Of course! Working with OpenStreetMap (OSM) data in Python is a very common and powerful task, used for everything from data analysis and visualization to building routing applications.
Here's a comprehensive guide covering the main ways to interact with OSM data in Python, broken down by use case.
What is OpenStreetMap?
First, a quick refresher: OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a free, open-source, collaborative map of the world. Think of it as "Wikipedia for maps." Anyone can contribute, and the data is licensed under the Open Data Commons Open Database License (ODbL). This makes it incredibly valuable for developers, researchers, and hobbyists.
Scenario 1: Just Want to Plot a Map? (Easy Visualization)
If your goal is to simply display a map or add some basic markers, the easiest way is to use a library that fetches map tiles on the fly (like a web map) and overlays your data.
Library: Folium
Folium is perfect for this. It builds on the data wrangling strengths of the Python ecosystem and the mapping strengths of Leaflet.js.
Installation:
pip install folium
Example: Plotting a map with a marker
import folium
# Create a map object, centered on a specific location (e.g., Berlin)
# The 'tiles' argument lets you choose the map style. 'OpenStreetMap' is the default.
m = folium.Map(location=[52.5200, 13.4050], zoom_start=13, tiles="OpenStreetMap")
# Add a marker to the map
folium.Marker(
location=[52.5200, 13.4050],
popup="Brandenburg Gate",
icon=folium.Icon(color="red", icon="info-sign")
).add_to(m)
# Save the map to an HTML file
m.save("berlin_map.html")
# To display it in a Jupyter Notebook or Google Colab, just run the map object
m
This will create an interactive berlin_map.html file that you can open in your browser.
Scenario 2: Need to Query OSM Data for a Specific Area? (The Overpass API)
The main OSM database is huge. You don't want to download the whole planet. Instead, you use the Overpass API to query for specific data within a geographic boundary (like a city, a bounding box, or around a point).
Library: requests (standard library)
You can query the Overpass API directly using Python's requests library.
Example: Find all restaurants in a specific area in Berlin The Overpass QL language is used to define the query.
import requests
import json
# Overpass API endpoint
overpass_url = "http://overpass-api.de/api/interpreter"
overpass_query = """
[out:json][timeout:25];
(
way["amenity"="restaurant"](52.4, 13.3, 52.6, 13.5);
relation["amenity"="restaurant"](52.4, 13.3, 52.6, 13.5);
);
out body;
>;
out skel qt;
"""
# Make the request
response = requests.get(overpass_url, data=overpass_query)
data = response.json()
# Save the results to a file for later use
with open("berlin_restaurants.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(data, f)
print(f"Found {len(data['elements'])} elements.")
This query fetches all ways and relations tagged with amenity=restaurant within the bounding box [52.4, 13.3, 52.6, 13.5] (which covers central Berlin).
Scenario 3: Need to Download, Analyze, and Manipulate OSM Data? (The OSMnx Library)
This is the most powerful and popular library for working with OSM data in Python. OSMnx lets you download street networks and other geospatial data, model them as NetworkX graphs, and perform topological and spatial analyses.
Installation:
pip install osmnx
Example 1: Downloading and plotting a street network
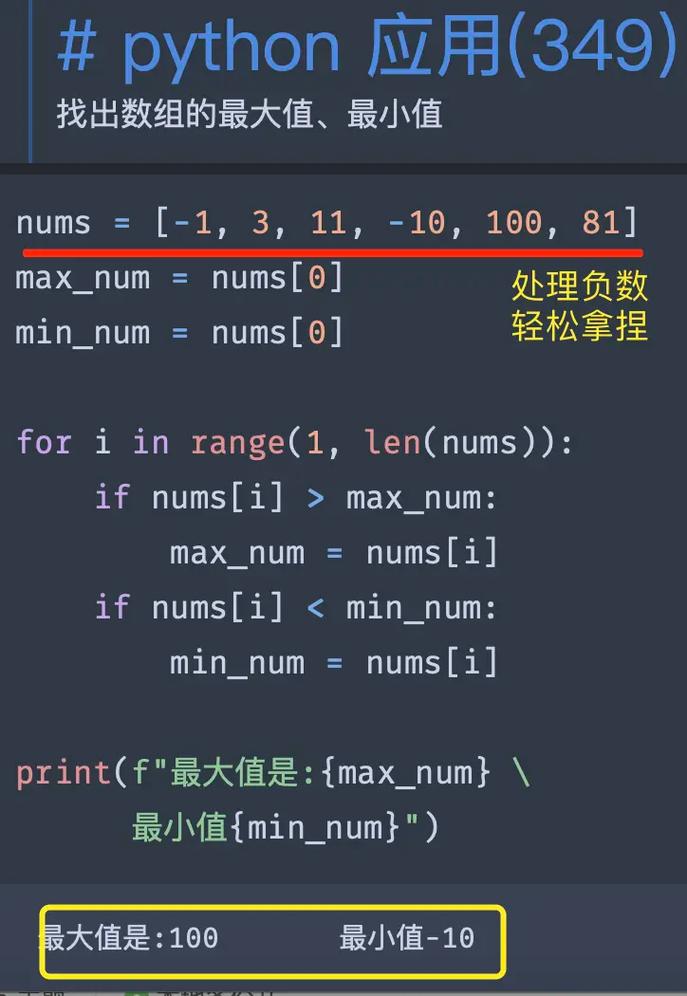
