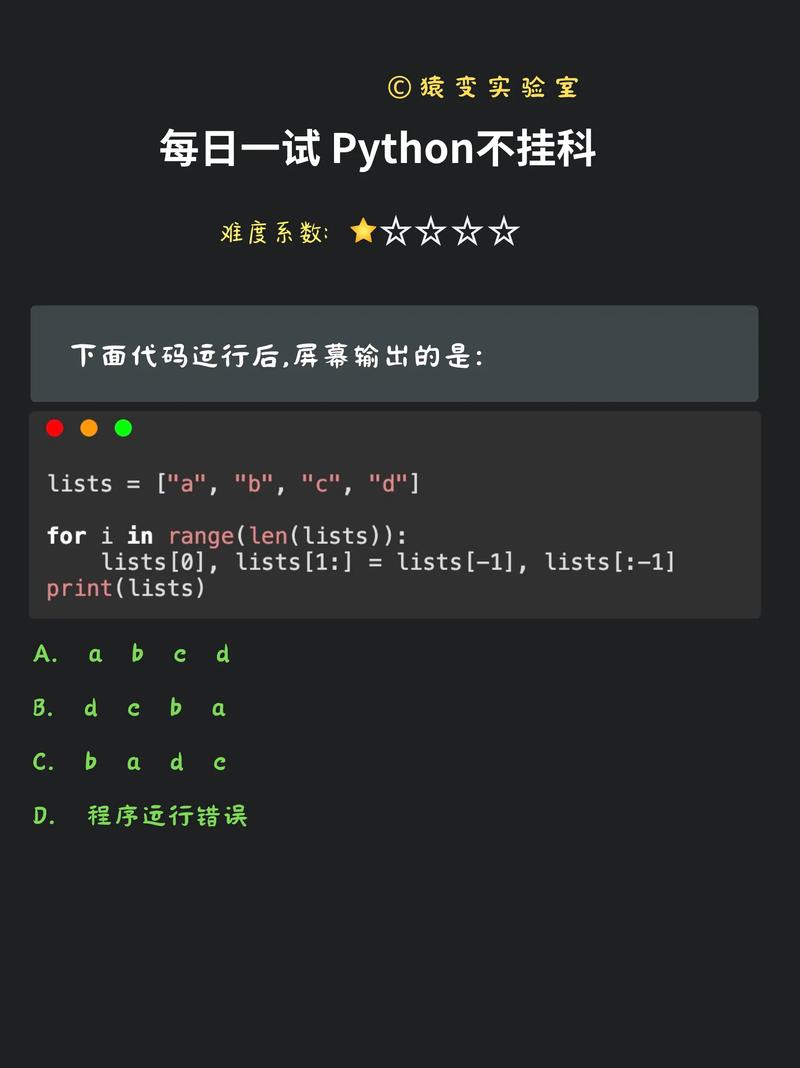
Of course! The EnumWindows function is a fundamental WinAPI (Windows API) function used to iterate through all top-level windows on the system. In Python, you access this function through the pywin32 library.

Here's a complete guide on how to use EnumWindows in Python, from basic usage to advanced examples.
Prerequisites: Install pywin32
First, you need to install the pywin32 library. Open your command prompt or terminal and run:
pip install pywin32
Basic Usage: Enumerating All Windows
The core idea is to provide a callback function that EnumWindows will call for every top-level window it finds.
The Code
import win32gui
import win32con
def enum_windows_callback(hwnd, extra):
"""
This function is called by EnumWindows for each top-level window.
Args:
hwnd (int): The handle (window ID) of the current window.
extra: Any extra data you passed to EnumWindows (we'll use None).
"""
# Get the window's title (text)
window_title = win32gui.GetWindowText(hwnd)
# Get the window's class name
class_name = win32gui.GetClassName(hwnd)
# Only print windows that have a title (ignore unnamed windows)
if window_title:
print(f"Window Handle: {hwnd}, Title: '{window_title}', Class: '{class_name}'")
# --- Main execution ---
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Enumerating all top-level windows...")
# Enumerate all top-level windows.
# The second argument (None) is extra data to pass to the callback.
win32gui.EnumWindows(enum_windows_callback, None)
print("\nEnumeration complete.")
How It Works:
import win32gui: This imports the necessary module frompywin32for GUI-related functions.enum_windows_callback(hwnd, extra): This is our callback function.hwnd: A unique integer representing the window's handle. This is the most important piece of information, as it's the key to getting more details about the window or interacting with it.extra: A parameter that allows you to pass your own data into the callback. We're not using it here, so we passNone.
win32gui.GetWindowText(hwnd): Retrieves the text in the title bar of the window.win32gui.GetClassName(hwnd): Retrieves the registered class name of the window. This is useful for identifying the type of application (e.g., "Notepad", "Chrome_WidgetWin_1").win32gui.EnumWindows(enum_windows_callback, None): This is the function that starts the enumeration.- It calls the
enum_windows_callbackfunction for every top-level window. - It passes the window's
hwndand theextradata (None) to each call.
