Apache HTTP Server Linux 完整教程
Apache HTTP Server(通常简称为 Apache)是世界使用最广泛的 Web 服务器软件,它稳定、功能强大且高度可配置,本教程将以当前主流的 Linux 发行版(如 Ubuntu/Debian 和 CentOS/RHEL) 为例,进行详细讲解。
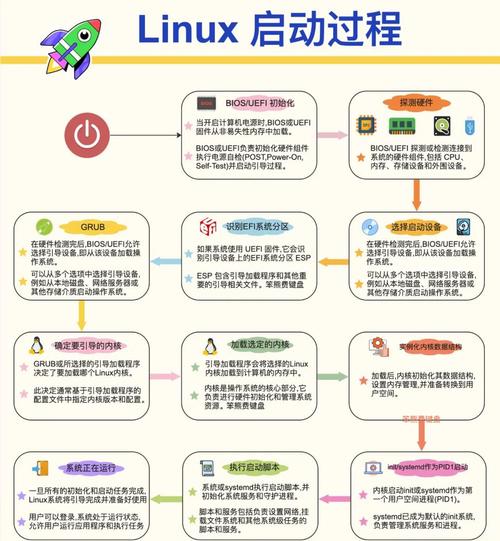
第一部分:安装与启动
1 在 Debian/Ubuntu 系统上安装
-
更新包列表 在安装新软件之前,最好先更新系统的软件包列表。
sudo apt update
-
安装 Apache 使用
apt包管理器安装 Apache。sudo apt install apache2
安装过程中,系统会自动启动 Apache 服务。
-
验证安装
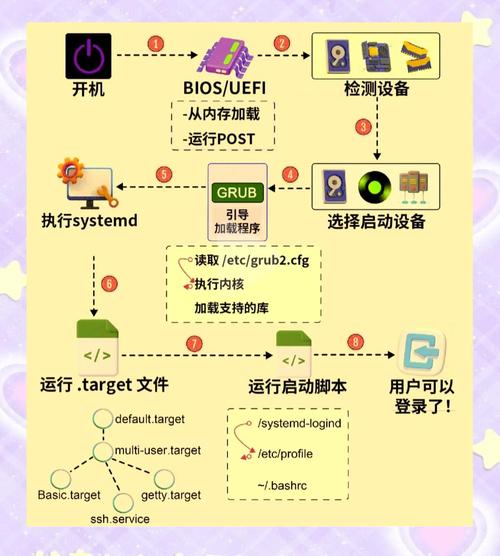 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- 检查服务状态
sudo systemctl status apache2
如果看到绿色的
active (running)字样,说明服务正在运行。 - 通过浏览器访问
打开你的浏览器,访问服务器的 IP 地址或
http://localhost。# 查看你的服务器IP地址 ip addr show
如果看到 "It works!" 页面,恭喜你,Apache 已经成功安装并运行!
