Spring 框架提供了非常灵活的定时任务支持,主要可以分为以下三类:
- 注解驱动(最常用、最简单):使用
@Scheduled注解,配置简单,适合大多数场景。 - 接口驱动(更灵活):实现
SchedulingConfigurer接口,可以更灵活地配置线程池。 - 外部化配置(最强大):集成
Quartz或Elastic-Job等专业调度框架,适合分布式、高可用的复杂场景。
下面我们逐一详细介绍。
@Scheduled 注解驱动(推荐)
这是 Spring Boot 中最流行、最简单的方式,你只需要在配置类上开启定时任务,然后在方法上使用 @Scheduled 注解即可。
添加依赖
在 pom.xml 中,确保引入 spring-boot-starter,它已经包含了定时任务的核心依赖 spring-context。
<!-- 对于 Spring Boot 项目,通常不需要手动添加,spring-boot-starter 已包含 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
开启定时任务
在你的 Spring Boot 启动类或者一个专门的配置类上,添加 @EnableScheduling 注解来启用对 @Scheduled 的支持。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling // 开启定时任务
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
编写定时任务方法
创建一个 Service 或 Component,然后在需要定时执行的方法上添加 @Scheduled 注解。
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
@Component
public class MyScheduledTasks {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyScheduledTasks.class);
private static final DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
/**
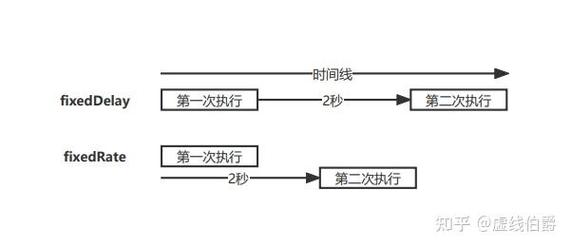
* fixedRate: 固定速率执行,意思是两次任务的开始时间间隔固定,不受任务执行时间影响。
* fixedRate = 5000,表示每5秒执行一次,如果上次任务执行了2秒,那么它会在3秒后立即开始下一次。
*/
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000)
public void taskWithFixedRate() {
log.info("=== Fixed Rate Task: 当前时间 {} ===", dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()));
// 模拟一个耗时3秒的任务
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
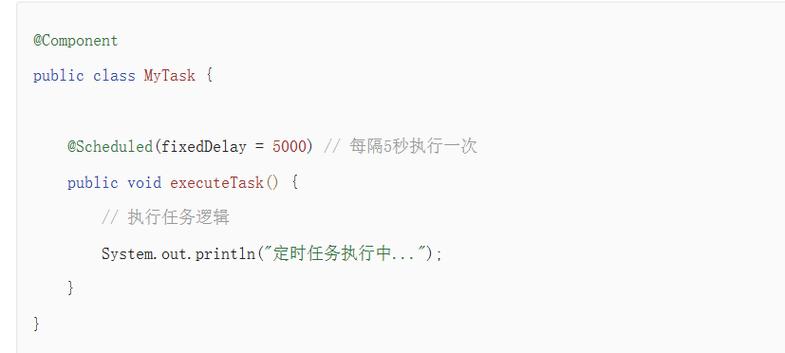
/**
* fixedDelay: 固定延迟执行,意思是上次任务**结束**后,等待固定时间再开始下一次。
* fixedDelay = 5000,如果上次任务执行了2秒,那么它会在任务结束后再等5秒,总共7秒后开始下一次。
*/
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000)
public void taskWithFixedDelay() {
log.info("=== Fixed Delay Task: 当前时间 {} ===", dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()));
}
/**
* initialDelay: 首次延迟执行,可以与 fixedRate 或 fixedDelay 组合使用,表示在应用启动后等待多久再开始第一次执行。
*/
@Scheduled(initialDelay = 10000, fixedRate = 5000)
public void taskWithInitialDelay() {
log.info("=== Initial Delay & Fixed Rate Task: 当前时间 {} ===", dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()));
}
/**
* cron: 功能最强大的表达式,可以设置更复杂的执行时间规则。
* cron = "0/10 * * * * ?" 表示从0秒开始,每10秒执行一次。
* 格式:[秒] [分] [时] [日] [月] [周几] [年(可选)]
* 通配符:
* * : 任意值
* ? : 不指定值(用于日和周几冲突时)
* - : 范围,如 1-5
* , : 列表,如 1,3,5
* / : 步长,如 0/10 表示从0开始,每10秒
*/
@Scheduled(cron = "0/15 * * * * ?")
