Of course! Converting a long to an int in Java is a common task, but it's not as simple as a direct cast because you risk losing data. Here’s a complete guide covering the different methods, their risks, and best practices.
The Core Problem: Data Loss
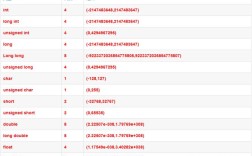
A long is a 64-bit integer, while an int is a 32-bit integer. This means a long can store numbers that are much larger (or smaller) than what an int can hold.
long:-9,223,372,036,854,775,808to9,223,372,036,854,775,807int:-2,147,483,648to2,147,483,647
If you try to fit a long value outside the int range into an int, the extra bits will be "chopped off," leading to a completely incorrect number.
Method 1: The Direct Cast (int)
This is the most common way to convert a long to an int. It's a narrowing primitive conversion, which means Java will automatically truncate the higher 32 bits of the long to fit it into the 32-bit int.
Syntax:
int myInt = (int) myLong;
The Crucial Risk: Silent Truncation
If the long value is outside the int range, the cast will succeed, but the result will be wrong. Java does not throw an exception by default.

Example:
public class LongToIntExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Safe Conversion (within int range)
long longValue1 = 150;
int intValue1 = (int) longValue1;
System.out.println("Safe conversion: " + longValue1 + " -> " + intValue1);
// Output: Safe conversion: 150 -> 150
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
// 2. Unsafe Conversion (value too large)
long longValue2 = 2147483650L; // This is > Integer.MAX_VALUE (2147483647)
int intValue2 = (int) longValue2;
// The value is truncated. The lower 32 bits are kept.
System.out.println("Unsafe conversion (value too large): " + longValue2 + " -> " + intValue2);
// Output: Unsafe conversion (value too large): 2147483650 -> -2147483646
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
// 3. Unsafe Conversion (value too small)
long longValue3 = -2147483650L; // This is < Integer.MIN_VALUE (-2147483648)
int intValue3 = (int) longValue3;
System.out.println("Unsafe conversion (value too small): " + longValue3 + " -> " + intValue3);
// Output: Unsafe conversion (value too small): -2147483650 -> 2147483646
}
}
Notice how 2147483650L becomes -2147483646. This is a classic example of silent data corruption and is a major source of bugs.
Method 2: Safe Conversion with Explicit Checks (Best Practice)
To avoid silent truncation, you should always check if the long value is within the valid range for an int before you perform the cast.
The Range Check:
An int must be between Integer.MIN_VALUE and Integer.MAX_VALUE, inclusive.
if (myLong >= Integer.MIN_VALUE && myLong <= Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
// It's safe to cast
int myInt = (int) myLong;
// ... use myInt
} else {
// Handle the error: the value is too large or too small
System.err.println("Error: Long value " + myLong + " is out of int range.");
// Or throw an exception
// throw new IllegalArgumentException("Long value is out of int range.");
}
Complete Example:
public class SafeLongToIntConversion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long[] longValues = {100L, 2147483648L, -2147483649L, 0L};
for (long value : longValues) {
try {
int convertedValue = safeLongToInt(value);
System.out.println("Success: " + value + " -> " + convertedValue);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("Failed: " + value + " -> " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
/**
* Safely converts a long to an int, throwing an exception if the value is out of range.
*
* @param value The long value to convert.
* @return The converted int value.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value is outside the int range.
*/
public static int safeLongToInt(long value) {
if (value < Integer.MIN_VALUE || value > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Value " + value + " is out of int range.");
}
return (int) value;
}
}
Output:
Success: 100 -> 100
Failed: 2147483648 -> Value 2147483648 is out of int range.
Failed: -2147483649 -> Value -2147483649 is out of int range.
Success: 0 -> 0Method 3: Using Math.toIntExact() (Java 8 and later)
Java 8 introduced a convenient utility method in the Math class specifically for this purpose: Math.toIntExact().
- If the
longvalue is within theintrange, it performs the conversion and returns theint. - If the
longvalue is outside theintrange, it throws anArithmeticException.
This is the cleanest and most idiomatic way to perform a safe conversion in modern Java.
Syntax:
try {
int myInt = Math.toIntExact(myLong);
// ... use myInt
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
// Handle the overflow
System.err.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
Example:
public class MathToIntExactExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long[] longValues = {123L, Long.MAX_VALUE, Long.MIN_VALUE};
for (long value : longValues) {
try {
int convertedValue = Math.toIntExact(value);
System.out.println("Success: " + value + " -> " + convertedValue);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Failed: " + value + " -> " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
Output:
Success: 123 -> 123
Failed: 9223372036854775807 -> integer overflow
Failed: -9223372036854775808 -> integer overflowSummary and Recommendations
| Method | How it Works | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
(int) cast |
Truncates higher bits. | Simple, fast. | Silent data loss if value is out of range. High risk of bugs. | Situations where you are 100% certain the value is within range, or you specifically want truncation (e.g., for hashing). |
| Explicit Check | Checks range before casting. | Safe, explicit, no silent failures. | More verbose code. | General-purpose, safe conversion. The standard approach in Java 7 and earlier. |
Math.toIntExact() |
Checks range and casts. Throws exception on overflow. | Safe, concise, idiomatic (Java 8+). | Requires Java 8+. | Recommended for modern Java (8+). It's the clearest and most robust way to safely convert. |
Final Recommendation
- If you are using Java 8 or later, always prefer
Math.toIntExact(). It's designed for this exact purpose and makes your code safer and more readable. - If you are using Java 7 or earlier, or cannot use
Math.toIntExact(), use an explicit range check before casting. This prevents silent data corruption. - Only use the naked
(int) castif you have a very specific reason to believe the value will always be in range, or if you intentionally want to truncate the value (for example, in a hash function where collisions are acceptable).