- It calls the
Advanced Example: Finding a Specific Window
A very common use case is to find a specific window (e.g., "Calculator") and get its handle. You can do this by modifying the callback to stop the enumeration once the window is found.
The Code
import win32gui
import win32con
# This list will store the handle of the found window
found_windows = []
def find_calculator_callback(hwnd, extra):
"""Callback to find windows with 'Calculator' in the title."""
window_title = win32gui.GetWindowText(hwnd)
# Check if the window title contains "Calculator"
if "Calculator" in window_title:
print(f"Found Calculator: Handle={hwnd}, Title='{window_title}'")
found_windows.append(hwnd) # Store the handle
# --- Main execution ---
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Searching for the Calculator window...")
# Enumerate all windows
win32gui.EnumWindows(find_calculator_callback, None)
if found_windows:
# Get the first handle found (in case there are multiple)
calculator_hwnd = found_windows[0]
print(f"\nSuccessfully found Calculator with handle: {calculator_hwnd}")
# You can now use this handle to get more info or control the window
# For example, let's get its position and size
rect = win32gui.GetWindowRect(calculator_hwnd)
print(f"Window Position and Size (left, top, right, bottom): {rect}")
print(f"Size: {rect[2] - rect[0]} x {rect[3] - rect[1]} pixels")
else:
print("\nCalculator window not found.")
Key Improvements:
found_windows = []: A list to store the handles of any matching windows.if "Calculator" in window_title:: The condition to check for our target window.found_windows.append(hwnd): If the window matches, we add its handle to our list.win32gui.GetWindowRect(hwnd): A powerful function that gets the bounding rectangle of the window. This gives you the screen coordinates of the top-left and bottom-right corners, from which you can calculate the position and size.
Making a Window Visible and Bringing it to the Front
Once you have a window's handle (hwnd), you can perform actions on it. A common task is to restore a minimized window and bring it to the foreground.
The Code
import win32gui
import win32con
import time
def bring_to_front_callback(hwnd, extra):
"""Callback to find Notepad and bring it to the front."""
window_title = win32gui.GetWindowText(hwnd)
if "Notepad" in window_title:
print(f"Found Notepad: Handle={hwnd}")
# 1. Check if the window is minimized
if win32gui.IsIconic(hwnd):
print(" - Window is minimized. Restoring...")
# SW_RESTORE: Activates and displays the window. If minimized or maximized,
# the system restores it to its original size and position.
win32gui.ShowWindow(hwnd, win32con.SW_RESTORE)
# Wait a moment for the window to be restored
time.sleep(0.5)
# 2. Bring the window to the foreground
print(" - Bringing window to the foreground...")
# SW_SHOW: Activates the window and displays it in its current size and position.
# This will also bring it to the front.
win32gui.ShowWindow(hwnd, win32con.SW_SHOW)
# SetForegroundWindow can sometimes be blocked by other applications.
# It's good practice to try it.
try:
win32gui.SetForegroundWindow(hwnd)
except Exception as e:
print(f" - Could not bring to foreground (might be blocked): {e}")
# Return False to stop enumerating, since we found our window
return False
# --- Main execution ---
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Searching for Notepad to bring it to the front...")
win32gui.EnumWindows(bring_to_front_callback, None)
print("Operation finished.")
Key New Functions:
win32gui.IsIconic(hwnd): ReturnsTrueif the window is minimized (iconic).win32gui.ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow): This is a versatile function for changing a window's state.win32con.SW_RESTORE: Restores a minimized or maximized window to its normal state.win32con.SW_SHOW: Activates the window and displays it.win32con.SW_MINIMIZE: Minimizes the window.win32con.SW_MAXIMIZE: Maximizes the window.
win32gui.SetForegroundWindow(hwnd): Attempts to bring the specified window to the foreground and activate it. Note that the system can restrict this behavior to prevent applications from stealing focus unexpectedly.return False: The callback function can returnFalseto signalEnumWindowsto stop enumerating further windows. This is a great optimization if you only need to find the first match.
Summary of Useful win32gui Functions
| Function | Purpose |
|---|---|
EnumWindows(callback, extra) |
Iterates through all top-level windows. |
GetWindowText(hwnd) |
Gets the window's title bar text. |
GetClassName(hwnd) |
Gets the window's registered class name. |
GetWindowRect(hwnd) |
Gets the window's position and size (bounding rectangle). |
IsIconic(hwnd) |
Checks if the window is minimized. |
IsWindowVisible(hwnd) |
Checks if the window is visible. |
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow) |
Shows, hides, minimizes, maximizes, or restores a window. |
SetForegroundWindow(hwnd) |
Brings the window to the foreground. |
GetParent(hwnd) |
Gets the handle of the window's parent. |
GetWindowThreadProcessId(hwnd) |
Gets the process and thread IDs of the window. |