在Java中获取当前Java文件的路径
在Java中获取当前Java文件的路径有几种方法,具体取决于你需要的路径类型(源文件路径、类文件路径或运行时路径)。
获取当前类文件的路径(编译后)
// 获取当前类文件的绝对路径(.class文件所在目录)
String classPath = YourClassName.class.getResource("").getPath();
System.out.println("类文件路径: " + classPath);
// 获取当前类文件的根路径(classpath根目录)
String rootPath = YourClassName.class.getResource("/").getPath();
System.out.println("类文件根路径: " + rootPath);
获取当前源文件的路径(编译前)
Java运行时无法直接获取源文件(.java)的路径,因为源文件在编译后会被转换为.class文件,如果你需要在编译时获取源文件路径,可以使用以下方法:
使用Maven构建工具时
// 在Maven项目中,可以通过以下方式获取源文件路径
String sourcePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/main/java";
System.out.println("源文件路径: " + sourcePath);
使用Gradle构建工具时
// 在Gradle项目中
String sourcePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/main/java";
System.out.println("源文件路径: " + sourcePath);
获取当前工作目录
// 获取当前Java进程的工作目录
String workingDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
System.out.println("工作目录: " + workingDir);
获取JAR文件路径(如果当前是JAR包运行)
// 获取当前JAR文件的绝对路径
String jarPath = YourClassName.class.getProtectionDomain()
.getCodeSource()
.getLocation()
.getPath();
System.out.println("JAR文件路径: " + jarPath);
注意事项
-
路径分隔符:不同操作系统使用不同的路径分隔符(Windows是
\,Linux/Mac是),建议使用File.separator来保持跨平台兼容性。 -
URL编码:路径中可能包含空格或特殊字符,需要进行URL解码:
String decodedPath = URLDecoder.decode(path, "UTF-8");
-
相对路径与绝对路径:注意区分相对路径(相对于工作目录)和绝对路径。
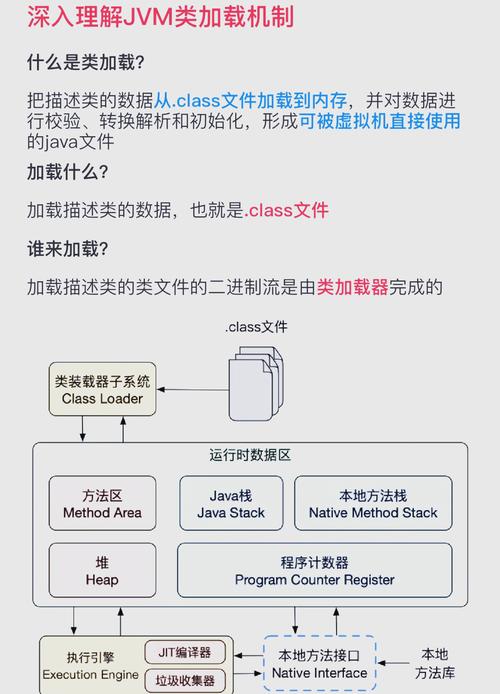 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删) -
类加载器:不同的类加载器可能会影响路径获取的结果。
完整示例
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.io.File;
public class PathExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 获取类文件路径
String classPath = PathExample.class.getResource("").getPath();
System.out.println("类文件路径: " + URLDecoder.decode(classPath, "UTF-8"));
// 获取类文件根路径
String rootPath = PathExample.class.getResource("/").getPath();
System.out.println("类文件根路径: " + URLDecoder.decode(rootPath, "UTF-8"));
// 获取工作目录
String workingDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
System.out.println("工作目录: " + workingDir);
// 获取JAR文件路径
String jarPath = PathExample.class.getProtectionDomain()
.getCodeSource()
.getLocation()
.getPath();
System.out.println("JAR文件路径: " + URLDecoder.decode(jarPath, "UTF-8"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
选择哪种方法取决于你的具体需求和使用场景。