- 检查服务状态
2 在 CentOS/RHEL 系统上安装
-
安装 EPEL 仓库(推荐) EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) 提供了更多更新的软件包。
sudo dnf install epel-release
-
安装 Apache 在 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 上,使用
dnf包管理器。 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)sudo dnf install httpd
在 CentOS/RHEL 6 上,使用
yum。sudo yum install httpd
-
启动并设置开机自启 CentOS/RHEL 默认不会在安装后自动启动 Apache。
# 启动 Apache 服务 sudo systemctl start httpd # 设置 Apache 开机自启 sudo systemctl enable httpd
-
验证安装
- 检查服务状态
sudo systemctl status httpd
- 检查防火墙
CentOS/RHEL 默认有防火墙(
firewalld),需要开放 HTTP (80) 和 HTTPS (443) 端口。sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https sudo firewall-cmd --reload
- 通过浏览器访问 和 Ubuntu 一样,在浏览器中输入服务器 IP 地址,应该能看到 "Apache 2 Test Page" 页面。
- 检查服务状态
第二部分:核心配置
Apache 的主要配置文件位于 /etc/apache2/ (Debian/Ubuntu) 或 /etc/httpd/ (CentOS/RHEL) 目录下。
1 目录结构
- 主配置文件:
- Debian/Ubuntu:
/etc/apache2/apache2.conf - CentOS/RHEL:
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- Debian/Ubuntu:
- 站点配置目录: 存放每个网站(虚拟主机)的配置文件。
- Debian/Ubuntu:
/etc/apache2/sites-available/(可用站点) 和/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/(已启用站点),通常通过a2ensite和a2dissite命令来管理。 - CentOS/RHEL:
/etc/httpd/conf.d/,在此目录下的.conf文件会被主配置文件自动加载。
- Debian/Ubuntu:
- 模块目录:
- Debian/Ubuntu:
/etc/apache2/mods-available/和/etc/apache2/mods-enabled/ - CentOS/RHEL:
/etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/
- Debian/Ubuntu:
- 网站根目录: 默认存放网站文件的地方。
- Debian/Ubuntu:
/var/www/html/ - CentOS/RHEL:
/var/www/html/
- Debian/Ubuntu:
2 修改主配置文件
使用 nano 或 vim 等编辑器打开主配置文件:
# Debian/Ubuntu sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf # CentOS/RHEL sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
常用配置项:
ServerTokens Prod: 控制服务器返回给客户端的 HTTP 头信息中包含的 Apache 版本信息。Prod表示只显示Apache,不显示版本号,增加安全性。ServerRoot "/etc/apache2"(或/etc/httpd): Apache 的安装根目录。Listen 80: Apache 监听的端口号,可以修改为其他端口,如Listen 8080。DocumentRoot "/var/www/html": 网站文件的根目录。<Directory />和<Directory "/var/www/html">: 定义对根目录及其子目录的访问权限,确保AllowOverride None或AllowOverride All(如果你需要使用.htaccess文件)。
3 管理服务
-
启动/停止/重启服务
# Debian/Ubuntu sudo systemctl start apache2 sudo systemctl stop apache2 sudo systemctl restart apache2 # 修改配置后常用 # CentOS/RHEL sudo systemctl start httpd sudo systemctl stop httpd sudo systemctl restart httpd
-
重新加载配置
reload命令会优雅地重新加载配置文件,不会中断现有的连接,这是推荐的做法。# Debian/Ubuntu sudo systemctl reload apache2 # CentOS/RHEL sudo systemctl reload httpd
-
查看错误日志 当配置出错时,错误日志是最好的朋友。
# Debian/Ubuntu tail -f /var/log/apache2/error.log # CentOS/RHEL tail -f /var/log/httpd/error_log
第三部分:配置虚拟主机
虚拟主机允许你在一台服务器上托管多个网站,每个网站都有独立的域名和配置。
我们将配置两个网站:example.com 和 test.com。
1 创建网站目录
# 创建网站根目录 sudo mkdir -p /var/www/example.com sudo mkdir -p /var/www/test.com # 创建测试页面 echo "<h1>Welcome to example.com</h1>" | sudo tee /var/www/example.com/index.html echo "<h1>Welcome to test.com</h1>" | sudo tee /var/www/test.com/index.html # 设置正确的所有者 sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/example.com sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/test.com
注意:
www-data是 Debian/Ubuntu 的默认 Apache 用户/组,在 CentOS/RHEL 上,通常是apache,如果不确定,可以用ps aux | grep httpd查看。
2 创建虚拟主机配置文件
Debian/Ubuntu (推荐)
-
在
