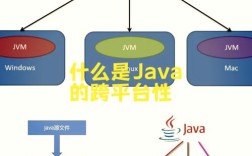
Of course! Thinking of Java often brings to mind a blend of history, enterprise power, and modern evolution. It's a language that has fundamentally shaped the software world.

Let's break down what makes Java so special, from its core philosophy to its current state.
The "Java-ness": Core Principles
What does it feel like to write Java? It's defined by a few key tenets:
- "Write Once, Run Anywhere" (WORA): This is the original promise. Java code is compiled into an intermediate format called bytecode, which runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). As long as a device has a JVM, it can run your Java application. This decouples your code from the underlying operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Strongly Typed and Statically Typed: You must declare the type of every variable (e.g.,
String name,int count). The compiler checks these types before you even run the code, catching many errors early. This leads to more robust and predictable applications. - Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): Java is fundamentally built around classes and objects. It encourages you to model your problem domain as a collection of interacting objects, which promotes organization, reusability, and scalability.
- Rich Standard Library: Java comes with a massive, well-documented standard library called the Java Class Library (JCL). Need to handle networking, data structures, file I/O, or concurrency? It's all there, ready to use.
- Automatic Memory Management (Garbage Collection): You don't have to manually allocate and deallocate memory like in C or C++. The JVM's Garbage Collector (GC) automatically reclaims memory that is no longer in use, dramatically reducing the chance of memory leaks and making development safer and faster.
The Pillars of Java's Ecosystem
When people think of Java, they're often thinking of its vast ecosystem.
The JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
The JVM is Java's magic. It's not just an interpreter; it's a highly optimized piece of technology that performs:
- Loading: It loads the compiled bytecode.
- Verifying: It ensures the code is safe and doesn't violate security constraints.
- Executing: It translates the bytecode into native machine code for the host processor.
- Optimizing: Modern JVMs use Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation to analyze running code and optimize "hot" paths for maximum performance.
This is why Java is incredibly fast. It trades a bit of startup time for sustained, high performance.
The Frameworks (Where Java truly shines)
Raw Java is the foundation, but its power is unlocked by frameworks.
- Spring Framework: This is the undisputed king of the Java world. Spring makes it incredibly easy to build complex, production-ready applications. Its flagship project, Spring Boot, has revolutionized Java development by embracing "convention over configuration," allowing developers to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based applications with minimal fuss.
- Jakarta EE (formerly Java EE): The standard for building large-scale, enterprise-grade applications. It provides specifications for APIs like servlets (for web servers), JPA (for database interaction), and more. Spring is often seen as a more modern and flexible alternative, but Jakarta EE is still a vital part of the enterprise landscape.
- Other Notable Frameworks:
- Quarkus / Micronaut: Modern, "from-the-ground-up" frameworks designed for cloud-native, serverless, and containerized environments. They aim for extremely fast startup times and low memory footprint.
- Apache Spark: The dominant framework for big data processing and analytics.
A Brief History: The Journey of a Giant
- 1995 (Birth): Created by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems. Its goal was to be a simple, platform-independent language for "smart" consumer electronics. It found its true calling on the web with applets.
- Late 90s/Early 2000s (Rise): The enterprise boom. Java's robustness, scalability, and security made it the default choice for large backend systems, banking, and e-commerce. The slogan "Java everywhere" became a reality.
- 2007 (Open Source): Sun open-sourced Java under the GPL license. This was a massive step that fostered community collaboration and cemented its place in the open-source world.
- 2025 (The Reboot - Project Jigsaw): Java 9 introduced modules. This was a huge change aimed at making the massive Java platform more scalable, secure, and maintainable, especially for modern microservices architectures.
- The Present (Constant Evolution): Oracle now releases a new Java version every 6 months. This rapid iteration brings new features, performance improvements, and language enhancements (like records, sealed classes, and pattern matching for
instanceof) to keep Java modern and competitive.
Where is Java Used Today? (Almost Everywhere!)
- Enterprise Backend Systems: The bedrock of large corporations for transaction processing, CRM, and ERP systems.
- Big Data: Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, and Elasticsearch are all written in or have major Java components.
- Android Development: While Google is pushing Kotlin, Java is still a supported and widely used language for Android app development.
- Web Applications: Millions of websites and web services run on Java-based backends, often powered by Spring or Jakarta EE.
- Scientific Computing: High-performance numerical libraries and simulations often use Java.
- The Cloud: Java's performance and robustness make it a natural fit for cloud-native applications and microservices.
Pros and Cons: The Trade-offs
| Pros ✅ | Cons ❌ |
|---|---|
| Platform Independent (WORA) | Verbose: Can require more boilerplate code than languages like Python or Kotlin. |
| Massive Ecosystem & Community | Slower Startup: Can be slower to start than native or compiled languages. |
| Excellent Performance & Scalability | High Memory Consumption: The JVM itself requires significant memory. |
| Robust & Mature (Battle-Tested) | Verbose Syntax: Can feel overly complex compared to modern JVM languages. |
| Strong Type Safety & Tooling | Verbose Syntax: Can feel overly complex compared to modern JVM languages. |
The Modern Contender: Kotlin
It's impossible to think about modern Java without thinking about Kotlin.
- Officially Supported by Google for Android development.
- Runs on the JVM: It's 100% interoperable with Java. You can call Java code from Kotlin and vice-versa.
- More Concise & Safer: It reduces boilerplate code and introduces powerful features like null safety, making many common bugs impossible to compile.
- The Future? Many new projects, especially on the JVM, are choosing Kotlin as their primary language. It's often seen as a more modern, pragmatic evolution of Java.
Conclusion
Thinking of Java is thinking of a reliable, powerful, and evergreen giant. It's not the newest or trendiest language, but its incredible ecosystem, performance, and continuous evolution ensure its relevance for decades to come. It's the steady, dependable engine that powers a significant portion of our digital world, from your bank's app to the services that process petabytes of data.