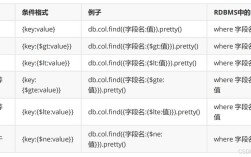
下面我将为你详细介绍几种主流的读取 Properties 文件的方法,从最传统到最现代,并附上完整的代码示例。
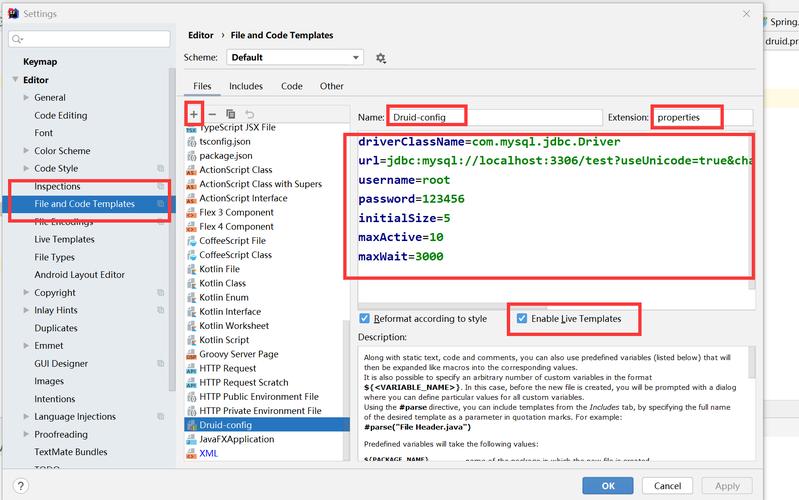
使用 java.util.Properties 类(最传统、最基础)
这是最经典、最直接的方法,适用于所有 Java 版本,核心思想是使用 InputStream 读取文件,然后加载到 Properties 对象中。
核心步骤:
- 获取文件输入流 (
InputStream):- 使用
ClassLoader:这是最推荐的方式,因为它会从 classpath(类路径)下查找文件,无论是从 JAR 包运行还是从 IDE 运行都适用。 - 使用
FileInputStream:直接从文件系统读取路径,灵活性较低,且需要处理绝对/相对路径问题。
- 使用
- 加载文件内容:调用
properties.load(inputStream)方法。 - 关闭流:使用
try-with-resources语句确保InputStream被正确关闭,防止资源泄漏。 - 获取属性值:使用
properties.getProperty("key")方法。
示例代码
假设你的项目结构如下:
my-project/
├── src/
│ └── main/
│ ├── java/
│ │ └── com/
│ │ └── example/
│ │ └── Main.java
│ └── resources/
│ └── config.propertiesconfig.properties 文件内容:
# Database Configuration db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb db.username=root db.password=secret db.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver # Application Settings app.name=My Cool App app.version=1.0.0
Main.java 代码:
package com.example;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建 Properties 对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// try-with-resources 确保 InputStream 被自动关闭
// 使用 ClassLoader 从 classpath 下加载文件
try (InputStream input = PropertiesReader.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config.properties")) {
if (input == null) {
System.out.println("Sorry, unable to find config.properties");
return;
}
// 2. 加载 properties 文件内容
properties.load(input);
// 3. 获取并打印属性值
System.out.println("Database URL: " + properties.getProperty("db.url"));
System.out.println("Database User: " + properties.getProperty("db.username"));
System.out.println("Database Password: " + properties.getProperty("db.password"));
System.out.println("App Name: " + properties.getProperty("app.name"));
System.out.println("App Version: " + properties.getProperty("app.version"));
// 如果属性不存在,可以提供默认值
System.out.println("Debug Mode: " + properties.getProperty("debug.mode", "false"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
关键点说明:
PropertiesReader.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config.properties"):这行代码会去src/main/resources目录下寻找config.properties文件。- 编码问题:默认情况下,
Properties.load(InputStream)使用 ISO-8859-1 编码读取,如果你的.properties文件包含中文等非 ASCII 字符,可能会乱码,解决方法是指定编码:// 使用 InputStreamReader 指定 UTF-8 编码 try (InputStream input = ...; Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(input, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) { properties.load(reader); }
使用 java.util.ResourceBundle 类(国际化场景)
ResourceBundle 是专门为国际化(i18n)设计的类,它不直接读取文件,而是根据不同的 Locale(语言环境)来加载对应的资源文件,对于简单的配置读取,它也是一个不错的选择。
文件命名规则:
- 基础文件名:
messages(可以自定义) - 语言和国家代码:
messages_en_US.properties,messages_zh_CN.properties - 默认文件:
messages.properties(当没有匹配的 Locale 时使用)
示例代码
假设资源文件名为 messages.properties,放在 src/main/resources 下。
messages.properties 文件内容:
greeting=Hello farewell=Goodbye
Main.java 代码:
package com.example;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class ResourceBundleReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 获取默认的 ResourceBundle (会加载 messages.properties)
ResourceBundle defaultBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages");
System.out.println("Default Greeting: " + defaultBundle.getString("greeting"));
// 2. 获取指定 Locale 的 ResourceBundle (美国英语)
// 假设存在 messages_en_US.properties
ResourceBundle usBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages", Locale.US);
System.out.println("US Greeting: " + usBundle.getString("greeting"));
// 3. 获取另一个 Locale 的 ResourceBundle (简体中文)
// 假设存在 messages_zh_CN.properties
ResourceBundle cnBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages", Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE);
// System.out.println("CN Greeting: " + cnBundle.getString("greeting")); // 如果文件不存在,会抛出 MissingResourceException
// 4. 获取父 Bundle (当指定 Locale 的文件不存在时)
// 如果 messages_zh.properties 不存在,会回退到 messages.properties
ResourceBundle fallbackBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages", new Locale("zh"));
System.out.println("Fallback Greeting: " + fallbackBundle.getString("greeting"));
}
}
优点:
- 天然支持国际化。
- 性能更好,
ResourceBundle会被缓存。
缺点:
- 文件名有固定格式,不够灵活。
- 不支持动态修改,因为内容是缓存的。
使用 Spring Framework 的 @Value 注解(在 Spring/Spring Boot 项目中)
如果你正在使用 Spring 或 Spring Boot 框架,这是最方便、最优雅的方式,它允许你直接将配置文件的值注入到字段中。
在 Spring Boot 中:
Spring Boot 默认会加载 application.properties 或 application.yml 文件,你可以在任何被 Spring 管理的 Bean(即带有 @Component, @Service, @Controller 等注解的类)中使用。
application.properties 文件内容:
app.name=Spring Boot App app.version=2.7.0
MyService.java 代码:
package com.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyService {
@Value("${app.name}")
private String appName;
@Value("${app.version}")
private String appVersion;
public void printAppInfo() {
System.out.println("App Name from @Value: " + appName);
System.out.println("App Version from @Value: " + appVersion);
}
}
MainApplication.java (启动类):
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
MyService myService = context.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.printAppInfo();
}
}
在传统 Spring 项目中:
你需要配置一个 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 来指定你的 properties 文件位置。
<!-- 在 XML 配置文件中 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:config.properties"/>
</bean>
<bean id="myService" class="com.example.MyService"/>
总结与对比
| 方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
java.util.Properties |
标准Java库,不依赖框架。 灵活,可读取任意路径的文件。 可动态修改和重新加载。 |
需要手动管理资源流(尽管 try-with-resources 很方便)。处理编码问题稍显麻烦。 |
纯Java项目(非Spring)。 需要动态加载配置。 作为基础工具类使用。 |
java.util.ResourceBundle |
性能好,内容被缓存。 天然为国际化设计 |