side effects.
Jupyter Notebooks / IPython
In a Jupyter Notebook, you can use the %cd magic command.
# This will change the working directory for the rest of the notebook session
%cd /path/to/my_project
# Now you can use relative paths
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('data/input.csv')
Command Line (Terminal)
When running a script from your terminal, the CWD is simply the directory you are in when you execute the command.
# This will fail if 'my_project' is not in the current directory $ python main_script.py # This works because you explicitly change the directory first $ cd /path/to/my_project $ python main_script.py
Summary: wdir vs. __file__
It's easy to confuse wdir with __file__. They are related but different:
-
__file__: A built-in Python variable that holds the path to the script file itself. It's absolute or relative depending on how the script was run.- Use
os.path.dirname(__file__)to get the directory containing the script.
- Use
-
wdir(Working Directory): The directory that the Python interpreter considers its "home" base for file operations. It's set before the script runs.
The key takeaway: wdir is a powerful tool for ensuring your script's environment is predictable and correct. It's the best practice to set it to your project's root directory to avoid path-related headaches. In Spyder, using Script directory is the most reliable way to do this.