Of course! Here is a comprehensive reference guide to Python's standard library, broken down into categories for easy navigation. This guide covers the most commonly used and powerful modules you'll encounter in Python development.
What is the Python Standard Library?
The Python Standard Library is a collection of modules and packages that are included with every Python installation. You don't need to download or install them separately using pip. They provide "batteries-included" functionality for common programming tasks, from data structures and algorithms to web services and system administration.
To use a module, you must first import it:
import math
import datetime
import json
Core & Built-in Functions
These are fundamental to the language and don't require an explicit import statement (though some are in the builtins module).
| Module/Function |
Description |
Example |
print() |
Outputs text or other data to the console. |
print("Hello, World!") |
len() |
Returns the number of items in an object. |
len([1, 2, 3]) |
type() |
Returns the type of an object. |
type(123) |
isinstance() |
Checks if an object is an instance of a class. |
isinstance("hello", str) |
open() |
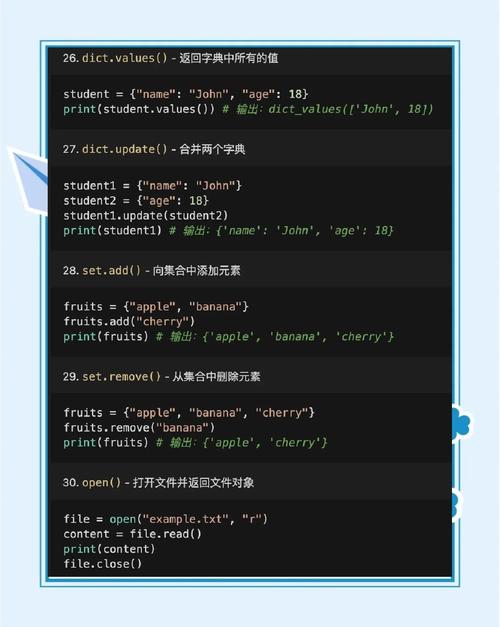
Opens a file and returns a file object. |
with open("file.txt", "r") as f: |
range() |
Generates a sequence of numbers. |
for i in range(5): |
enumerate() |
Returns an enumerate object (index and value). |
for i, item in enumerate(my_list): |
zip() |
Combines two or more iterables element-wise. |
list(zip([1, 2], ['a', 'b'])) |
input() |
Reads a line from standard input. |
name = input("Enter your name: ") |
Data Structures & Algorithms
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
collections |
High-performance container datatypes. |
Counter, defaultdict, deque, namedtuple, OrderedDict, ChainMap |
itertools |
Functions for creating iterators for efficient looping. |
cycle, chain, permutations, combinations, groupby, islice |
array |
Efficient arrays of numeric types. |
A more memory-efficient version of a list for homogeneous data. |
heapq |
Implementation of the heap queue algorithm. |
heappush, heappop, heapify. Useful for priority queues. |
bisect |
Maintains lists in sorted order. |
bisect_left, bisect_right, insort. Fast for searching sorted lists. |
Data Persistence & Serialization
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
json |
JSON encoder and decoder. |
json.dumps(), json.loads(). Standard for web APIs. |
pickle |
Python object serialization. |
pickle.dump(), pickle.load(). Warning: Not secure! Do not use with untrusted data. |
shelve |
Persistent object storage using a dictionary-like interface. |
Simple way to save Python objects to a file. |
csv |
Reading and writing CSV files. |
csv.reader, csv.writer. Handles parsing and formatting. |
sqlite3 |
DB-API 2.0 interface for SQLite databases. |
Built-in SQL database engine. |
Text Processing
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
re |
Regular expression operations. |
re.search(), re.findall(), re.sub(). Essential for pattern matching. |
string |
Common string operations. |
string.punctuation, string.digits, string.ascii_letters. |
difflib |
Helpers for computing deltas. |
difflib.SequenceMatcher. Useful for comparing sequences of lines. |
unicodedata |
Access to the Unicode Character Database. |
unicodedata.name(), unicodedata.category(). |
stringprep |
RFC 3454 StringPrep profile implementation. |
Used for preparing internationalized domain names (IDNA). |
Binary Data
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
struct |
Packing and unpacking binary data. |
struct.pack(), struct.unpack(). For converting between Python values and C structs. |
codecs |
Register and access the standard codecs. |
codecs.open(). Opens files with specific encodings (e.g., UTF-8). |
Numeric & Mathematical
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
math |
Mathematical functions. |
math.sqrt(), math.factorial(), math.pi, math.sin(). |
statistics |
Mathematical statistics functions. |
mean(), median(), stdev(), variance(). |
random |
Generating pseudo-random numbers. |
random.randint(), random.choice(), random.shuffle(), random.random(). |
decimal |
Decimal fixed-point and floating-point arithmetic. |
High precision for financial and scientific calculations. |
fractions |
Rational number arithmetic. |
Fraction class for working with fractions. |
Functional Programming
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
functools |
Higher-order functions and operations on callable objects. |
functools.lru_cache (caching), functools.partial (partial function application), functools.reduce. |
operator |
Functions corresponding to intrinsic operators. |
operator.add, operator.itemgetter, operator.attrgetter. Useful for functional-style programming. |
File System & Directories
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
os |
Miscellaneous operating system interfaces. |
os.listdir(), os.path.join(), os.getcwd(), os.mkdir(), os.environ. |
shutil |
High-level file operations. |
shutil.copy(), shutil.move(), shutil.rmtree() (recursively delete a directory). |
glob |
Unix style pathname pattern expansion. |
glob.glob("*.txt") to find all files ending in .txt. |
tempfile |
Generate temporary files and directories. |
tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(). |
Operating System Interaction
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
sys |
System-specific parameters and functions. |
sys.argv (command-line arguments), sys.path (module search path), sys.exit(). |
subprocess |
Spawn new processes, connect to their I/O, and get their return codes. |
subprocess.run(). The modern, recommended way to run external commands. |
argparse |
Command-line option, argument, and sub-command parser. |
The standard way to create powerful command-line interfaces for your scripts. |
Internet Protocols & Support
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
urllib |
URL handling modules. |
urllib.request (opening URLs), urllib.parse (parsing URLs). |
http.client |
Low-level HTTP client. |
For making HTTP requests. |
requests (not standard lib) |
Highly recommended third-party library. |
Simpler, more elegant API for HTTP requests. (pip install requests) |
smtplib |
SMTP protocol client. |
For sending emails. |
email |
Package for managing email messages. |
For parsing and constructing email messages. |
socket |
Low-level networking interface. |
The fundamental building block for all network programming. |
ssl |
TLS/SSL wrapper for socket objects. |
For secure (HTTPS) connections. |
Multithreading & Concurrency
| Module |
Description |
Key Features |
threading |
High-level interface for working with multiple threads. |
Thread class, Lock, Event. |
multiprocessing |
Process-based parallelism. |
Process class. Bypasses the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) for CPU-bound tasks. |
asyncio |
Asynchronous I/O. |
async/await syntax. For writing concurrent code using a single thread and an event loop. |
concurrent.futures |
High-level interface for asynchronously executing call |