import osmnx as ox # Define the place you're interested in place_name = "Piedmont, California, USA" # Download the street network for the place # The `network_type` can be 'drive', 'bike', 'walk', etc. graph = ox.graph_from_place(place_name, network_type="drive") # You can plot the network directly fig, ax = ox.plot_graph(graph, node_size=0, edge_linewidth=0.5) # You can also convert the graph to a GeoDataFrame for analysis nodes, edges = ox.graph_to_gdfs(graph) print(edges.head())
Example 2: Finding the shortest path between two points
import osmnx as ox
import networkx as nx
# Get the street network for Manhattan
G = ox.graph_from_place("Manhattan, New York, USA", network_type="walk")
# Get the coordinates for two points (e.g., Empire State Building and Times Square)
point1 = (40.7484, -73.9857)
point2 = (40.7580, -73.9855)
# Find the nearest nodes to these points in the graph
orig_node = ox.distance.nearest_nodes(G, point1[1], point1[0])
dest_node = ox.distance.nearest_nodes(G, point2[1], point2[0])
# Calculate the shortest path using Dijkstra's algorithm
route = nx.shortest_path(G, orig_node, dest_node, weight="length")
# Plot the route
fig, ax = ox.plot_graph_route(G, route, route_color="y", route_linewidth=6, node_size=0)
Scenario 4: Working with Large, Pre-Downloaded OSM Data Files (.osm, .pbf)
Sometimes, you need to work with a full dump of a region (e.g., a country or a city) stored in a .osm or .pbf (Protocolbuffer Binary Format) file. These files can be gigabytes in size. For this, you need a parser.
Library: osmium
osmium is a fast C++ library with Python bindings, designed specifically for handling large OSM files efficiently.
Installation:
pip install osmium
Example: Counting the number of schools in a .osm.pbf file
import osmium
class CounterHandler(osmium.SimpleHandler):
def __init__(self):
super(CounterHandler, self).__init__()
self.school_count = 0
def way(self, w):
# Check if the way has a 'amenity' tag and its value is 'school'
if 'amenity' in w.tags and w.tags['amenity'] == 'school':
self.school_count += 1
# Create an instance of your handler
handler = CounterHandler()
# Apply the handler to the OSM file
# This reads the file and calls the 'way' method for every <way> element
osmium.apply_file("germany.osm.pbf", handler=handler)
print(f"Found {handler.school_count} schools in the file.")
osmium is extremely fast and memory-efficient because it doesn't load the entire file into memory at once.
Summary: Which Library Should I Use?
| Your Goal | Recommended Library | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Quickly plot an interactive map | folium |
Easy, creates HTML files with Leaflet.js. Great for dashboards. |
| Query for specific data points (POIs, etc.) | requests |
Direct access to the Overpass API. Flexible and powerful. |
| Analyze street networks, routing, geographics | osmnx |
The gold standard. Integrates with NetworkX, GeoPandas, and Matplotlib. |
| Process huge, local OSM data files | osmium |
Blazing fast and memory-efficient. The only choice for very large files. |
| Simple geocoding (address to lat/lon) | geopy + Nominatim |
Uses the OSM Nominatim service. Simple and effective. |
Important Considerations
- API Etiquette (Overpass API): Don't hammer the Overpass API with huge, complex queries. It's a public service. For heavy or repeated use, consider setting up your own Overpass API instance.
- Data Attribution: When you use OSM data in a product or publication, you must provide attribution. The standard format is:
© OpenStreetMap contributors
- License (ODbL): The OSM data is licensed under the ODbL. If you use the data in a way that is "derivative" (e.g., you create a new product primarily from OSM data), you may be required to share your work under the same license. Always check the