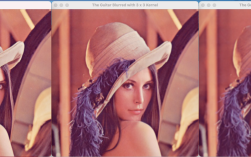
Of course! The term "imagefilter" in Python most commonly refers to the ImageFilter module from the Pillow (PIL) library. This is a powerful and easy-to-use tool for applying various convolution filters to images.

Let's break down everything you need to know about it.
What is the ImageFilter Module?
The ImageFilter module provides a set of predefined filters (like BLUR, SHARPEN, EDGE_ENHANCE) and a way to create your own custom filters using convolution kernels.
A convolution filter works by sliding a small matrix (called a kernel or mask) over the image. At each pixel, it calculates a new value based on the weighted average of its neighbors and the values in the kernel. This is the fundamental operation behind most image effects.
Installation
First, you need to have the Pillow library installed. If you don't, open your terminal or command prompt and run:
pip install Pillow
Basic Usage: Applying a Predefined Filter
The workflow is simple:
- Open an image using
Image.open(). - Filter the image using the
filter()method. - Save or display the result.
Here's a complete, runnable example.
Example: Blurring an Image
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter
# 1. Open an image
# Make sure you have an image file named 'my_image.jpg' in the same directory
# or provide the full path to your image.
try:
original_image = Image.open('my_image.jpg')
except FileNotFoundError:
# If no image is found, let's create a simple one for demonstration
print("my_image.jpg not found. Creating a sample image...")
original_image = Image.new('RGB', (400, 200), color = 'skyblue')
from PIL import ImageDraw
d = ImageDraw.Draw(original_image)
d.text((150,90), "Hello Pillow!", fill=(0,0,0))
# 2. Apply a filter
# Let's apply a simple blur filter
blurred_image = original_image.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)
# You can try other filters too:
# sharpened_image = original_image.filter(ImageFilter.SHARPEN)
# edge_enhanced_image = original_image.filter(ImageFilter.EDGE_ENHANCE)
# embossed_image = original_image.filter(ImageFilter.EMBOSS)
# 3. Save the result
blurred_image.save('blurred_image.jpg')
# 4. Display the original and filtered images (optional, requires a display)
original_image.show()
blurred_image.show()
print("Original and blurred images have been displayed and saved.")
Common Predefined Filters
Pillow comes with a handy set of built-in filters. Here are the most useful ones:
| Filter Name | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
ImageFilter.BLUR |
A simple blurring filter. | Softening skin, removing noise, creating a background effect. |
ImageFilter.SHARPEN |
Sharpen the image. | Making details in a photo more crisp. |
ImageFilter.SMOOTH |
Smooth the image. | Reducing noise while keeping a softer look than BLUR. |
ImageFilter.EDGE_ENHANCE |
Enhance the edges in the image. | Creating a sketch-like effect or highlighting features. |
ImageFilter.EMBOSS |
Apply a 3D-like emboss effect. | Creating a textured, raised appearance. |
ImageFilter.FIND_EDGES |
Find all edges in the image. | A more aggressive edge detection than EDGE_ENHANCE. |
ImageFilter.CONTOUR |
Outline the edges with a 1-pixel wide line. | Creating a line-art effect. |
ImageFilter.GaussianBlur |
Apply a Gaussian blur (more customizable). | A high-quality, adjustable blur. |
ImageFilter.UnsharpMask |
Sharpen the image using the Unsharp Mask algorithm. | A professional method for sharpening without amplifying noise. |
Example: Applying Multiple Filters
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter
# Open image
img = Image.open('my_image.jpg')
# Apply a combination of filters
# First, blur slightly, then sharpen the result
combined_effect = img.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR).filter(ImageFilter.SHARPEN)
combined_effect.save('combined_effect.jpg')
combined_effect.show()
Custom Filters with Kernel
This is where the real power of the ImageFilter module lies. You can define your own convolution kernels to create unique effects.
A kernel is represented as a multi-dimensional array. For a standard RGB image, you'll have a 3D kernel: (height, width, bands). The bands are usually (R, G, B).