public void taskWithCron() {
log.info("=== Cron Task: 当前时间 {} ===", dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()));
}
}
配置线程池(可选)
默认情况下,Spring Boot 使用一个单线程的 ThreadPoolTaskScheduler 来执行所有定时任务,如果你的任务很多或某个任务耗时很长,可能会导致任务阻塞或延迟。
你可以通过在 application.properties 或 application.yml 中配置来优化:
application.properties
# 核心线程池大小 spring.task.scheduling.pool.size=5 # 线程名前缀 spring.task.scheduling.thread-name-prefix=scheduling- # 等待任务在关闭时完成的最大秒数 spring.task.scheduling.shutdown.await-termination=10
application.yml
spring:
task:
scheduling:
pool:
size: 5
thread-name-prefix: scheduling-
shutdown:
await-termination: 10
SchedulingConfigurer 接口驱动
当你需要更灵活地配置线程池(动态设置线程池大小)时,可以实现 SchedulingConfigurer 接口。
创建配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.SchedulingConfigurer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.config.ScheduledTaskRegistrar;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@Configuration
public class SchedulingConfig implements SchedulingConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar taskRegistrar) {
// 使用一个固定大小的线程池
// 这里创建一个大小为10的线程池
taskRegistrar.setScheduler(Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10));
}
}
这种方式让你可以完全控制任务调度器的创建,但通常 application.properties 的配置已经足够,所以此方法用得相对较少。
集成专业调度框架(Quartz)
当你的应用是分布式部署,或者对任务的高可用性、持久化、集群管理有很高要求时,@Scheduled 就显得力不从心了,这时,集成 Quartz 是最佳选择。
Quartz 是一个功能强大、开源的作业调度库。
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-quartz</artifactId>
</dependency>
创建 Job(任务)
Quartz 的任务需要继承 QuartzJobBean。
import org.quartz.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyQuartzJob implements Job {
@Override
public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
// 获取 JobDetail 中的数据
JobDataMap dataMap = context.getJobDetail().getJobDataMap();
String taskName = dataMap.getString("taskName");
System.out.println("Quartz Task is running... Task Name: " + taskName);
// 这里编写你的业务逻辑
}
}
配置和触发 Job
你可以在配置类中定义 Job 和 Trigger(触发器),并启动调度。
import org.quartz.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class QuartzConfig {
// 1. 定义 Job
@Bean
public JobDetail myQuartzJobDetail() {
// 关联我们自己的 Job 类
// 使用持久化,这样即使应用重启,任务信息也不会丢失
return JobBuilder.newJob(MyQuartzJob.class)
.withIdentity("myQuartzJob") // 任务名称
.usingJobData("taskName", "这是一个Quartz任务") // 传递给Job的数据
.storeDurably() // 即使没有关联Trigger也进行保存
.build();
}
// 2. 定义 Trigger
@Bean
public Trigger myQuartzTrigger() {
// 简单的触发器,每10秒执行一次
SimpleScheduleBuilder scheduleBuilder = SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule()
.withIntervalInSeconds(10)
.repeatForever();
return TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.forJob(myQuartzJobDetail()) // 关联Job
.withIdentity("myQuartzTrigger") // 触发器名称
.withSchedule(scheduleBuilder)
.build();
}
}
Quartz 的优势
- 持久化:可以将任务信息保存到数据库中,应用重启后任务不会丢失。
- 集群:支持多节点部署,自动实现任务的负载均衡和故障转移。
- 丰富的 API:提供了更复杂的调度功能,如日历、任务依赖等。
- 管理界面:可以通过管理界面查看、暂停、恢复、删除任务。
总结与如何选择
| 特性 | @Scheduled 注解 |
SchedulingConfigurer 接口 |
Quartz 框架 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 使用复杂度 | 非常简单 | 简单 | 较复杂 |
| 适用场景 | 单机应用,简单、固定的定时任务 | 需要自定义线程池配置 | 分布式、高可用、复杂调度 |
| 持久化 | 不支持 (应用重启任务丢失) | 不支持 | 支持 (数据库存储) |
| 集群支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 灵活性 | 一般(依赖cron表达式) | 较高(线程池控制) | 非常高 (API丰富) |
| 依赖 | Spring 内置 | Spring 内置 | 需要额外引入 Quartz |
选择建议:
- 如果你只是想在 Spring Boot 应用里加几个简单的定时任务,比如每天凌晨清理数据、每小时同步一次信息,直接使用
@Scheduled,这是 90% 的场景下的最佳选择。 - 如果你的定时任务很多,或者某个任务可能耗时较长,导致其他任务被延迟,可以通过配置
application.properties中的线程池来解决,如果还不够灵活,再考虑SchedulingConfigurer。 - 如果你的应用是微服务架构,部署在多台机器上,需要确保定时任务在集群中只执行一次,或者要求任务在应用崩溃重启后能自动恢复,那么必须使用 Quartz 或其他分布式调度框架(如 Elastic-Job)。