Of course! The Windows Command Prompt (cmd.exe) is a fundamental tool for running Python scripts and managing your Python environment. Here’s a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic checks to advanced usage.
Verifying Your Python Installation
Before you can run Python, you need to make sure it's installed and that Windows knows where to find it.
Step 1: Check if Python is Installed
Open the Command Prompt. You can do this by:
- Pressing the Windows Key, typing
cmd, and pressing Enter. - Pressing Win + R, typing
cmd, and pressing Enter.
Once the black command window is open, type the following command and press Enter:
python --version
or the more modern py command (which is recommended as it's version-agnostic):
py --version
Possible Outcomes:
- ✅ Success: You'll see a version number, like
Python 3.11.4.If this works, skip to the next section.
- ❌ Error
'python' is not recognized...or'py' is not recognized...: This means Python is either not installed or its location is not in your system's PATH.
Step 2: Add Python to Your PATH (If Needed)
The "PATH" is an environment variable that tells Windows where to look for executable files.
How to Fix It:

-
Install/Re-install Python correctly: The easiest way is to download the latest Python from python.org. During installation, make sure to check the box that says:
Add Python to PATH
-
If Python is already installed: You'll need to manually add it.
- Find your Python installation path. It's usually something like
C:\Users\YourUsername\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311orC:\Python311. - Open the Start Menu, type "Environment Variables", and select "Edit the system environment variables".
- In the System Properties window, click the "Environment Variables..." button.
- In the "System variables" section (the bottom half), find and select the
Pathvariable, then click "Edit...". - Click "New" and paste your Python installation path (e.g.,
C:\Python311). - Also, click "New" and paste the path to your Python
Scriptsfolder (e.g.,C:\Python311\Scripts). This is crucial for tools likepip. - Click OK on all windows to save.
- Close and re-open your Command Prompt for the changes to take effect.
- Find your Python installation path. It's usually something like
Running Python Code
There are two main ways to run Python code from the command prompt.
Method 1: Interactive Mode (The REPL)
This is great for quick tests, experimenting, and learning. You type a command, and Python executes it immediately.
-
Open
cmd. -
Type
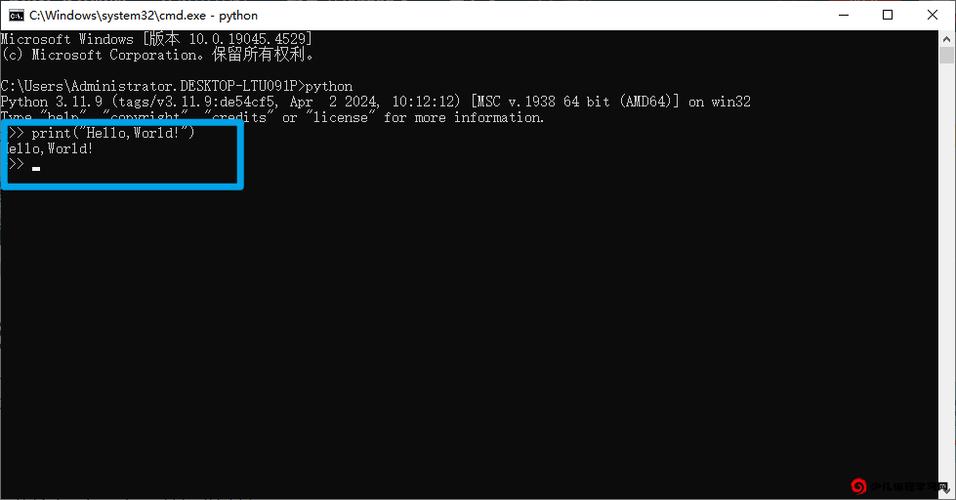
pythonorpyand press Enter. You'll see the Python>>>prompt.C:\Users\YourName> py Python 3.11.4 (main, Jun 7 2025, 12:45:35) [MSC v.1934 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>>
-
Now you can type Python code directly.
>>> print("Hello from Python!") Hello from Python! >>> 2 + 2 4 >>> my_name = "Alice" >>> print(f"Hello, {my_name}!") Hello, Alice! -
To exit the interactive mode, type
exit()or pressCtrl + Zfollowed by Enter.
Method 2: Running a Script File (Most Common)
This is how you run your actual Python programs (.py files).
-
Create a Python file:
-
Open a text editor (like Notepad, VS Code, or Sublime Text).
-
Type some code:
# hello.py import time import sys print("Hello, World!") print("Script name:", sys.argv[0]) for i in range(5): print(f"Counting: {i}") time.sleep(1) print("Done!") -
Save the file as
hello.pyon your Desktop for easy access.
-
-
Navigate to the file's location in
cmd:- In your Command Prompt, you need to go to the directory where you saved the file. Use the
cd(change directory) command. - If you saved it on your Desktop, your command might look like this (replace
YourUsernamewith your actual username):cd C:\Users\YourUsername\Desktop
- Pro Tip: You can type
dirand press Enter to list the files in the current directory. You should seehello.pyin the list to confirm you are in the right place.
- In your Command Prompt, you need to go to the directory where you saved the file. Use the
-
Run the script:
- Now, type
pythonorpy, followed by the name of your file, and press Enter.C:\Users\YourUsername\Desktop> python hello.py
- Output:
Hello, World! Script name: hello.py Counting: 0 Counting: 1 Counting: 2 Counting: 3 Counting: 4 Done!
- Now, type
Essential pip Commands (Installing Packages)
pip is Python's package installer. You'll use it all the time. The py command is often better than python here to avoid version conflicts.
-
Install a package:
# Install the 'requests' library py -m pip install requests
-
Upgrade a package:
# Upgrade 'pip' itself py -m pip install --upgrade pip
-
Uninstall a package:
py -m pip uninstall requests
-
List installed packages:
py -m pip list
-
Show information about a package:
py -m pip show requests
Useful Command Prompt Tips for Python
- Clear the Screen: If your terminal is getting messy, type
clsand press Enter to clear it. - Auto-completion: Press the Tab key to auto-complete file or directory names. For example, if you type
py hello.pyand then pressTab, it might complete topython hello.py. - Get Help: Type
py --helporpython --helpto see a list of command-line options for the Python interpreter. For example, you can usepython -c "print('hello')"to run a single line of code from the command line without a script file.
Modern Alternative: PowerShell
Windows also comes with PowerShell, which is more powerful and modern than the traditional cmd. Most Python commands work identically, but there are a few differences in syntax.
- How to open: Search for "PowerShell" in the Start Menu.
- Basic Commands:
- Get current location:
Get-Location(alias:pwd) - List items:
Get-ChildItem(alias:ls) - Change directory:
Set-Location -Path "C:\Path\To\Dir"(alias:cd) - Run Python:
python .\hello.pyorpy .\hello.py(the.\is good practice in PowerShell).
- Get current location:
For most day-to-day Python work, cmd is perfectly fine, but knowing PowerShell is a valuable skill.