The ImageFilter.Kernel() constructor takes:
size: A tuple(width, height)of the kernel.kernel: A sequence of floats representing the kernel values.scale(optional): The value to divide the sum of the kernel by. If omitted, it's the sum of the kernel's values.offset(optional): A value to add to the result after scaling.
Example: Custom Edge Detection Kernel
The Sobel operator is a classic edge detection kernel. We'll create one for the horizontal edges.
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter
# Open image
img = Image.open('my_image.jpg').convert('L') # Convert to grayscale for simplicity
# Define a custom kernel for horizontal edge detection (Sobel operator)
# The kernel is a 3x3 matrix
# The values are flattened into a sequence
sobel_kernel_horizontal = ImageFilter.Kernel(
(3, 3),
[-1, 0, 1,
-2, 0, 2,
-1, 0, 1],
1, 0 # scale=1, offset=0
)
# Apply the custom kernel
edge_detected_img = img.filter(sobel_kernel_horizontal)
edge_detected_img.save('edge_detected_horizontal.jpg')
edge_detected_img.show()
Example: Custom Sharpening Kernel
This kernel enhances the center pixel by adding the difference between it and its neighbors.
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter
img = Image.open('my_image.jpg')
# A simple sharpening kernel
sharpen_kernel = ImageFilter.Kernel(
(3, 3),
[ 0, -1, 0,
-1, 5, -1,
0, -1, 0],
1, 0
)
sharpened_img = img.filter(sharpen_kernel)
sharpened_img.save('custom_sharpened.jpg')
sharpened_img.show()
Advanced: ImageFilter.Filter (Base Class)
For even more control, you can create a class that inherits from ImageFilter.Filter. This is useful if your filter logic is too complex for a simple kernel (e.g., non-linear filters like median or minimum filters).
You must implement the filter method, which takes an image argument and returns the filtered image.
Example: A Median Filter (Noise Reduction)
A median filter replaces each pixel's value with the median of its neighbors, which is excellent at removing "salt-and-pepper" noise.
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter
import numpy as np
class MedianFilter(ImageFilter.Filter):
"""A custom median filter to reduce noise."""
name = "Median"
def filter(self, image):
# Convert PIL image to a NumPy array for easier processing
img_array = np.array(image)
# Handle different image modes (L, RGB, RGBA)
if image.mode == 'L':
channels = 1
else:
channels = img_array.shape[2]
# Pad the image to handle borders
padded_array = np.pad(img_array, ((1, 1), (1, 1), (0, 0)), mode='edge')
# Create an output array
output_array = np.zeros_like(img_array)
# Iterate over the image (excluding the padding)
for i in range(img_array.shape[0]):
for j in range(img_array.shape[1]):
# Extract the 3x3 neighborhood
neighborhood = padded_array[i:i+3, j:j+3, :]
# Reshape to get a list of pixels in the neighborhood
pixels = neighborhood.reshape(-1, channels)
# Calculate the median for each channel
median_pixel = np.median(pixels, axis=0)
# Assign the median value to the output
output_array[i, j] = median_pixel
# Convert the NumPy array back to a PIL Image
return Image.fromarray(output_array.astype(np.uint8))
# --- Usage ---
img = Image.open('my_image.jpg')
# Apply our custom median filter
denoised_img = img.filter(MedianFilter())
denoised_img.save('denoised_image.jpg')
denoised_img.show()
Summary
| Feature | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Predefined Filters (BLUR, SHARPEN, etc.) |
Quick and easy to apply for common effects. | For standard, everyday image manipulation tasks. |
Kernel Class |
Define your own filters using a matrix of weights. | When you need a specific, custom linear filter (e.g., custom blur, edge detection). |
Filter Subclass |
Full control by writing a custom filtering function. | For non-linear filters (median, min/max) or complex, multi-step operations. |
The ImageFilter module is a cornerstone of image processing in Python, providing a flexible and powerful way to manipulate images with just a few lines of code.