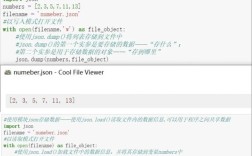
Of course! This is a very common and important issue to understand when working with Excel in Python.
The number 65,535 (or more precisely, 65,536) is not a random limitation. It's a hard, historical limit from older versions of Excel.
The Root Cause: Excel's Legacy Row Limit
- Excel 97-2003 (
.xlsfiles): These older spreadsheet files had a fundamental limitation of 65,536 rows (from row 1 to row 65,536) and 256 columns (from A to IV). - Why 65,536? This limit comes from the 16-bit integer format used by the legacy BIFF (Binary Interchange File Format) that these
.xlsfiles use. A 16-bit unsigned integer can hold a maximum value of 65,535 ($2^{16} - 1$). This was the index for the last row.
When you try to write more than 65,536 rows of data to an .xls file using a Python library like pandas or openpyxl, it will often fail, truncate your data, or behave unexpectedly.
The Modern Solution: Excel 2007 and Later (.xlsx)
Microsoft introduced a new file format with Excel 2007: Office Open XML, which uses the .xlsx extension.
This new format solved the old limitations:
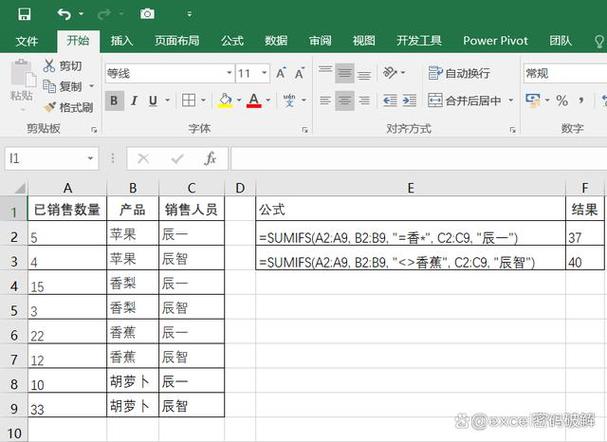
- Row Limit: 1,048,576 rows (that's over 1 million!)
- Column Limit: 16,384 columns (from A to XFD).
The .xlsx format is now the standard, and it's what you should almost always be using.
How This Affects You in Python (and How to Fix It)
The problem you encounter depends on which library you are using to write the Excel file.
Scenario 1: Using pandas (Most Common)
The pandas library is excellent for data analysis and can export DataFrames directly to Excel. The default engine it uses can sometimes cause issues.
Problem Code (that might fail or truncate):
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Create a DataFrame with more than 65,536 rows
# This will have 100,000 rows
data = {'ID': range(100000), 'Value': np.random.rand(100000)}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Try to save to an old .xls format - THIS WILL LIKELY FAIL OR TRUNCATE
try:
df.to_excel('large_data.xls', index=False)
print("Saved to large_data.xls (this might be incomplete!)")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error saving to .xls: {e}")
# Try to save to the modern .xlsx format - THIS WILL WORK
df.to_excel('large_data.xlsx', index=False)
print("Successfully saved to large_data.xlsx")
The Fix:
- Use the
.xlsxextension. As shown above, this is the primary and most important fix. - Explicitly specify the engine. For
.xlsxfiles,pandasuses theopenpyxlengine. Being explicit is good practice.
# The recommended way to do it
df.to_excel('large_data_recommended.xlsx',
index=False,
engine='openpyxl')
Scenario 2: Using openpyxl (Low-Level Control)
openpyxl is a powerful library for reading and writing .xlsx files. It is designed to handle the modern .xlsx format and its large row/column limits.
Problem Code:
You might not get a direct error, but if you were somehow trying to save in an old format, you'd run into issues. openpyxl primarily works with .xlsx.
from openpyxl import Workbook
import numpy as np
# Create a workbook and worksheet
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
# Add headers
ws.append(['ID', 'Value'])
# Add more than 65,536 rows of data
# This will work perfectly fine with .xlsx
for i in range(100000):
ws.append([i, np.random.rand()])
# Save the file. The .xlsx extension is key.
wb.save('large_data_openpyxl.xlsx')
print("Successfully saved 100,000 rows using openpyxl.")
The Fix:
The fix is simply to ensure you are saving with the .xlsx extension, which openpyxl is built for. There is no row limit you'll likely hit in normal use.
Summary and Best Practices
| File Format | Row Limit | Column Limit | When to Use in Python | How to Handle in Python |
|---|---|---|---|---|
.xls |
65,536 | 256 | Almost never. Only for compatibility with very old software (pre-2007). | Avoid if possible. If you must, be aware of the limit. Libraries might fail or truncate data. |
.xlsx |
1,048,576 | 16,384 | The standard. Use this for all modern work. | This is your default choice. Use pandas with engine='openpyxl' or the openpyxl library directly. |
Key Takeaways
- The 65,535 limit is real but outdated. It applies only to the old
.xlsfile format from Excel 97-2003. - The modern
.xlsxformat has a limit of over 1 million rows, which is sufficient for almost all use cases. - Always use the
.xlsxextension when saving files from Python to avoid hitting the old row limit. - If using
pandas, it's good practice to explicitly specify the engine:df.to_excel('file.xlsx', engine='openpyxl').