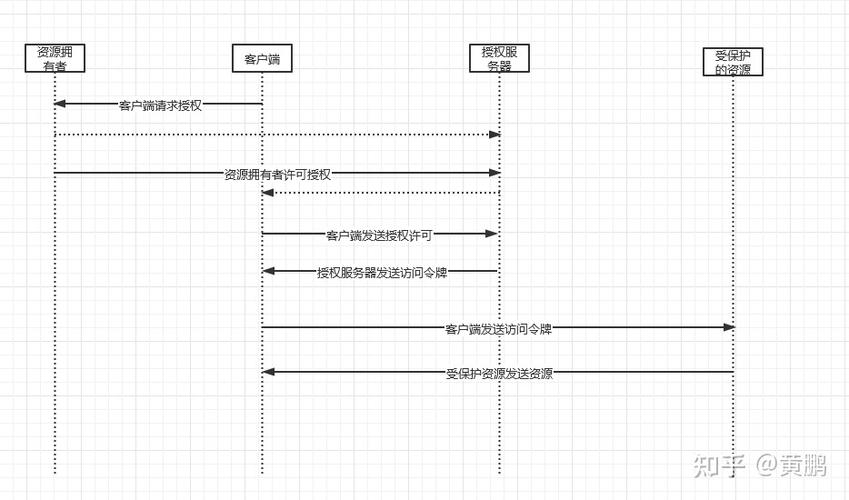
- 资源所有者:用户,他们授权第三方应用访问他们的受保护资源。
- 客户端:想要访问用户资源的应用程序(你的 Web 应用或移动 App)。
- 授权服务器:负责颁发访问令牌 的服务器,它验证用户身份并获取用户授权。
- 资源服务器:托管用户受保护资源的服务器,它使用访问令牌来请求进行身份验证和授权。
在实际项目中,授权服务器 和 资源服务器 通常是同一个应用或服务,它们共享密钥。

我们将使用目前 Java 生态中最流行、最强大的库之一:Spring Security 来构建一个完整的 OAuth 2.0 授权服务器和资源服务器。
核心概念回顾
在开始编码前,快速回顾一下 OAuth 2.0 的四种核心授权模式:
- 授权码模式:最安全、最常用,适用于服务器端应用,流程是:客户端引导用户到授权服务器 -> 用户登录并授权 -> 授权服务器重定向回客户端并附上一个授权码 -> 客户端用授权码向授权服务器请求访问令牌。
- 简化模式:适用于纯前端应用,直接从授权服务器获取访问令牌,没有授权码步骤。
- 密码模式:用户直接将用户名和密码提供给客户端,客户端再用这些信息去请求令牌。仅适用于你完全信任的客户端(你自己的官方第一方应用)。
- 客户端模式:用于服务到服务的通信,没有用户参与,客户端直接使用自己的凭据(Client ID/Secret)向授权服务器请求令牌。
项目实战:使用 Spring Security 6 构建 OAuth 2.0 服务
我们将创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目,它同时扮演授权服务器和资源服务器的角色。
第 1 步:创建 Spring Boot 项目
使用 Spring Initializr 创建项目,并添加以下依赖:

- Spring Web: 用于构建 Web 应用。
- Spring Security: 核心安全框架。
- Spring Security OAuth2 Authorization Server: 这是 Spring Security 5.7+ 引入的官方 OAuth 2.0 授权服务器实现,取代了旧的
spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure。 - Spring Security OAuth2 Resource Server: 用于实现资源服务器功能。
点击 "Generate" 下载项目并导入你的 IDE(如 IntelliJ IDEA 或 VS Code)。
第 2 步:配置授权服务器
在 src/main/java/com/example/demo 目录下,创建一个配置类来启用和配置授权服务器功能。
SecurityConfig.java
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.security.config.Customizer;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.AuthorizationGrantType;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.ClientAuthenticationMethod;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.oidc.OidcScopes;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.client.InMemoryRegisteredClientRepository;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.client.RegisteredClient;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.client.RegisteredClientRepository;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.config.annotation.web.configuration.OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.config.annotation.web.configurers.OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.settings.AuthorizationServerSettings;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.settings.ClientSettings;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.authorization.settings.TokenSettings;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.UUID;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
// 1. 配置授权服务器 SecurityFilterChain
@Bean
@Order(1)
public SecurityFilterChain authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration.applyDefaultSecurity(http);
http.getConfigurer(OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer.class)
.oidc(Customizer.withDefaults()); // 启用 OpenID Connect 1.0
http.exceptionHandling(exceptions ->
exceptions.authenticationEntryPoint(new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login"))) // 设置登录页面
.oauth2ResourceServer(resourceServer -> resourceServer.jwt(Customizer.withDefaults())); // 配置资源服务器以验证 JWT
return http.build();
}
// 2. 配置常规应用的 SecurityFilterChain
@Bean
@Order(2)
public SecurityFilterChain defaultSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults()); // 启用表单登录
return http.build();
}
// 3. 配置用户存储(用于演示,生产环境应使用数据库)
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(
User.withUsername("user")
.password(passwordEncoder().encode("password"))
