Of course. Here is a comprehensive guide to setting up and using Python 2.7 with PyQt on a Mac.
This is a legacy setup, as Python 2.7 reached its official end-of-life in 2025, and PyQt5/6 are the modern standards. However, this is necessary for maintaining or running very old applications.
⚠️ Important Warning: Why You Should Avoid This
Before we begin, it's crucial to understand the context:
- Python 2.7 is End-of-Life: It no longer receives security updates, bug fixes, or improvements. Using it in a production environment is a security risk.
- Qt5/6 are Modern: Modern versions of Qt (the framework behind PyQt) are no longer compatible with Python 2.7.
- PyQt4 is the Target: For Python 2.7, you must use PyQt4, not PyQt5 or PyQt6. PyQt4 is also ancient and unsupported.
This guide is for legacy maintenance only. For any new project, you should absolutely use a modern version of Python (3.8+) and PyQt5 or PyQt6.
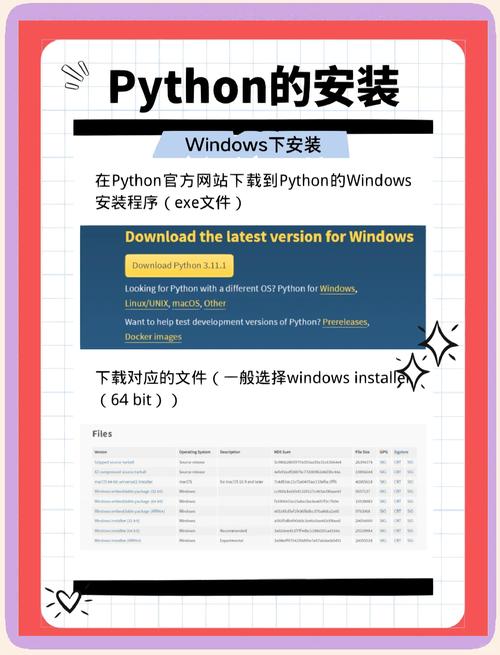
Step 1: Install Python 2.7
The easiest and recommended way to manage multiple Python versions on a Mac is with a version manager like pyenv.
Method 1: Using pyenv (Recommended)
-
Install Homebrew (if you don't have it): Open Terminal and run:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
-
Install
pyenvusing Homebrew:brew install pyenv
-
Configure your Shell: You need to add
pyenvto your shell's path. The commands depend on your shell (usually Zsh for modern macOS or Bash for older versions).For Zsh (macOS Catalina and later):
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)echo 'eval "$(pyenv init --path)"' >> ~/.zshrc echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.zshrc
For Bash (macOS Mojave and earlier):
echo 'eval "$(pyenv init --path)"' >> ~/.bash_profile echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bash_profile
-
Restart your Terminal or run
source ~/.zshrc(orsource ~/.bash_profile). -
Install Python 2.7:
pyenvwill build Python from source, which can take a few minutes.pyenv install 2.7.18
-
Set Python 2.7 as your Global Version (Optional): If you want this to be the default Python for your user account, run:
pyenv global 2.7.18
You can verify the installation:
python --version # Should output: Python 2.7.18 pip --version # Should output: pip X.X.X from ...
Method 2: Using Official Installer
- Go to the official Python 2.7 download page: Python 2.7.18 Release
- Download the macOS 64-bit installer (e.g.,
python-2.7.18-macosx10.9.pkg). - Run the installer. It will install Python 2.7 to
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/. - The installer usually adds the correct paths to your shell configuration files automatically. You may need to restart your Terminal.
Step 2: Install PyQt4 for Python 2.7
Now that you have Python 2.7, you need to install PyQt4. The best tool for this is pip.
-
Ensure
pipis up-to-date for Python 2.7:pip install --upgrade pip
-
Install PyQt4: This command will download and compile PyQt4 against your Python 2.7 installation.
pip install PyQt4
Note: The compilation can sometimes fail due to missing Xcode command-line tools. If you encounter errors, run:
xcode-select --install
Then try the
pip installcommand again. -
Verify the Installation: Run a simple Python script to check if the imports work.
Create a file named
test_qt.py:import sys from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore print("PyQt4 version:", QtCore.PYQT_VERSION_STR) print("Qt version:", QtCore.QT_VERSION_STR) app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) window = QtGui.QMainWindow() window.setWindowTitle("PyQt4 on macOS Test") window.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300) window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())Run it from your Terminal:
python test_qt.py
If a small window titled "PyQt4 on macOS Test" appears, your installation is successful!
Step 3: Running Your PyQt4 Application
You have two primary ways to run your scripts.
A. Using the Terminal (Command Line)
This is the most straightforward method. Navigate to your project directory in the Terminal and run:
python your_script.py
Example:
cd /Users/yourname/Desktop/my_pyqt_app python my_app.py
B. Creating a Standalone .app Bundle (for Distribution)
To share your application with others who might not have Python/PyQt installed, you can package it into a standard macOS .app bundle. The best tool for this is py2app.
-
Install
py2app:pip install py2app
-
Create a
setup.pyfile: In the same directory as your main script, create a file namedsetup.py. This file tellspy2apphow to package your application.For our
test_qt.pyscript, thesetup.pywould look like this:from setuptools import setup APP = ['test_qt.py'] DATA_FILES = [] OPTIONS = { 'argv_emulation': False, 'iconfile': None, # Optional: path to your .icns icon file } setup( app=APP, data_files=DATA_FILES, options={'py2app': OPTIONS}, setup_requires=['py2app'], ) -
Build the Application: From your Terminal, in the same directory, run the build command:
python setup.py py2app
-
Find Your Application: After the build process completes, a new
distfolder will be created. Inside, you will find your application, namedtest_qt.app.You can now double-click
test_qt.appto run it, or share it with others.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
-
"ImportError: No module named PyQt4":
- Cause: You are likely running the wrong Python interpreter (e.g., the system Python 2.7 or a different Python 3 version).
- Solution: Check your active Python version with
which pythonandpython --version. If you usedpyenv, ensure you are in the correct shell session wherepyenv global 2.7.18was set.
-
Build errors during
pip install PyQt4orpy2app:- Cause: Missing build dependencies like Xcode Command Line Tools or other libraries.
- Solution: Run
xcode-select --installto get the necessary compilers and headers.
-
Application crashes on launch (from .app bundle):
- Cause: Often related to missing Qt plugins (like the style plugins). The
.appbundle might not be able to find them. - Solution: You can try using a tool like
delocateto copy the necessary Qt frameworks into your bundle'sFrameworksdirectory, or use a more advancedpy2appconfiguration to specify plugin directories. This is a common challenge with legacy Qt packaging.
- Cause: Often related to missing Qt plugins (like the style plugins). The