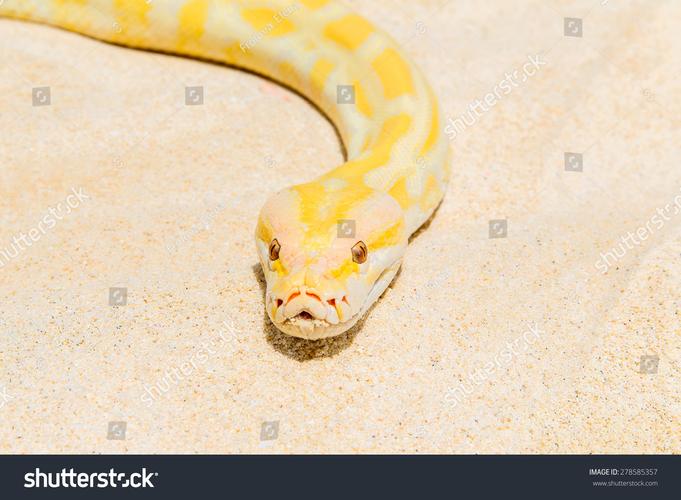
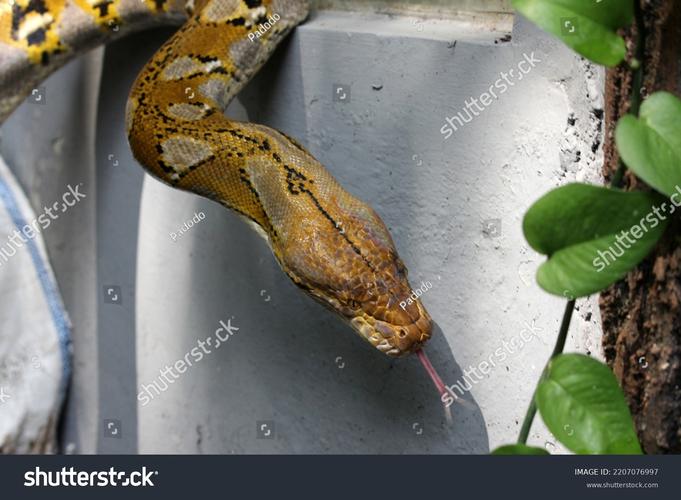
The reticulated python (Malayopython reticulatus) is a snake species found in South and Southeast Asia. It is widely recognized as the longest snake in the world and is among the heaviest.

Here is a comprehensive overview of its characteristics, behavior, and habitat:
Size and Physical Appearance
- Length: The reticulated python holds the record for the longest snake species. While they commonly grow to lengths of 10 to 20 feet (3–6 meters), exceptional specimens can exceed 22 feet (6.7 meters). The longest recorded individual was approximately 25 feet (7.6 meters) long.
- Weight: They are heavy-bodied, with large adults often weighing between 70 to 150 pounds (32–68 kg), though massive individuals can weigh over 200 pounds.
- Appearance: The name "reticulated" refers to the net-like pattern of their skin. They typically have a complex geometric pattern of diamond shapes outlined in black, brown, or yellow against a background of tan or light gray. This coloration provides excellent camouflage in the leaf litter of the rainforest.
Habitat and Distribution
- Range: They have a vast range across Southeast Asia, including countries such as Indonesia, the Philippines, Vietnam, Thailand, Myanmar, and Malaysia.
- Environment: They are highly adaptable and can be found in rainforests, woodlands, and grasslands. However, they are excellent swimmers and are frequently found near bodies of water like rivers, lakes, and swamps. They have even been spotted far out at sea, allowing them to colonize small islands.
Diet and Hunting
- Method: Reticulated pythons are constrictors. They are ambush predators that wait for prey to come close before striking. They seize the prey with their sharp teeth and wrap their powerful coils around it, tightening until the prey suffocates or goes into cardiac arrest.
- Prey: Their diet is varied and depends on their size. Young pythons eat rodents and lizards. Adults can take down much larger animals, including wild boars, deer, monkeys, and even small sun bears.
- Digestion: Like other snakes, they have slow metabolisms. After a large meal, a python may not need to eat again for several weeks or even months.
Behavior and Reproduction
- Temperament: In the wild, they are generally solitary and nocturnal. While they have a reputation for being aggressive, many attacks on humans are the result of the snake feeling threatened or cornered.
- Reproduction: Females lay clutches of 20 to 100 eggs. They exhibit maternal care by wrapping around the eggs to protect them and shivering (rapid muscle contractions) to generate heat and incubate them. The eggs hatch after about 80 to 90 days.
Interaction with Humans
- Danger: Reticulated pythons are one of the few snake species that can pose a genuine threat to adult humans. While attacks are rare, they have been documented, particularly involving handlers or people entering the snake's territory.
- Conservation: They are currently listed as a species of "Least Concern" by the IUCN due to their wide range. However, they are heavily hunted for their skin (used in leather), meat, and for the pet trade.
- Pet Trade: Due to their pattern and size, they are popular in the exotic pet trade. However, they require specialized care, massive enclosures, and experienced handling due to their potential size and strength.