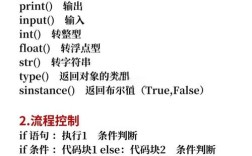
Of course! In Python, you use the print() function to display output.

To print the word "orange", you put the word inside the parentheses, enclosed in either single () or double () quotes.
The Basic Code
Here is the simplest way to do it:
print("orange")
Output:
orangeExplanation
print(): This is Python's built-in function that outputs text or other data to the console.- or These are called quotation marks. They tell Python that the text inside is a string** (a sequence of characters). You can use either single or double quotes, as long as they match at the beginning and end of the string.
# Both of these lines work exactly the same
print("orange")
print('orange')
Variations
Here are a few other common ways you might see this used.
Printing Multiple Items
You can print multiple things at once by separating them with a comma. Python will automatically add a space between them.
print("I like", "orange")
Output:
I like orangePrinting a Variable
You can store "orange" in a variable and then print the variable.
fruit = "orange" print(fruit)
Output:

orangeFormatted Strings (f-strings)
This is a modern and popular way to embed variables directly inside a string. You put an f before the opening quote and use curly braces around the variable name.
fruit = "orange"
color = "orange"
print(f"The fruit is {fruit} and its color is {color}.")
Output:
The fruit is orange and its color is orange.For your immediate need, the first and simplest example is all you need:
print("orange")