.roles("USER")
.build(),
User.withUsername("admin")
.password(passwordEncoder().encode("admin"))
.roles("ADMIN")
.build()
);
}
// 4. 配置客户端存储(用于演示,生产环境应使用数据库)
@Bean
public RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository() {
RegisteredClient client = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.clientId("client-app") // 客户端 ID
.clientSecret(passwordEncoder().encode("secret123")) // 客户端密钥
.clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC) // 客户端认证方式
.authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE) // 授权码模式
.authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.REFRESH_TOKEN) // 刷新令牌模式
.authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.CLIENT_CREDENTIALS) // 客户端凭据模式
.redirectUri("http://127.0.0.1:8080/login/oauth2/code/client-app") // 授权码回调地址
.scope(OidcScopes.OPENID) // OpenID Connect Scope
.scope("read") // 自定义 Scope
.scope("write")
.clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder().requireAuthorizationConsent(true).build()) // 要求用户同意授权
.tokenSettings(TokenSettings.builder().accessTokenTimeToLive(Duration.ofMinutes(30)).build()) // 令牌有效期
.build();
return new InMemoryRegisteredClientRepository(client);
}
// 5. 配置授权服务器设置
@Bean
public AuthorizationServerSettings authorizationServerSettings() {
return AuthorizationServerSettings.builder()
.issuer("http://auth-server:9000") // 授权服务器地址
.build();
}
// 6. 密码编码器
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
代码解释:
authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain: 这是授权服务器的核心配置,它设置了端点(如/oauth2/authorize,/oauth2/token)、OIDC 支持、登录入口点和资源服务器验证。defaultSecurityFilterChain: 这是为应用其他部分(如/login页面)配置的安全过滤器链。userDetailsService: 定义了用户信息,这里我们使用内存中的两个用户user/password和admin/admin。registeredClientRepository: 定义了客户端信息,这是 OAuth 2.0 的核心,它告诉授权服务器哪些客户端是合法的,它们可以请求什么授权类型和 Scope。clientId:client-appclientSecret:secret123authorizationGrantType: 我们支持AUTHORIZATION_CODE,REFRESH_TOKEN, 和CLIENT_CREDENTIALS。redirectUri: 授权码模式成功后的回调地址。scope: 客户端可以请求的权限范围。
authorizationServerSettings: 设置授权服务器的基本信息,如issuerURI。passwordEncoder: 用于对客户端密钥和用户密码进行加密。
第 3 步:配置资源服务器
资源服务器负责验证传入的访问令牌并保护 API 端点,幸运的是,Spring Security 会自动处理大部分事情,我们只需要创建一个受保护的 API 端点。
ResourceController.java
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.core.annotation.AuthenticationPrincipal;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jwt.Jwt;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ResourceController {
// 这是一个公开的端点,不需要认证
@GetMapping("/public")
public String publicEndpoint() {
return "This is a public endpoint.";
}
// 这是一个需要 "read" Scope 的受保护端点
@GetMapping("/resource")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('SCOPE_read')")
public String resourceEndpoint(@AuthenticationPrincipal Jwt jwt) {
return "Hello, " + jwt.getSubject() + "! You have accessed a protected resource with 'read' scope.";
}
// 这是一个需要 "write" Scope 的受保护端点
@GetMapping("/admin")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('SCOPE_write')")
public String adminEndpoint(@AuthenticationPrincipal Jwt jwt) {
return "Hello, Admin " + jwt.getSubject() + "! You have accessed a protected resource with 'write' scope.";
}
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('SCOPE_read')"): 这是 Spring Security 的方法级安全注解,它确保只有拥有readScope 的有效访问令牌才能访问此端点。@AuthenticationPrincipal Jwt jwt: 将当前认证的主体(即解析后的 JWT)注入到方法中,方便我们获取用户信息(如jwt.getSubject())。
