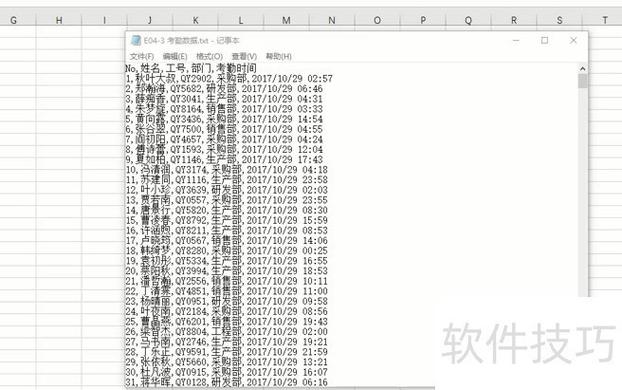
Of course! Converting a text file (.txt) to an Excel file (.xlsx) is a common task in Python. The best tool for this job is the pandas library, which is powerful, flexible, and relatively easy to use.
I'll guide you through it, starting with the simplest case and moving to more complex scenarios.
The Short Answer (The Simplest Case)
If your text file is a simple comma-separated values (CSV) file, this is all you need:
import pandas as pd
# 1. Read the text file into a pandas DataFrame
# 'sep=',' tells pandas the values are separated by commas.
df = pd.read_csv('your_data.txt', sep=',')
# 2. Write the DataFrame to an Excel file
df.to_excel('your_data.xlsx', index=False) # index=False prevents writing row numbers
print("Conversion complete!")
Detailed Guide: Handling Different Text File Formats
Real-world text files can be tricky. They might use different separators, have headers in a certain format, or contain inconsistent data. Let's break down how to handle them.
Step 1: Install Necessary Libraries
If you don't have pandas and openpyxl (the Excel engine for pandas) installed, open your terminal or command prompt and run:

pip install pandas openpyxl
Scenario 1: Comma-Separated Values (CSV)
This is the most common format. Your data.txt looks like this:
Name,Age,City Alice,30,New York Bob,24,Los Angeles Charlie,35,Chicago
Python Code:
import pandas as pd
# The 'sep=',' is the default, so you can often omit it.
df = pd.read_csv('data.txt')
# Save to Excel, excluding the DataFrame's index column
df.to_excel('data.xlsx', index=False)
print("CSV to Excel conversion complete!")
Scenario 2: Tab-Separated Values (TSV)
Your data.txt file uses tabs to separate values.
Name Age City David 40 Houston Eve 28 Phoenix Frank 50 Philadelphia
Python Code:
You just need to tell pandas the separator is a tab (\t).
import pandas as pd
# Use sep='\t' to specify tab separation
df = pd.read_csv('data.txt', sep='\t')
df.to_excel('data.xlsx', index=False)
print("TSV to Excel conversion complete!")
Scenario 3: Fixed-Width or Space-Separated Files
Sometimes columns are separated by a fixed number of spaces, or just a single space.
Example data.txt:
Name Age City
Grace 45 San Antonio
Heidi 33 San DiegoPython Code:
Use delim_whitespace=True for simple space separation. For more complex fixed-width, you'd use pd.read_fwf().
import pandas as pd
# delim_whitespace=True handles one or more spaces as a separator
df = pd.read_csv('data.txt', delim_whitespace=True)
# For truly fixed-width columns, use read_fwf()
# df = pd.read_fwf('data.txt', widths=[10, 5, 15]) # Specify width of each column
df.to_excel('data.xlsx', index=False)
print("Space-separated to Excel conversion complete!")
Scenario 4: Files Without Headers
If your file doesn't have a first row for column names, pandas will name them 0, 1, 2, ... by default. You can provide your own names.
Example data.txt:
Ivy,50,Dallas
Judy,29,San JosePython Code:
Use the names parameter to assign column names.
import pandas as pd
# Provide a list of column names
column_names = ['EmployeeName', 'EmployeeAge', 'OfficeLocation']
df = pd.read_csv('data.txt', sep=',', names=column_names)
df.to_excel('data.xlsx', index=False)
print("No-header to Excel conversion complete!")
Scenario 5: Complex Scenarios (Skipping Rows, Custom Encoding)
You might need to skip irrelevant lines at the top of the file or handle special characters.
Example data.txt:
This is a report header. Ignore this line.
Another line to ignore.
Name,City,Country
Oscar,60,Toronto,Canada # Note: This row has an extra column
Karl,55,Vancouver,CanadaPython Code:
Use skiprows and on_bad_lines='skip' to handle these issues.
import pandas as pd
# Skip the first 2 header lines
# on_bad_lines='skip' will ignore row 4 which has the wrong number of columns
df = pd.read_csv(
'data.txt',
sep=',',
skiprows=2,
on_bad_lines='skip'
)
df.to_excel('data.xlsx', index=False)
print("Complex file to Excel conversion complete!")
Complete, Runnable Example
Let's put it all together. Imagine you have a file named sales.txt with the following content:
Region,Product,Sales East,Widget,500 West,Gadget,750 East,Widget,600 North,Doodad,450 West,Gadget,800
Here is the full Python script to convert it:
# import the pandas library
import pandas as pd
# Define the input text file and output excel file
input_file = 'sales.txt'
output_file = 'sales_report.xlsx'
try:
# Read the text file into a DataFrame.
# Pandas is smart enough to detect the comma separator.
df = pd.read_csv(input_file)
# Write the DataFrame to an Excel file.
# index=False prevents pandas from writing the DataFrame index as a column.
# engine='openpyxl' is the default, but it's good to be explicit.
df.to_excel(output_file, index=False, engine='openpyxl')
print(f"Successfully converted '{input_file}' to '{output_file}'")
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Error: The file '{input_file}' was not found.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
Summary of Key pd.read_csv() Parameters
| Parameter | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|
sep or delimiter |
Specify the separator character. | sep='\t' for TSV, sep=';' for semicolon-separated. |
header |
Specify which row to use for column names. | header=None if there's no header, header=2 to use the 3rd row. |
names |
Provide a list of column names when header=None. |
names=['Col1', 'Col2', 'Col3'] |
skiprows |
Skip a number of rows at the beginning of the file. | skiprows=3 |
on_bad_lines |
How to handle rows with the wrong number of columns. | on_bad_lines='warn', on_bad_lines='skip' |
encoding |
Specify the file encoding if you get errors. | encoding='utf-8', encoding='latin1' |