Of course! Here's a comprehensive guide to using NetBeans for Python development, covering its pros, cons, setup, and workflow.

Is NetBeans a Good Choice for Python?
The short answer is: It's a viable option, but it's not the most popular or feature-rich IDE for Python today.
NetBeans is a powerful, mature, and cross-platform IDE developed by Apache. It has excellent support for Java, but its Python support, while functional, is not as deeply integrated as its Java support.
✅ Pros of Using NetBeans for Python
-
Excellent Code Editor: NetBeans has a very robust editor with features like:
- Syntax highlighting
- Code completion (intellisense)
- Code folding
- Multi-cursor editing
- Built-in terminal
-
Integrated Debugger: This is a major plus. You can set breakpoints, inspect variables, step through code line-by-line, and watch expressions, all within the IDE.
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删) -
Cross-Platform: It runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux, providing a consistent experience.
-
Free and Open Source: As an Apache project, it's completely free to use.
-
Good for Beginners: The user interface is clean and straightforward, making it easy for newcomers to understand the basics of an IDE.
❌ Cons of Using NetBeans for Python
- Lagging Language Support: The Python support is a plugin and doesn't receive the same level of active development as the core Java features. This can mean slower updates for new Python syntax or features.
- Weaker Ecosystem Integration: Compared to dedicated Python IDEs, the integration with the Python ecosystem is less seamless.
- Virtual Environments: Support exists, but it can be clunkier than in PyCharm or VS Code.
- Package Management: While it can run
pipcommands, it doesn't have the same level of deep integration withpip,conda, orpoetry.
- Not the Industry Standard: The vast majority of Python developers use either PyCharm (from JetBrains) or Visual Studio Code (from Microsoft). This means fewer tutorials, community support, and plugins specifically tailored to the "NetBeans for Python" workflow.
How to Set Up NetBeans for Python
Follow these steps to get started.
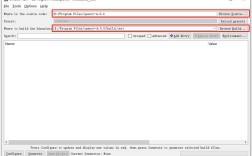
Step 1: Install NetBeans
- Go to the official NetBeans download page: https://netbeans.apache.org/download/
- Download the "Java SE" or "All" bundle. You need a Java Development Kit (JDK) installed for NetBeans to run, and the installer will usually check for this.
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
Step 2: Install the Python Plugin
NetBeans does not come with Python support by default.
- Open NetBeans.
- Go to Tools -> Plugins.
- Switch to the Available Plugins tab.
- In the filter box, type
Python. - You should see the "Python" plugin. Check the box next to it and click Install.
- Accept the license agreement and let the plugin install. You may need to restart NetBeans.
Step 3: Configure the Python Interpreter
This is the most crucial step. You need to tell NetBeans which Python installation to use.
- Go to Tools -> Python.
- A dialog box will appear. In the Python Platform section, click Add....
- A "Select Python Platform" dialog will open.
- NetBeans will likely auto-detect your Python installations. If it finds one, select it from the list and click Finish.
- If it doesn't find your Python, select "Browse..." and navigate to your Python executable. This is typically:
- Windows:
C:\Python39\python.exe(or your version number) - macOS:
/usr/bin/python3(or/usr/local/bin/python3if installed via Homebrew) - Linux:
/usr/bin/python3
- Windows:
- Click OK to close the dialogs. You are now ready to create a project.
A Typical Workflow in NetBeans
Let's walk through creating a simple project, writing code, and debugging it.
Create a New Python Project
- Go to File -> New Project.
- Choose Python from the categories on the left.
- Select Python Application and click Next.
- Give your project a name (e.g.,
MyPythonApp) and choose a project location. - Ensure the correct Python Platform is selected in the "Python Platform" dropdown.
- Click Finish.
NetBeans will create a project with a default file named main.py.
Write Code
Open main.py and write some Python code. Notice the syntax highlighting and code completion.
# main.py
def greet(name):
"""This function greets the person passed in as a parameter."""
return f"Hello, {name}!"
if __name__ == "__main__":
user_name = "Alice"
message = greet(user_name)
print(message)
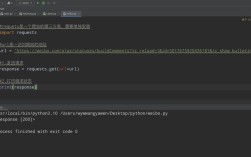
Run Your Code
There are two main ways to run your code:
- Run the File: Right-click on
main.pyin the Projects panel and select Run File. - Run the Project: Click the green "Run" button (▶) in the main toolbar. This will execute the
mainmodule specified in your project properties.
The output will appear in the Output window at the bottom of the screen.
Hello, Alice!Debug Your Code
Debugging is where NetBeans really shines.
- Set a Breakpoint: Click in the grey margin to the left of line 10 (
user_name = "Alice"). A red dot will appear. - Start the Debugger: Click the "Debug" button (a small bug icon ▶️) in the toolbar, or right-click the project and select Debug.
- Step Through the Code: The program will pause at your breakpoint. You can now use the debugger controls in the toolbar:
- Step Over (F8): Executes the current line and moves to the next one.
- Step Into (F7): If the current line is a function call, it will step into that function.
- Step Out (Shift+F8): Finishes executing the current function and returns to the caller.
- Inspect Variables: While debugging, you can hover your mouse over variables like
user_nameto see their current value. You can also add them to the "Variables" window for continuous monitoring. - Stop Debugging: Click the red "Stop" button to end the debugging session.
Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | NetBeans for Python | PyCharm (Community) | Visual Studio Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Good for beginners. | Excellent, but can be overwhelming at first. | Excellent, highly customizable. |
| Python Support | Good, but a plugin. | Excellent, first-class citizen. | Excellent, via extensions. |
| Debugger | Very Good, integrated. | Excellent, powerful and intuitive. | Excellent, highly configurable. |
| Virtual Env. | Functional, but clunky. | Excellent, seamless management. | Excellent, great extension support. |
| Community/Plugins | Small for Python. | Huge, dedicated Python ecosystem. | Massive, vast extension marketplace. |
| Best For | Java developers who occasionally use Python, or beginners who want a simple all-in-one IDE. | Professional Python development (web, data, scientific). | Versatile development (Python, web, front-end, etc.). |
Final Verdict
Should you use NetBeans for Python?
-
Maybe, if:
- You are already a heavy NetBeans user for Java and want to do some Python scripting on the side.
- You are a complete beginner to both programming and IDEs and find the VS Code/PyCharm interfaces intimidating.
- You need a free, cross-platform IDE with a solid debugger and don't care about advanced ecosystem features.
-
Probably not, if:
- You are serious about Python development.
- You work on web frameworks (Django, Flask), data science (Pandas, NumPy), or machine learning.
- You want the best tooling, the largest community, and the smoothest integration with the Python package ecosystem.
For almost everyone, PyCharm Community Edition (for dedicated Python work) or Visual Studio Code (for more general-purpose development) are the superior choices. However, NetBeans is a capable tool and perfectly functional for smaller projects.