sites-available目录下创建配置文件。sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/example.com.conf
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com ServerAlias www.example.com DocumentRoot /var/www/example.com <Directory /var/www/example.com> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error_example.com.log CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access_example.com.log combined </VirtualHost> -
启用站点。
sudo a2ensite example.com.conf
-
对
test.com重复以上步骤。 -
禁用默认站点(可选)。
sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf
CentOS/RHEL
-
在
conf.d目录下创建配置文件。sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf ```和上面 Debian/Ubuntu 的例子一样,只是 `${APACHE_LOG_DIR}` 变量在 CentOS/RHEL 中不适用,直接写路径即可: ```apache <VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com ServerAlias www.example.com DocumentRoot /var/www/example.com <Directory /var/www/example.com> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/error_example.com.log CustomLog /var/log/httpd/access_example.com.log combined </VirtualHost> -
conf.d目录下的文件会被自动加载,无需额外命令。
3 配置本地hosts文件进行测试
在你的本地电脑(不是服务器)上,找到 hosts 文件:
- Windows:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts - macOS/Linux:
/etc/hosts
添加以下两行,将域名指向你的服务器 IP:
你的服务器IP地址 example.com
你的服务器IP地址 test.com4 重启 Apache 并测试
# Debian/Ubuntu sudo systemctl restart apache2 # CentOS/RHEL sudo systemctl restart httpd
在你的浏览器中分别访问 http://example.com 和 http://test.com,应该能看到不同的欢迎页面。
第四部分:安全优化
1 基本安全配置
-
隐藏 Apache 版本信息 在主配置文件 (
apache2.conf或httpd.conf) 中添加或修改:ServerTokens Prod ServerSignature Off
-
禁用目录列表 在
<Directory>指令中,确保Options没有Indexes。<Directory /var/www/html> Options -Indexes FollowSymLinks # -Indexes 表示禁用目录列表 AllowOverride None Require all granted </Directory>如果访问一个没有
index.html的目录,会显示 "403 Forbidden" 而不是列出文件,更安全。 -
限制访问IP 如果你只想允许特定IP访问你的网站,可以在虚拟主机配置中添加:
<RequireAll> Require ip 192.168.1.100 # 允许的IP Require all denied # 拒绝所有其他IP </RequireAll>
2 安装 Let's Encrypt 免费 SSL 证书
为了让你的网站支持 HTTPS,推荐使用 Let's Encrypt。
-
安装 Certbot Certbot 是 Let's Encrypt 的官方客户端。
Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-apache
CentOS/RHEL:
sudo dnf install certbot python3-certbot-apache
-
获取并安装证书 Certbot 会自动检测你的 Apache 虚拟主机配置,并引导你完成证书的申请和安装。
sudo certbot --apache
按照提示操作,它会询问你为哪些域名启用 HTTPS,以及是否将 HTTP 流量重定向到 HTTPS。
-
自动续订 Let's Encrypt 证书有效期为90天,Certbot 会自动设置一个定时任务来续订证书,你可以手动测试续订:
sudo certbot renew --dry-run
第五部分:常见问题排查
-
[crit] (13: Permission denied)错误- 原因: Apache 进程没有权限访问你配置的网站目录或文件。
- 解决: 确保网站目录和文件的所有者是 Apache 运行用户(
www-data或apache)。# Debian/Ubuntu sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www # CentOS/RHEL sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www
-
[emerg] AH00558: apache2: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name...警告- 原因: Apache 不知道服务器的完整域名。
- 解决: 在主配置文件中添加
ServerName指令,指向你的服务器域名或 IP。ServerName your_server_ip_or_domain
-
修改配置后不生效
-
检查语法错误:
# Debian/Ubuntu sudo apache2ctl configtest # CentOS/RHEL sudo apachectl configtest
如果提示
Syntax OK,说明语法没问题,如果提示错误,根据提示修改文件。 -
重新加载/重启服务:
sudo systemctl reload apache2 # 或 httpd
如果修改了
Listen端口等核心配置,可能需要restart。
-
本教程涵盖了 Apache 在 Linux 系统上的安装、基本配置、虚拟主机、安全优化和故障排查,从“能跑起来”到“跑得安全、跑得好”,这只是一个开始,Apache 的功能非常强大,建议你阅读其官方文档,并根据你的实际需求进行更深入的探索和实践。