第 4 步:测试流程
我们可以启动应用了,主应用类 DemoApplication.java 应该可以直接运行。
启动后,你将拥有以下服务:
- 授权服务器:
http://localhost:8080(默认端口) - 资源服务器:
http://localhost:8080/api(与授权服务器同端口)
我们将使用 Postman 或 curl 来测试整个流程。
流程 1:获取授权码
-
在浏览器中访问以下 URL:
http://localhost:8080/oauth2/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=client-app&redirect_uri=http://127.0.0.1:8080/login/oauth2/code/client-app&scope=read+write&state=abc123response_type=code: 指定使用授权码模式。client_id: 填写我们在配置中定义的客户端 ID。redirect_uri: 必须与配置中的redirectUri完全匹配。scope: 请求read和write权限。state: 一个随机字符串,用于防止 CSRF 攻击。
-
浏览器会重定向到
/login页面,输入我们定义的用户凭据,user / password。 -
登录后,你会看到一个授权页面,询问你是否授权
client-app访问你的read和write权限,点击 "Authorize"。 -
页面会重定向到
redirect_uri,URL 中会包含一个授权码,http://127.0.0.1:8080/login/oauth2/code/client-app?code=YOUR_AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=abc123复制
code的值。
流程 2:使用授权码换取访问令牌
我们使用上一步获取的授权码来请求访问令牌,这通常是在你的后端服务器(客户端应用)中完成的,而不是在浏览器中。
使用 curl 命令:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/oauth2/token \ -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \ -H "Authorization: Basic Y2xpZW50LWFwcDpzZWNyZXQxMjM=" \ -d "grant_type=authorization_code" \ -d "code=YOUR_AUTHORIZATION_CODE" \ -d "redirect_uri=http://127.0.0.1:8080/login/oauth2/code/client-app"
参数解释:
-H "Authorization: Basic Y2xpZW50LWFwcDpzZWNyZXQxMjM=": 这是client-id:client-secret进行 Base64 编码的结果。client-app:secret123->Y2xpZW50LWFwcDpzZWNyZXQxMjM=。grant_type=authorization_code: 指定授权类型。code: 填入你刚刚获取的授权码。redirect_uri: 必须与请求授权码时使用的redirect_uri一致。
如果成功,你会收到类似以下的 JSON 响应,包含了 access_token, refresh_token, expires_in 等:
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9...",
"refresh_token": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9...",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 1799,
"scope": "read write openid",
"jti": "..."
}
流程 3:使用访问令牌访问受保护的资源
我们使用刚刚获取的 access_token 来访问之前创建的 /api/resource 端点。
curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/api/resource \ -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN"
将 YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN 替换为上面返回的 access_token 的值。
如果成功,你会得到:
Hello, user! You have accessed a protected resource with 'read' scope.
如果你尝试访问 /api/admin 端点,并且你的 access_token 只有 read scope,你会收到 403 Forbidden 错误。
curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/api/admin \ -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN"
响应:
{
"error": "insufficient_scope",
"error_description": "The token does not contain the required scopes."
}
总结与最佳实践
- 不要在生产环境使用内存存储:本示例中的
InMemoryRegisteredClientRepository和InMemoryUserDetailsManager仅用于演示,在生产环境中,你必须将客户端和用户信息存储在数据库中(如 MySQL, PostgreSQL)。 - 选择合适的授权模式:
- 对于 Web 应用,授权码模式 是首选。
- 对于纯前端 SPA (React, Vue),可以使用 授权码模式 + PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange),以增强安全性。
- 对于服务到服务通信,使用 客户端凭据模式。
- 安全性:
- 始终使用 HTTPS。
- 对客户端密钥进行安全存储。
- 合理设置令牌的有效期 (
accessTokenTimeToLive)。 - 使用强密码哈希算法(如 BCrypt)。
- Spring Security 的版本:注意,Spring Security 5.7 引入了新的
spring-security-oauth2-authorization-server依赖,与旧的spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure有很大不同,新版本功能更强大,配置更灵活,是未来的方向。
通过以上步骤,你已经成功地在 Java (Spring Boot) 中实现了一个功能完备的 OAuth 2.0 授权服务器和资源服务器,并完整地测试了最常用的授权码流程。